Types of television signals
There are only three main types of TV broadcasting - it depends on the method of receiving the signal.
- Terrestrial television broadcasting—broadcast from a television tower to a room antenna, without the use of additional equipment.
- Cable television—from a special server in the operator’s distribution center, the signal is transmitted via cable to network subscribers.
- Satellite system - a pulse from a satellite hits a parabolic antenna, and then is converted by a receiver and sent through a cable to the TV.
The first two options can use analogue or digital channels, the latter has a very high quality of audio and video signal transmission, but to view it you need to install additional equipment - a tuner (read more in the article about connecting satellite television).
Next, we will look in detail at setting up analog TV channels manually or automatically. Setting up cable channels has virtually no fundamental differences, i.e. digital channels are set up identically.
Upper first molar
Contours of access to the upper premolars.
This tooth usually has three roots and four root canals. Additionally, the canal is located in the mediobuccal root. The shape of the channel system was studied both in vivo and in vitro. In in vitro studies, an additional channel was found in 55–69% of cases. The canal configuration is usually type II, but type IV with two separate apical foramina is present in more than 48.5% of cases. In in vivo studies, an additional second channel was less frequently found and there were difficulties in finding it. It was detected in 18 - 33% of cases.
Upper first molar.
The palatal and distal roots usually contain a type I canal. In Caucasians, the length of this tooth is about 22 mm, the palatal root is slightly longer than the cheek roots. In the teeth of Mongoloids, there is a tendency for the roots to be closer and denser, and the average tooth length is slightly shorter.
The pulp chamber is quadrangular in shape and wider in the bucco-palatal direction than in the mediodistal direction. It has four pulp horns, of which the mediobuccal one is the longest and sharpest in outline, and the distal buccal horn is smaller than the mediobuccal horn, but larger than the two palatine ones. The bottom of the pulp chamber is usually located below the level of the neck and is rounded with a convexity towards the occlusal surface. The mouths of the main canals are funnel-shaped and lie in the center of the roots. The lesser mediobuccal canal, if present, lies on the line connecting the orifices of the mediobuccal and palatine canals. If this line is divided into three parts, then the mouth of the additional canal will lie about the first third, closer to the medial buccal main canal.
It must be remembered that the shape of the incisions in the neck area and at the level of the middle of the crown of the pulp chamber are of different configurations (the shape of the incision in the neck area is more diamond-shaped than quadrangular). In this regard, the mouth of the mesiobuccal canal is closer to the buccal wall than the mouth of the distal canal is to the distal wall. Therefore, the distal buccal root, and therefore the mouth of its canal, is closer to the middle of the tooth than the distal wall of the chamber. The mouth of the palatine canal is usually easy to find.
There is considerable variation across cross sections. The mesiobuccal canals are usually the most difficult to instrument because they run in a medial direction. The lesser medial buccal canal is often very narrow and tortuous and connects to the main canal. Since both medial buccal canals lie in the buccopalatal plane, they often overlap each other on the radiograph. Additional difficulties are encountered due to the frequent curvature of the mesiobuccal root in the distal direction in the apical third of the root.
The distobuccal canal is the shortest and often narrowest of the three canals and extends distally from the chamber, being oval in shape before becoming round towards the apex. Typically the canal curves medially in the apical half of the root.
The palatine canal is the largest and longest of all three main canals and has a round cross-section along its entire length, tapering towards the apex.
About 50% of the palatine roots are not straight, but curve towards the buccal side in the apical part (4-5 mm from the apex). This curvature is not visible on the x-ray.
With age, the canals become narrower and their mouths are more difficult to find. Secondary dentin is deposited mainly on the roof of the pulp chamber and, to a lesser extent, on the floor and walls. Due to this, the pulp chamber becomes very narrow between the roof and the bottom. This can lead to furcation perforation, especially when using a turbine handpiece, if the operator does not notice the narrow chamber. To prevent this complication, it is advisable to limit the use of a turbine handpiece to the preparation of enamel and, partially, dentin, and to complete the formation of access at low speeds. You can estimate the distance between the bump and the roof of the chamber on the radiograph. This distance is marked on the forest and serves as a guide.
