Digital television is a modern alternative to standard analog TV. With this technology, image quality becomes significantly better at the same cost. The essence of this technology is that television signals are a sequence of digital combinations of electrical impulses. Digital technologies provide new opportunities for transmitting and receiving data.
This means that one frame of a television image is transmitted in two parts - even lines, odd lines. This transmission mode was previously imposed on analogue TV because the frequency bands did not reach the transmission of the entire television signal. This frequency is not randomly chosen - it is very slightly higher than the minimum frequency at which the human eye does not detect screen flickering. The idea is simple and brilliant at the same time - it is actually transmitted at 25 frames per second, but the human eye perceives them at 50 Hz - as a full image without blinking. It is often called inter-row scanning, but in a more advanced sequence, all lines of the frame are transmitted sequentially, which is made possible by the introduction of new technologies and, of course, higher image quality and accuracy, especially when displaying moving objects - this is the latest and highest quality format, and will also be supported by digital television.
- The standard definition scheme is almost always intertwined.
- At a frequency of 50 Hz.
The most widely used satellite and cable TVs around the world.
Digital television has its advantages. For example, mobility. There is no longer any need to run wires and cables; all you need is a TV, an antenna, a digital receiver and a power outlet. This is an autonomous system that you can take with you, for example, to the country and watch TV programs with the same high-quality signal as in the city. In addition, digital TV has a large number of broadcast channels, and you can also access the Internet, TV guide, etc.
They are supported by all sorts of larger and larger companies and networks, so it's difficult to make accurate statistics, and perhaps no one has hired this one. And most TVs, especially cable ones, cover limited areas with a limited number of users, so they are not such a significant factor. And while more consumers rely solely on cable television, what happens with digital television, which is available to absolutely everyone in the country or region, is very important.
Currently in Luxembourg and Sweden television is completely digital. The situation in our country is always difficult. And again we are late - while the Netherlands, Finland, Luxembourg and Sweden have already completely switched to digital terrestrial television, the organizational procedures are just beginning, and the prospect of having clarity on this issue at the very beginning of June this year.
Why does the quality or signal level on the DVB T2 tuner fluctuate?
This is not a very common malfunction, and it cannot be called a malfunction, meaning when the quality of the received DVB T2 signal fluctuates. Most often this is due to the position of the cable from the antenna to the TV, reception conditions and a number of other reasons. Why this happens is simply incomprehensible to an inexperienced user in such matters, and he can explain this behavior of the tuner as a malfunction of the set-top box or antenna, but that is not the point. However, let's take things in order.
Causes
The most common case when a digital TV signal jumps can be observed if the television (coaxial) cable, when laying it from the antenna to the TV, has horizontal sections. Without going into details of this mechanism, I will say that this is due to parasitic interference in the cable.
The intensity with which the dvb-t2 signal jumps depends on the height at which the cable has such a horizontal section and how long it is; if it is located close to the ground, then the influence of interference is minimal. It is clear that the longer such a section is, the more the useful signal will be suppressed. To avoid this, place the antenna close to the set-top box; using a high-quality cable also helps.
The digital TV signal also begins to jump when it is tilted, for example when it descends from the ridge of the roof to the wall. It is worth noting that there is a known case when, with an inclined cable, the receiver showed for quite a long time after tuning, and with the onset of summer and hot weather, the signal level began to change abruptly from 0 to 100, and the quality signal remained at 5%.
There have been cases in practice when, in urban conditions, with a nearby tower located, an active indoor antenna was used to receive the first and second multiplex. The signal arriving at the tuner was very large, which led to the protection being triggered and, as a result, the signal began to jump on the digital tuner.
There were also opposite cases when the signal was artificially lowered. This refers to obstacles in the form of buildings or trees. Moreover, if there is a tree between the antenna and the tower, the reception is excellent in winter, but in summer the foliage dampens the signal and jumps in its level also occur. In this case, it is enough to move the antenna. By the way, for this reason, the signal also fails on satellite TV; the installed dish was showing correctly for several years and suddenly glitches began to occur, the picture crumbles into squares. It turned out that the tree had grown over the years and began to block the dish from the satellite.
