INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING SATELLITE TV
Before you begin installing satellite television, you need to decide on the main points: - what channels do you want to watch:paid, free, scientific, entertainment, news;
- what is your monthly budget?
Do you agree to pay a subscription fee or want to watch only free channels;
-which satellites carry the channels you are interested in;- which receiver (receiver) do you prefer:
a simple one with a minimum set of functions and limitations in reception, or a modern HD tuner, with rich recording functionality, reception of HD and 3D channels, high quality channels and sound. Accordingly, the price of the latest receivers is higher;
- what antenna do you choose?
simple stationary or rotating; for rotating, a free view in the direction of the satellites is required.
Next, we will briefly discuss the steps for installing a satellite dish:
1. Selecting a location for installing a satellite dish
So you have decided on the channels and satellites.
Now you need to choose a place to install the antenna. It is necessary to take into account that the satellites are located in the aisles from the southwest to the southeast. Elevation angle and azimuth - the main angles that are set on the antenna can be determined using the appropriate formulas; in practice, tables are used; these angles are individual for each satellite. The installation site must be open and free from any obstacles (houses, trees, power lines, towers) on the path from the antenna to the satellite. The video that you will find on this page quite clearly presents all the points regarding choosing a location, choosing equipment and setting up a satellite dish. 2. Mounting and installing the antenna
Assemble the antenna according to the assembly video. At the prepared site, it is necessary to install and secure the crossbar (support). When installing on the surface of the ground, the support must be filled with cement mortar and allowed to stand. When installing the mount on the wall of a building, holes with a diameter of 14-20 mm are drilled in it and anchor bolts and dowels are used. When installing the antenna on a balcony or loggia, a thin partition must be drilled through and the support must be tightened with long bolts. Next, we mount the antenna and point it at the desired satellite using the compass. We set the convector, connect a device to determine the signal strength or a control receiver with the transponder set. The position of the converter is determined by moving it in the holder while simultaneously assessing the quality of the picture on the TV screen. To do this, the antenna must be located in a place convenient for tuning.
Satellite television
We will talk about a universal linear converter of the KU range .
Today, with developed networks of online stores, it is quite easy to view products and compare prices. Without leaving home it is possible to buy everything you need... So let's see what the market offers us.
I understand that it is impossible to cover all the varieties of satellite converters, but we will focus on the most popular ones and those that most attract attention.
So, let's start with the cheapest Single (with one output) converters, since they are more accessible to the buyer and will be more common. The cheapest converters in online stores are offered at a price of about $2, or even less.
The figure shows satellite converters of the budget line
TECHNOSAT T-131 Single
Sat-Integral T-800 Single
SINGLE Tiger TL-1411
SINGLE Pauxis PX-2100
SINGLE WinQuest WL 804U
What I would like to note. For the most part, all such converters are short-focus and are suitable for corresponding antennas, such as supral, with an opening angle of 90 *. They also work in Kharkov, but you understand - the opening angle of the Kharkov satellite dish is 70*. In this case, the level and strength of the signal will not be what you expected.
I have a Sat-Integral T-800 Single and a SINGLE Pauxis PX-2100. The latter shows itself better. They work on Kharkov models of satellite antennas. Regarding the Sat-Integral T-800 satellite converter, I am completely dissatisfied. Yes, it works stably on strong transponders, but with weak ones it’s really bad...
Average option for choosing a satellite LNB head.
The price ranges from $3 - $4.
EUROSAT,Eurosky EHKF-P3101A
Eurosky Pro EHKF-7101A
SINGLE Inverto Classic, Red Extend, Black series
Gi 211 Single Universal
I would like to note that the EUROSAT and Eurosky EHKF-P3101A satellite converters have been performing well for a long time (more than 5 years). And LNBs of the Inverto brand have more compact irradiators, which facilitates better tuning to closely spaced satellites. Often used before the advent of narrow converters like Eurosky Pro EHKF-7101A.