Relatively recent clinical observations highlight variations in the anatomy of the dental canals of these teeth. There are reports of teeth with two palatal canals.
Preparing the equipment
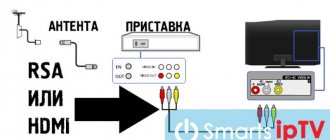
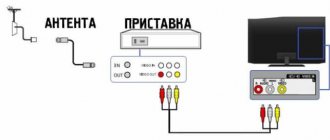
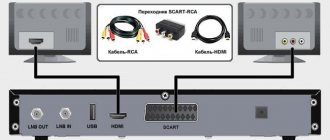
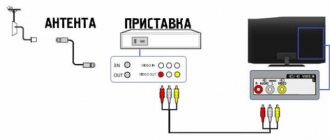
Setting up channels on a TV begins with connecting it to the signal source: for analog and cable television, connect the cable to the antenna input (see photo).
If you have two or more TVs in your home, they can also be connected to one antenna. But for stable distribution, you need to use a special splitter or splitter that has two or more outputs, which depends on your needs.
\
Search by alphabet
By default, on Tricolor devices, the channels are organized in order. The earlier a specific television channel was found, the lower the number it is assigned. But remembering digital designations is not always convenient, especially when it comes to three-digit numbers.
Sorting TV channels alphabetically helps solve the problem of quick access to the desired content. You can arrange Tricolor TV channels alphabetically by following these steps:
- Press the “Ok” button and call up the full list of channels.
- Press the green button and call up the alphabet.
- Select the desired letter and click Ok.
The system will display all TV channels whose names begin with the selected letter. You can exit the list using the Exit button.
How to set up digital terrestrial channels
Setting up TV channels on modern TVs has been significantly simplified thanks to smart automation. But users who are inexperienced in these matters experience serious difficulties. In addition, in some cases manual adjustment of values is required.
You can set over-the-air channels using either a TV or third-party equipment: set-top box, console, receiver, etc. Let's look at the settings in automatic and manual mode, taking into account the TV brand.
General procedure
This is a universal and simplest method, available for almost all modern TV devices . We connect the antenna to the TV and perform the following procedure.
Algorithm for setting up broadcast channels:
- Open the TV menu using the remote control.
- Go to the settings section.
- Click on the “Signal source” item.
- From the list, select the TV antenna or the corresponding output (AV, AV+).
- There should also be an item “Automatic channel search”.
- Go to the section and click on “Search”.
- At the end of the procedure, all found channels will appear.
- We save the set and change the numbering if necessary.
In rare cases, the TV will need to reboot, as indicated by the corresponding system message.
Manual setting
If the algorithm described above is not successful, then you should try setting up digital broadcasting manually.
Manual channel tuning:
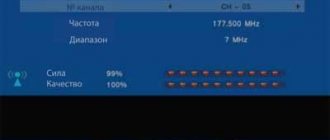
- Go to the list of TV channels page;
- We look at the channel name and carrier frequency.
- Open the menu on the TV and go to settings.
- Select the signal source (TV antenna).
- Click on “Manual channel tuning”.
- We fill in the field with the frequency (MHz) and multiplex number from the previously recorded data.
- Let's turn on the search.
- We save the data.
If the number of channels is less than 20, then you must repeat step 7, selecting the second multiplex in the values.
How to move and swap TV channels?
Tricolor users can swap and move channels, this requires:
- Open the menu, select the channel editing tab, also called “channel editor” or “channel manager”.
- Select this tab and confirm your choice with the OK button.
- A window will appear with the name of the TV channels, click on it and confirm.
- In the window that opens, click on edit, this is moving. Typically this section is highlighted in yellow.
- You will be asked to enter a password, usually the standard 0000.
- Below you will see various inscriptions, choose move or move.
- A pointer will appear in the window with which you can move channels up or down.
- Select the one you want to move.
- After moving, click OK and save the result.
Setting up channels on TVs of different brands
Some models run on proprietary operating systems. For example, Samsung has Tizen, LG has WebOS, and Sony and Philips have Android OS. Let's look at the features of adjusting broadcast channels with an eye to the TV brand.
Samsung
The procedure depends on the TV series. The first step is to update the device, otherwise conflicts and other problems may arise.