There are many nuances here and they can have an impact - weather, cable quality, tower location range (signal strength), so you need to understand each case when the signal starts to jump when receiving or configuring T2, and it doesn’t matter what World Vision console you have, Rolsen, etc..
Useful tips
Avoid twisting the wire into a coil, as well as long sections with horizontal and inclined cable positions; use high-quality cable in these cases.
To avoid interference, the cable must be placed away from power electrical wires and avoid crossing the cable with power lines, and when crossing, make it at a right angle.
Wire the TV cable in one piece; if breaks cannot be avoided, then use special connectors with reliable wire contact and shielding, and not twisted with electrical tape.
Related Posts
Possible causes of interference
A digital signal is generally reliable and much better than an analog signal, but even it is not immune to various types of interference. In any case, if the quality of the broadcast deteriorates, you will have to find out the reason why this happened. For example, if the TV shows poorly and there is interference, you need to check the antenna. Maybe it was installed poorly or just went wrong. The antenna can also break due to a large snowball or piece of ice. In addition, the TV may not show well due to a broken television cable, a failed receiver, etc.
If, when connecting digital TV, the technicians fed the cable into the apartment, and further wiring was done independently (especially if there is more than one TV in the apartment), then there may be a bad contact in the tee. There may also be interference if there is also a computer next to the TV and they are connected via an HDMI cable. As a rule, interference on TV begins when the computer is turned on, and as soon as the computer is turned off, the image becomes high-quality again. In this case, interference may occur due to the fact that the computer (or more precisely, a video card with an HDMI port) is not working.
If you live on the top floor and the signal is weak, the nuts on the dividers may have oxidized or burned, the equipment has not been configured, or the optical receiver has failed. There can be many reasons for the appearance of interference, and the easiest way would be to call a specialist so that he can find the true cause and eliminate it.
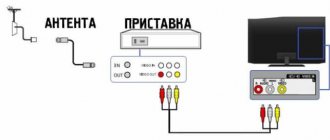
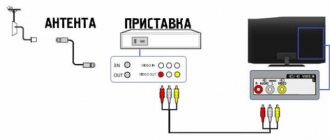
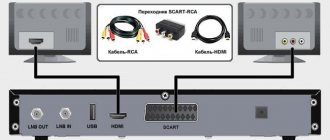
These may be the following devices. Cable receiver, free-standing, standard DVB-C (when using cable networks) or DVB-T (for regular broadcasting), having a separate control panel. The receiver should connect to the audio-video inputs of almost any TV, both analog and digital; A modern TV that has a built-in DVB-C and/or DVB-T tuner. In this case, simply connect the cable through which you receive the network signal to the antenna socket, and you can receive the signal after setting up the TV. Computer, however, viewing here requires an additional PC card or an external tuner connected via a USB port.
You need to configure the digital tuner to receive digital television in the following sequence. First, connect the digital TV cable to the antenna socket of the tuner. Then you need to connect the tuner and the audio-video input of the TV, and turn on the TV receiver. Next, in the TV menu, select the appropriate AV input and connect the tuner's power. Wait first for the screen saver, and then for the offer from the tuner to tune channels
How to check the signal level of dvb t2 digital television from an antenna
This article was written in connection with a large number of requests in the comments with the question “How to check the signal level of a DVB T2 antenna.” And although the instructions provide explanations on this matter, most often we turn to the Internet. It’s a sin, I do this myself, because I have to look for instructions, and the Internet is nearby.
This option is very useful, as in some cases it allows you to understand who is to blame for the lack of signal, the antenna or the set-top box itself. For example, when the programs are configured, the reception suddenly disappears, and there is an inscription on the screen about the absence of a signal.
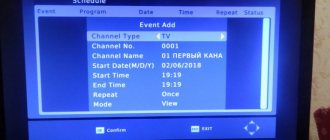
So, with the set-top box configured and not configured, you can check the level of the digital television signal by pressing the “INFO” button several times. Why several times and not an exact number? This number differs for different manufacturers. For example, for Rolsen receivers, you need to press three times, but for the “Cascade” and “Oriel” consoles only two times.
During the initial setup in manual mode, if you see a picture like this
Display of signal level during manual tuning
and if the quality and intensity levels on it are high, then you can safely move on to searching for channels; if this is not the case, you need to deal with the antenna.
When the channels are already configured, when you press the “INFO” button, you will see the following pictures:
Menu for displaying the DVB T2 level of the Rolsen set-top box
Displaying the digital signal level of the “Cascade” set-top box
If, when checking the signal level of digital terrestrial TV, you see that the quality, strength or intensity of the signal is quite high, but there is no image, then for the most part you just need to reconfigure the device. This happens when working on broadcast equipment and changing any settings, or for some reason the settings of the set-top box itself are lost.
No signal
There is another way to check the signal level coming from the antenna, this is a special device, for example, a DVB T2 signal meter - IT-15T2.
DVB T2 signal meter IT-15T2
The thing is very expensive and is perhaps necessary only for masters.
Related Posts
Analog antenna or satellite dish?
The principle of operation from a satellite dish
.
You need to buy and install a set of signal receiving equipment: a “dish”, an access card to satellite channels and a set-top box (satellite receiver), which ensures the transformation of the received digital signal into an analogue one that is understandable to the TV. A satellite receiver
is a device that provides signal transformation from DVB (various decoding systems) into a format perceived by a household TV.
You can connect a cable operator’s wire or a familiar terrestrial television antenna to such a set-top box. Intermediate equipment may not be needed, since many modern TVs support the DVB-T
, which means compatible with MPEG-4 compression, and a special antenna is not required to receive a digital signal.
In order not to change the TV, there is an alternative - a CAM module
. It is a kind of expansion card that is inserted into the TV and gives it the functionality of a set-top box, but to use this component the TV must have a CAM interface. I will tell you more about the CAM module in the section on digital cable TV.
Satellite platforms officially operating in Russia use DVB-S and DVB-S2 standards. For reception, you need a correctly installed antenna (the diameter of which depends on the geographical location of the subscriber and the selected satellite), a receiver with a valid access card and a TV.
DVB-T2 antenna for receiving a digital signal. Right choice.
The question of choosing an antenna for receiving a DVB-T2 digital signal is not that difficult. You can take any antenna that you used to receive an analog signal and with the help of it you MAY get a picture on your TV. But if it were all that simple, there would not be a very wide selection of antennas on the market. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
To receive a high-quality digital DVB-T2 signal, you will need a UHF antenna, because Broadcasting of digital packages (multiplexes) is carried out in the UHF range, and already in the package itself all channels of other ranges are broadcast.
Such antennas are conditionally classified according to the type of signal amplification, the range of received frequencies, and the location of installation.
An indoor antenna is installed indoors in an area of reliable reception where the signal level is quite high. In reality, such zones are located approximately 10 km away. in direct line of sight from the transmitting repeater. Consequently, there is little chance of getting a high-quality picture on your TV using an indoor antenna in remote places, for example, in a village or in a country house.
If you are still in the area of reliable reception, then you just need to point the indoor antenna towards the repeater, and you will receive a stable signal. If the transmitter power is high (in cities, regional centers), then it will be enough to install even such a simple antenna on the windowsill and enjoy your favorite TV shows.
There is an opinion that if an antenna receives a signal well in one room, then it should also perform well in others - this is wrong. The antenna must be selected for each case separately.
Outdoor antennas, compared to indoor ones, have the best parameters and can be used in various places, including in dachas and villages at a considerable distance from the transmitter. An outdoor antenna requires some effort and experience to install, but also provides the best reception quality.