Procedure for models of the M, Q, LS and K series:
- We activate the menu on the TV using the Home button from the remote control.
- Go to the “Settings” section and open the “Broadcast” branch.
- Click on the “Auto Configuration” item.
- In the drop-down list, select the signal source – TV antenna.
- Be sure to specify the type of channels - digital, otherwise the TV will look for analogue ones, too.
- Leave the values in the “Operator” and “Search Mode” sections as they are.
- Let's start scanning.
- At the end of the TV, it will record all found channels into memory.
Settings on J, H, F and E series models:
- Press the Source button on the control panel and set the signal source to the TV antenna.
- Open the settings and go to the “Broadcast” section.
- Select the type of channels - digital.
- Click “Scan”.
- We agree to save the data, or change the numbering.
Sometimes the TV may pause for a few seconds after the search ends. This is fine. In less than a minute, a list of all channels available for viewing will appear on the screen.
LG
Here you also need to first update the operating system. Before starting the procedure, it is recommended to reboot the device and wait a couple of minutes until the platform stabilizes.
Setting algorithm:
- Click on the Settings button on the control panel.
- Go to the “Channels” section.
- In the window that appears, select “Autosearch”.
- We set the signal source – TV antenna.
- In the search interface, check the “Digital only” line.
- We start the procedure by pressing the OK button.
- If necessary, change the numbering of the found channels.
The procedure is similar for all TVs of this brand. The platform is completely localized, so there should be no problems with setup. In some cases, the interface design may change, but the menu branches remain the same.
Philips
TVs running on the Android platform are more flexible in terms of individual settings, but certain difficulties still arise. As in other cases, the first step is to update the operating system to the latest version.
Steps for setting up digital channels:
- We activate the menu by pressing the Home key on the control panel.
- Open “Configuration” and go to the “Installation” section.
- Select the item “Channel settings”.
- Click on the line “Automatic mode” and “Start”.
- From the drop-down list, select the signal source - TV antenna.
- When the search is complete, click on “Done” to save the results.
Some operating system versions may require you to select a country. If Russia is not on the list, then click on Germany or Finland. These countries use similar TV broadcasting protocols.
Sometimes the system asks for a password. Typically this is "0000" or "1111". The specific code will be indicated in the “Channel setup” section.
Features of the structure of teeth, their roots and canals
There are no two identical root dental systems, which is explained by the purely individual structure of a person’s teeth. In addition, the root system of incisors, canines and molars is arranged in accordance with their purpose:
- Ones and twos (incisors) are needed for biting food.
- Fours and fives (premolars) perform the initial chewing function.
- Sixes and sevens completely grind food.
Based on this, it becomes clear that the seventh tooth requires more nutrients than the fifth. It must be strong and hardy, therefore it has a more developed channel system. Despite the fact that the 6th tooth in the lower jaw performs the same functions as the seventh, it usually has fewer canals. This is due to the fact that there is less chewing load on it.
For a detailed study of the structure of the dentofacial apparatus of a particular patient, radiographic examination is used.
Tooth structure
Each dental unit consists of:
- crowns - the area above the gum;
- neck - the area between the crown and the root;
- root - the area under the gum.
Inside the crown is the pulp, which passes into the root canals. At the end of the root there is a small apical opening through which blood vessels and nerve endings pass, starting from the main neurovascular bundle and ending in the pulp.
When a person’s pulp becomes inflamed, not only it, but also all root canals need to be cleaned of infected tissues, since they are “communicating vessels.” If even one canal is left uncleaned, pathogenic microorganisms will continue to develop inside the dental unit, which will lead to its removal. That is why the doctor must know the exact number of canals in the tooth.
How many nerves are there in a human tooth?
Thanks to the nerve, the tooth can respond to external stimuli. After removing the pulp and filling the canals, the dental unit loses sensitivity, as it is deprived of a nerve. But due to the removal of blood vessels, problems begin with its blood supply and mineralization. The crown becomes less durable and more prone to various chips and breaks. The enamel quickly darkens, and it cannot be properly bleached even with strong chemicals.
Before removing the pulp, the patient is sent for an x-ray to find out how many canals are in the operated tooth: a person has only one dental nerve in a tooth, but there may be several canals . This preparation allows for depulpation to be carried out competently and quickly.