To choose the right outdoor antenna, you need to take into account the power of the repeater, at what distance from the transmitter you plan to receive the signal, what is the number of floors of buildings, building density, and whether there will be domestic and industrial interference.
An antenna is an electronic device that has various parameters and characteristics. All these parameters are described in the product data sheet. For the average user, all these parameters are hardly necessary to know and understand. But there is a parameter without which it is difficult to select an antenna - this is the gain, which is measured in decibels (dB). The higher the gain, the higher the antenna's ability to receive a signal. But more decibels does not always correspond to a better picture on the TV. The gain is selected depending on the installation location. Sometimes unscrupulous manufacturers indicate exorbitant gains, which may not correspond to reality. Figures of 45-50 dB should alert you, but if 90-120 dB, this is definitely a hoax.
World digital TV standards
In America, the ATSC standard, developed by the Advanced Television Systems Committee group, is widespread, in Japan ISDB (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting) is rapidly developing, Russia has followed the European path, adopting the DVB (Digital Video Broadcasting) standard as a basis.
Let's go digital
A massive transition to digital television broadcasting standards in the world took place in the early 2000s. In our country, state broadcast channels began the transition to digital in 2009 as part of the federal program “Development of television and radio broadcasting in the Russian Federation for 2009-2015.” DVB-T2 was chosen as a unified digital broadcasting standard, which allows more digital channels to be placed on the frequency band than its predecessor DVB-T, but this does not mean an increase in the resolution of the broadcast picture. We should expect HD quality on air only in the distant future. Today, DVB-T2 transmitters operate almost throughout the country. In some places, only the first multiplex (package of 10 digital channels) is currently on; in other areas, the second is already available. This means that if you have an appropriate TV or an additional set-top box, you can receive and watch 20 channels for free in decent quality and almost without interference. The program for the development of digital television in Russia involves updating only distribution and transmission equipment. Viewers have to think about replacing receivers on their own, because to receive a digital terrestrial television signal you need a DVB-T2 TV tuner
, and a similar one is provided only in . To receive a signal with older devices, TV viewers will have to purchase and install a set-top box at home.
Why does the quality or signal level on the DVB T2 tuner fluctuate?
This is not a very common malfunction, and it cannot be called a malfunction, meaning when the quality of the received DVB T2 signal fluctuates. Most often this is due to the position of the cable from the antenna to the TV, reception conditions and a number of other reasons. Why this happens is simply incomprehensible to an inexperienced user in such matters, and he can explain this behavior of the tuner as a malfunction of the set-top box or antenna, but that is not the point. However, let's take things in order.
Causes
The most common case when a digital TV signal jumps can be observed if the television (coaxial) cable, when laying it from the antenna to the TV, has horizontal sections. Without going into details of this mechanism, I will say that this is due to parasitic interference in the cable.
The intensity with which the dvb-t2 signal jumps depends on the height at which the cable has such a horizontal section and how long it is; if it is located close to the ground, then the influence of interference is minimal. It is clear that the longer such a section is, the more the useful signal will be suppressed. To avoid this, place the antenna close to the set-top box; using a high-quality cable also helps.
The digital TV signal also begins to jump when it is tilted, for example when it descends from the ridge of the roof to the wall. It is worth noting that there is a known case when, with an inclined cable, the receiver showed for quite a long time after tuning, and with the onset of summer and hot weather, the signal level began to change abruptly from 0 to 100, and the quality signal remained at 5%.
There have been cases in practice when, in urban conditions, with a nearby tower located, an active indoor antenna was used to receive the first and second multiplex. The signal arriving at the tuner was very large, which led to the protection being triggered and, as a result, the signal began to jump on the digital tuner.
There were also opposite cases when the signal was artificially lowered. This refers to obstacles in the form of buildings or trees. Moreover, if there is a tree between the antenna and the tower, the reception is excellent in winter, but in summer the foliage dampens the signal and jumps in its level also occur. In this case, it is enough to move the antenna. By the way, for this reason, the signal also fails on satellite TV; the installed dish was showing correctly for several years and suddenly glitches began to occur, the picture crumbles into squares. It turned out that the tree had grown over the years and began to block the dish from the satellite.
There are many nuances here and they can have an impact - weather, cable quality, tower location range (signal strength), so you need to understand each case when the signal starts to jump when receiving or configuring T2, and it doesn’t matter what World Vision console you have, Rolsen, etc..
Useful tips
Avoid twisting the wire into a coil, as well as long sections with horizontal and inclined cable positions; use high-quality cable in these cases.
To avoid interference, the cable must be placed away from power electrical wires and avoid crossing the cable with power lines, and when crossing, make it at a right angle.
Wire the TV cable in one piece; if breaks cannot be avoided, then use special connectors with reliable wire contact and shielding, and not twisted with electrical tape.
Related Posts
Video compression formats in the DVB standard
DVB standard
is not a complete description of the digital television format, but a method for a specific broadcast implementation. Various video encoding systems can be used within this standard (MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, etc.), but not all of them are backward compatible. The most common compression formats are MPEG-2 (the best picture quality) and MPEG-4 (which has the best compression). Russian digital TV will use MPEG-4 compression. TVs that support the MPEG-4 standard can also work with MPEG-2, but not vice versa, since MPEG-2, in turn, is used by cable operators who are not limited in frequency band and the picture compressed with this codec is much higher quality.
How to check the signal level of dvb t2 digital television from an antenna
This article was written in connection with a large number of requests in the comments with the question “How to check the signal level of a DVB T2 antenna.” And although the instructions provide explanations on this matter, most often we turn to the Internet. It’s a sin, I do this myself, because I have to look for instructions, and the Internet is nearby.
This option is very useful, as in some cases it allows you to understand who is to blame for the lack of signal, the antenna or the set-top box itself. For example, when the programs are configured, the reception suddenly disappears, and there is an inscription on the screen about the absence of a signal.
So, with the set-top box configured and not configured, you can check the level of the digital television signal by pressing the “INFO” button several times. Why several times and not an exact number? This number differs for different manufacturers. For example, for Rolsen receivers, you need to press three times, but for the “Cascade” and “Oriel” consoles only two times.
During the initial setup in manual mode, if you see a picture like this
Display of signal level during manual tuning
and if the quality and intensity levels on it are high, then you can safely move on to searching for channels; if this is not the case, you need to deal with the antenna.
When the channels are already configured, when you press the “INFO” button, you will see the following pictures:
Menu for displaying the DVB T2 level of the Rolsen set-top box Displaying the level of the digital signal of the “Cascade” set-top box
If, when checking the signal level of digital terrestrial TV, you see that the quality, strength or intensity of the signal is quite high, but there is no image, then for the most part you just need to reconfigure the device. This happens when working on broadcast equipment and changing any settings, or for some reason the settings of the set-top box itself are lost.
No signal
There is another way to check the signal level coming from the antenna, this is a special device, for example, a DVB T2 signal meter - IT-15T2.
DVB T2 signal meter IT-15T2
The thing is very expensive and is perhaps necessary only for masters.
Related Posts
Television over the Internet
An Internet channel is also used to transmit a digital television signal between the telecom operator and the viewer’s TV. Globally, network television projects can be divided into IPTV and OTT. Although OTT is a type of IPTV, they are usually considered as different services. It is generally accepted that IPTV is a service within the operator’s network that provides broadcast of channels in real time, and OTT (Over The Top) is any video service (not only broadcast of channels, but also cinema, that is, video on demand) provided via the Internet . Many common operator platforms support both options within the same service, so it makes no sense to talk about a strict separation of IPTV and OTT.