Types of Root Canals
There are several options for the structure of dental canals:
- in the root there is one canal passage, which corresponds to one apical foramen;
- in the root there are several canal branches that connect in the area of a single apical foramen;
- two different branched passages have one mouth and two apical openings;
- canal cavities in one root merge and diverge several times;
- three root canal passages emerge from the same orifice, but have 3 different apical openings.
There can be as many channels as there are roots, but often their number differs. Several types of canals may be present in one molar and premolar.
How many canals in a person’s teeth - table
According to statistics, the number of canals depends on the depth of the tooth : the deeper it is located in the jaw, the more canals it has. This is due to the increased load on the molars located at the base of the dentition.
Typically, teeth in the upper jaw have more canals. But this pattern is not observed in all patients.
The table below presents average statistical data on how many canals are in a person’s teeth above and below.
| Dental unit | Number of channel passages | |||
| Fangs | Upper | 1 | ||
| Lower | 2 | |||
| Incisors | Upper | 1 | ||
| Lower | Central | in most cases 1, less often 2 | ||
| Lateral | 1 or 2 (about the same probability) | |||
| Premolars | Upper | First | most often 2, but sometimes first premolars with 1 or 3 canals are found | |
| Second | in most cases 2, sometimes 1 or 3 | |||
| Lower | First | 1 or 2 | ||
| Second | 1 | |||
| Molars | Upper | First | 3 or 4 with equal probability | |
| Second | in most cases 3, sometimes 4 | |||
| Third | around 5 | |||
| Lower | First | most often 3, sometimes 2 or 4 | ||
| Second | usually 3, but there are roots with 4 channels | |||
| Third | no more than 3 | |||
Number of canals in teeth in the lower jaw
The teeth on the lower and upper jaws are significantly different from each other. This is partly due to the uneven load and different functions. Typically, teeth in the lower jaw have fewer canals. But each specific case requires detailed study. Therefore, the dentist first sends the patient for an x-ray, and only then proceeds to open the crown and treat pulpitis.
It is impossible to start treating caries and pulpitis based only on encyclopedic information, because:
- The 6th tooth of the lower jaw can have any number of canals - from 2 to 4;
- in the 5th tooth below there is usually only 1 canal, but in approximately 10% of patients there are quints with 2 canals;
- In the 4th tooth there is usually only 1 canal, but in about a third of cases there are 2.
The eighth tooth on the lower jaw is the most “unpredictable”. Exactly how many canals are in the wisdom tooth located below can only be determined using x-rays. Officially, there are no more than 3 of them, but during the treatment of caries, additional cavities usually open. It is precisely because of its incomprehensible structure and inconvenient location that the figure eight is most often removed.
It is impossible to treat a dental unit without studying the structure of its root and canal system. This can only aggravate the pathology and lead to complications.
Number of canals in teeth in the upper jaw
The root system of the teeth of the upper jaw is more complex and branched. This explains the longer treatment of upper molars and the frequency of repeat visits due to incompletely sanitized dental cavities.
Features in the structure of the canal system of teeth in the upper jaw:
- The 6th tooth of the upper jaw is most often three-channel. But sometimes there are also four-channel first molars.
- The fourth and fifth teeth from above are most often two-canal, but sometimes single-canal and three-canal premolars are found.
- The 4th upper tooth usually has 2 canals, but sometimes there are premolars with 1 or 3 canals.
The “wise” eight on the upper jaw is a four-channel tooth. Third molars with 5 canals are extremely rare. However, in dentistry, even cases of the presence of eight-channel wisdom teeth located at the top have been recorded.
Setting up cable TV
You have finally installed modern television and are now wondering how to set up high-quality digital channels on your TV. When setting up, it is better to adhere to the following recommendations.
- It is necessary to enter into an official agreement with the provider that provides cable TV services in your area of the city.
- When turned on, the message “digital channels are not configured” appears on the screen.
- You need to take the control panel of the equipment and enter the Menu by pressing the appropriate button.
- In the “Channel setup” section, select the “Auto-tune” sub-item, then press the “OK” button - the product begins to scan the signal and independently tune to all existing channels. At the same time, doubles and variants of incorrect images are recorded: stripes all over the screen, low-quality sound, distorted or completely absent. Such channels are removed manually after downloading is completed by selecting the appropriate items from the menu of your TV.
- Automatic downloading ends within a few minutes, depending on the number of channels received. After scanning is completed, the device will sequentially show all saved channels.
- You can also tune TV channels manually, but then you will have to search for the appropriate frequency for a long time. You will spend the same amount of time on each channel you configure as a full automatic setup would take.
Each user should understand that we have proposed an average option for setting up television channels; each TV has its own nuances, which are described in the operating instructions. For example, setting up and organizing channels on Tricolor TV is extremely easy for the user.
Users often ask the following question: is it possible to set up the TV without using the remote control? Of course, you can, if the body of your product model has the corresponding buttons.
Information site - about Tricolor TV
Home » For subscribers
Reading time: 3 min Published: 02/12/2020 Category: Subscribers
The question of how to organize channels is faced by every Tricolor subscriber who wants to make the search for suitable content easier and faster. The operator took care of this possibility.
The user can use predefined lists, arrange them alphabetically, and he can also create his own lists of TV channels. This allows you to conveniently organize access to the desired content and enjoy watching it, rather than wasting time searching for the right programs.
Satellite channels
Users who have a parabolic antenna are interested in the question of how to set up satellite channels? Let us immediately warn you that these operations are slightly different from the actions described above.
So, the dish (as the satellite dish is popularly called) has already been installed and pointed in the right direction, all that remains is to figure out how to set up the TV. Along with the dish on the balcony, a receiver or tuner appears in the room, connected to it with a cable. Your equipment is switched to ordinary monitor mode.
Few buyers know that a satellite dish, due to the influence of natural conditions - strong wind, heavy rain, etc., can change its original position, so you need to periodically check the device and adjust the position so that there is a stable signal without distortion.
The tuner has its own remote control, on which you need to press the “Menu” button. Following the prompts, which are described in detail in the instructions, satellite channels are configured. There are many of them, so choose only the ones you need that you will look at at least occasionally. From the practice of using satellite television, it follows that many channels are offered, but the most popular are educational, about travel and the mysteries of the planet, and sports. Therefore, when setting up, do not get carried away by the abundance of saved channels: as a rule, you simply do not have enough free time to watch everything.
Access to lower incisors and canines
Essentially, the approach is identical to that in the upper teeth. However, with a pronounced curvature towards the lingual side of the crowns of the incisors and due to very thin (especially in older people) canals, it is sometimes necessary to involve the cutting edge and, sometimes, the labial surface of the tooth into access to avoid bending of the instrument.
The outlines of the access in the lower canine are shown in Fig.
Access contours in the lower incisors.
Access contours in the lower canine.
Setting up an old TV model
On an old TV without a remote control, settings are made using special controls located on the panel under the channel switching buttons. As a rule, in such models a drawer is pulled out where channel frequency controls are located - with their help, the TV is tuned to all active channels. Adjusting the image of an old-style TV is done only manually using the rotary control on the front panel; there are also similar volume and brightness controls.
Often, a TV configured in this way needs to be manually adjusted when turned on again, since they do not have a storage system.
Access to the canals of the upper incisors and canines
The access may vary in size and shape depending on the size of the pulp chamber. It should be such that the instruments can reach the apical constriction without bending or obstruction by the canal walls.
If access is too close to the cingulum, this will result in significant bending of the instruments and possible perforation or staircase formation.
An incorrectly formed access cavity in the incisors and canines leads to the formation of a ledge on the labile surface of the canal due to a sharp curvature of the instrument in the canal. This approach leads to failure to remove remaining pulp.
Ideally, the access should be close enough to the incisal edge to allow unimpeded entry of instruments to the apex. Sometimes the cutting edge and labial surface of the tooth are involved in the access (see figure). At first glance, this is contraindicated from an aesthetic point of view. However, if the root canal is not fully processed, it will not ensure long-term health of the periodontal tissues.
Access to the upper incisors: a) view from the palate; b) side view.
On the other hand, modern whitening and restorative techniques make it possible to ensure aesthetics, strength and other requirements in restoring these defects.