Equipment for IPTV or OTT
At the moment, TV manufacturers have not yet agreed on a single standard for IPTV (OTT) services. Therefore, for now, viewers are forced to choose between several available options for watching TV over the Internet:
- – operators provide applications to connect to the service. It is important that you cannot use a third-party solution here: the only one who can release such a program for this particular network is the operator providing the service.
- – the ability to connect IPTV to a TV is determined by the presence of connectors for connecting a set-top box. The cost of such devices, however, is somewhat higher than that of broadcast consoles. There are even universal devices that work in the networks of different operators (reconnection may require changing the gadget’s firmware, but at least not purchasing new equipment), and also serving as a home media center (for example, Dune HD).
- watching channels on a computer -
often the “computer” package is smaller and you can rarely find HD channels there. - television on mobile devices.
Note that IPTV can broadcast HD, 3D and even channels. But to view them you need a set-top box and TV that support these standards and resolutions.
TV on mobile devices
The idea of mobile television has become widespread when high-speed mobile Internet and IPTV are combined. Its advantage compared to terrestrial, cable and satellite digital standards is that potentially a television signal can be received not only on specially produced devices, but also using any mobile device, including a smartphone or tablet. This is what many telecom operators who have previously launched IPTV (OTT) projects take advantage of. To work with encoded content, telecom operators release applications for mobile gadgets. Moreover, such programs often allow you to manage subscriptions to channels or a home set-top box. Recently, many projects have appeared that are not associated with any telecom operator or provider at all, but only offer video content for smartphone users, such as Amediateka, free IVI, etc.
I hope you now understand the differences between the types of digital TV: cable, Internet television, satellite and terrestrial.
In general, calculating the reception range is extremely difficult. Dozens of factors influence the reception range, including even the time of year and day.
However, especially for Moscow residents
, we present 3 boundary graphs (Fig. 1) for receiving digital DVB-T2 packets (multiplexes).
All 3 graphs are built for 3 reception conditions:
1
– long-range reception (receiving antennas with a gain of 16-18 dB, “long-range” class);
2
– average reception (receiving antennas with a gain of 10-12 dB, class balcony antennas);
3
– short-range reception (indoor “Delta” antenna).
In all cases, it is assumed that either an active antenna with a built-in mast amplifier is used, or an external low-noise mast amplifier (F = 2 dB) is used. Of course, the use of more expensive “long-range” antennas will provide much better (reliable) reception even in all weather conditions and over many years of operation. The higher the price of the antenna, the more attractive its appearance and greater durability in use.
Length of reduction cable with mast amplifier
(of any type) does not make any difference either to the quality of reception or to its “range”.
In the absence of a mast amplifier,
the length of the reduction cable (especially when working on 2 or more TVs) is already very important.
When using indoor antennas
(Amplification = 6 dB) it is necessary to remember that the walls (and radio waves will certainly pass through the window opening or walls) have shielding (attenuation of radio waves). In the calculations, a radio shielding coefficient of 6 dB was assumed. In practice, it can reach 14...18 dB. In other words, this means that the actual range can be reduced by 2-3 times, depending on the installation location of the indoor antenna and the radio shielding factor of the walls.
Curve with Acceleration=0 dB
corresponds to common active indoor foreign antennas (as a rule, they are powered by mains voltage ~220 V/50 Hz). Such antennas have zero gain (without a built-in amplifier), but are quite aesthetic in appearance.
For residents of the regions
The figure below shows similar dependences of the reception range R 0 depending on the height of the receiving antenna
h for
different installation heights of the transmitting antennas -
H. The curves are plotted for “long-range” antennas with a radiated transmitter power of 4 kW at a frequency of 600 MHz.
If your real transmitter power P differs from 4 kW, then the calculation of the real reception range must be adjusted using the formula
: It is useful to note that if the height of the receiving antenna is over 15 meters, then you can calculate the reception range R for a height of 15 m, and then recalculate
using the formula
:
Thus, for a receiving antenna elevation height of 30 meters, the reception range increases by approximately 1.4 times (for example, from 48.3 km to 68.1 km).