Because the pulp chamber is wider at the incisal edge than at the neck, the access contour should be triangular and sufficiently extended medially and distally to include the pulp horns. With proper access, it is necessary to widen the cervical narrowing for adequate instrumentation of the canal.
Access contours in incisors:
a) correct access contours in the incisors and canines; b) the dotted line shows an incorrect access contour in which infected material can remain in the pulp chamber and be pushed into the canal during further instrumental processing. (by Harty)
Correct access is especially important in older patients, as a narrowed canal requires thinner instruments that can bend sharply or even break. In such patients, it is better to immediately make access closer to the cutting edge than usual, since due to the narrowing of the pulp chamber, a straight line of transition of this chamber into the canal is formed. This will ensure effective preparation.
Access contours in the upper canine.
Setting up HD channels
High Definition Television (HDTV) is a completely new standard that provides much better pictures when compared to analog and digital options. This format allows for highly compressed video and audio signals and uses only digital technology to transmit the signals, resulting in very impressive image fidelity and surround sound.
If you have already set up digital channels on your new TV, then to add channels in HD mode you need to automatically rescan - they will appear in the product list.
Editing lists
All created and preset lists can be modified. To edit them, use the colored buttons on the receiver remote control:
- Blue allows you to rename an existing list.
- Red deletes the previously created list of TV channels.
- Yellow opens the section for creating a new list.
Using the remote control it is quite easy to distribute all channels into the desired categories. Most often, subscribers use thematic sorting. With it, you can create suitable lists (for example, “Cinema”, “Children’s”, etc.), and then place suitable channels in them (for example, “Film screening” can be wisely added to the “Cinema” list). You can change the sorting at any time if you wish.
How to watch TV without an antenna
Today, any user can watch TV without an antenna: just connect the Internet provider cable to the TV set-top box - now you have more than a hundred channels from different countries of the former CIS, entertainment programs, news, educational and children's channels.
The broadcast does not depend on weather conditions, besides, if you missed the program, you can watch it in the recording and without annoying advertising.
You can watch the best films in excellent quality, almost like in a cinema; if you need to go away, press pause. Views: 4818
Upper canine
It is the longest tooth in the mouth, averaging 26.5 mm (range 20-38 mm). It is extremely rare to have more than one root canal. The pulp chamber is relatively narrow and has only one horn; it is much wider in the vestibulo-oral section than in the mediodistal section. The root canal is type I and becomes round only in the apical third. The apical constriction is not as pronounced as in the incisors. This fact, and the fact that often the apical part of the root is significantly narrowed, causing the canal to become very narrow at the apex, makes it difficult to determine the length of the canal.
Upper canine
The canal is usually straight, but sometimes at the apex it bends towards the distal (in 32% of cases) and, less often, the lateral side. In 13% of cases, vestibular deviation of the canal was recorded. The frequency of occurrence of lateral (side) canals is about 30%, and additional apical ones - 3%. The apical foramen is located in 70% of cases in the range from 0 to 1 mm in relation to the root apex, and in 30% in the range of 1 - 2 mm.
Lower third molar
This tooth is often underdeveloped with numerous and poorly developed cusps. Usually there can be as many canals as there are cusps. The root canals are relatively larger than those of other molars, possibly due to the late development of this tooth.
Despite these disadvantages, it is usually less difficult to fill the roots of a lower than an upper wisdom tooth because access is usually easier due to the mesial inclination of the tooth and because they more often follow normal anatomy, resembling a second molar, and are less likely to be deviated from the norm.
Lower second molar
In Caucasians, the second molar resembles a small version of the first, with an average length of 20 mm. There are two canals in the medial root, and only one in the distal root. The medial canals tend to merge in the apical third and form a single apical foramen.
Lower second molar. (By Harty).
Studies conducted in 1988 showed a high tendency for root fusion in the Chinese (33-52% of cases). In a longitudinal section, such teeth resemble a horseshoe. Where there is incomplete root separation, incomplete canal separation may occur, which is accompanied by a dense network of anastomoses between the canals and can lead to unpredictable localization of the orifices. One of the locations was called the middle buccal orifice with the middle buccal canal. In Caucasians, this anomaly is recorded in 8% of cases, which is significantly less than in the Chinese.