In conclusion, here are a number of useful practical tips on digital DVB-T2 reception:
Tip 1
Currently, it makes no practical sense to install bulky MV antennas. Taking into account the emerging digital DVB-T2 broadcasting, it is more profitable to spend money on one single high-quality UHF antenna complete with a built-in or externally connected mast amplifier.
Tip 2
Choose a mast amplifier with
a gain of 12-20 dB and a minimum noise figure (no more than 3 dB)
. If you purchase a mast amplifier on the market, then take into account the fact that they are not specialists selling there. Therefore, without listening to their recommendations, try to choose an amplifier with the maximum current consumption (about 40-70 mA). Higher current consumption corresponds to greater dynamic range (minimization of distortion).
Tip 3
Try to ensure that the mast on which the antenna is mounted is grounded.
It is advisable to install a lightning protection device between the antenna and the mast amplifier
. If the reception is carried out in a house where a standard lightning protection system is already provided, then you will not need any additional system.
Tip 4
It is advisable
to choose an antenna with the highest possible gain
.
This criterion for the UHF range when receiving digital DVB-T2 signals is the main one. All other things being equal, choose an antenna with minimal wind load and weight. Tip 5
Try to minimize the length of the reduction cable (between the antenna and the first amplifier).
A reduction cable length of 5-10 meters
is considered acceptable for most practical applications.
Tip 6
It is convenient
to use a mast amplifier with a supply voltage of 5 V
instead of the traditional 12 V or 24 V. A 5 V remote power source is present in almost every DVB-T2 receiver, which is very convenient, because no additional power supply required.
Tip 7
For normal readability of digital DVB-T2 packets, a signal level at the antenna output of 36 dBµV is sufficient.
The mast amplifier serves only to compensate for losses
in the reduction cable and the splitter for several TVs.
Tip 8
To increase the reception range,
choose a receiving antenna
with
the highest possible gain
and install it
as high as possible relative to the Earth's surface
. The mast amplifier should be located as close to the antenna as possible or immediately purchase an active antenna.
When it comes to buying a new TV, most people pay attention only to the quality of the transmitted image, as well as the technical characteristics on which it depends. The price of the device is also important. But the presence or absence of a digital tuner, as well as its type and quantity, interests few people. Not many people pay attention to this. As a result, when you want to connect and watch DTV for free, problems arise and you have to spend money on buying a DVB-T2 tuner separately.
Today we will look at what a digital tuner is, what it can be and how it works. This will allow you to approach the choice of a new TV more carefully and decide for yourself whether you need such a device, built into the TV or not. Moreover, as already mentioned, a digital tuner can always be purchased separately.
Broadcast Standards
As already mentioned, the tuner built into the TV can receive one or more signals of different broadcast formats. Let's look at the most common options.
- DVB-T. Such a receiver can receive a digital television signal, which transmits a picture of a higher level of quality and clarity. To connect it, you need a regular TV antenna.
- DVB-T2. This is the second generation of DVB-T decoders, which differs from its predecessor in increased channel capacity, higher signal characteristics and its architecture. In Russia, this DTV signal format is mainly used. It is impossible to receive it through a DVB-T decoder, as these formats are incompatible.
- DVB-C. A very popular format capable of decoding digital cable television signals. To start using it, you need to insert your provider card into the appropriate slot.
- DVB-S. With it, you can directly connect a satellite dish to your TV.
- DVB-S2. Like T2, S2 is the second generation of DVB-S receivers. S and S2 are also incompatible, so to receive this type of signal you need a corresponding decoder. This format is distinguished by increased channel capacity and the use of new types of modulation.
When purchasing a TV, you should pay special attention to the labeling. So, you can see the inscription DVB-T2/S2. This means that the TV will be able to receive both terrestrial and satellite digital channels.