Premium version of Single (with one output) satellite converters. Price more than 5$
Megasat Multifeed
Inverto MultiConnect IDLB-SINL20
Inverto ULTRA IDLB-SINL40
Inverto Universal Single (IDLP 401 SST)
What I would like to note. Satellite Single converters with a higher price are almost no different in the level and quality of reception from their cheaper counterparts. The main feature is perhaps the lower noise figure. Although LNB Inverto ULTRA IDLB-SINL40, according to numerous reviews, behaves more stable and does not sag on weak transponders.
As for TWIN and QUATTRO satellite converters, their choice is not significantly different from Single.
Converters of brands that behave well in the Single version will be reliable in two or four outputs.
You might also be interested
Satellite converter
C band converter
Narrow View Satellite Converter
If the cover of the satellite converter has burst
Satellite dish assembly
If the location is determined, it's time to start assembling the antennas. If the antennas will be installed on the roof of a high-rise building, it is worth considering where to assemble the antenna - in an apartment or on the roof, since the assembled antenna may be larger than the roof exit opening. If the assembled antenna does not “climb” through the entrance to the roof, and it is extremely difficult to assemble it on the roof, the assembled antenna can be lifted onto the roof with a rope from the outside.
On the next page you will find a description and detailed instructions for assembling a Kharkov satellite antenna
It is extremely important to understand that all work at height is very dangerous and it is necessary to take all possible precautions and, of course, be well insured.
What tools will you need to assemble and install antennas:
- Open-end wrench 13mm
- 2 open-end wrenches 10mm
- crosshead screwdriver
- Pliers with wire cutters
- Sharp knife
- Hammer with drill
Basic parameters of converters for receiving satellite signals
Scientific sources define a converter as a receiver for processing a satellite signal. In fact, this is not one, but two devices in one monolithic block.
One of them is designed to enhance the signal coming from the satellite. Its operation is characterized by the level of (additional) noise produced. Everything is simple here - the lower the values, the less interference there will be during transmission. In modern devices, this parameter ranges from 0.3 to 0.5 dB. These are quite adequate indicators that fit the definition of “low noise device” or LNA (English abbreviation). Another name associated with the amplifier is the satellite converter - LNB or low noise unit.
Important: not very conscientious manufacturers indicate more attractive data (0.1 - 0.3 dB), but they should not be taken as truthful.
A second device is needed to convert wave frequencies. It leads them to parameters under which the signal can be transmitted to a receiver or TV with a conditional access module without instant attenuation in the cable.
Important: converters are only capable of operating with certain frequency ranges. This characteristic largely determines which converter is best to choose for Tricolor. The device must process the frequencies on which Russian operators broadcast - in the range from 10.7 to 12.75 GHz (the so-called Ki-band).
Polarization of converters for Tricolor
Having decided on the noise characteristics and operating range of the unit, you can move on to the next important parameter - the polarization of the satellite signal. The average satellite subscriber needs to know one thing - that it can be circular or linear (it differs among different operators).
Since Tricolor TV works with a circularly polarized signal, the converter must be selected accordingly. This can be concluded from the inscription “Circular” in the block name. On the contrary, a head marked with the word “Universal” is not initially suitable.
Appearance of Tricolor converters and number of outputs
The LNB unit, hermetically sealed in a metal casing, is placed in an L-shaped plastic case with a rounded cap at the end (hence the common name “head”). The mechanism is mounted on the remote rod of the antenna (so that the signal collected by the dish is focused directly on it). The unit is connected to the receiver via a coaxial cable.
Just by the appearance of the devices, you can determine that they differ in the number of connectors to which the coaxial cable is connected. The classic case is a converter for Tricolor TV with 1 output. An increase in the number of plugs makes it possible to connect not one TV to one satellite dish, but two or even more. Each of them will be able to work in tandem with its own receiver, that is, completely autonomously.
We recommend that you find out why Tricolor TV clients should sign a subscription agreement and where to find the form.
Read: how to install a Tricolor smart card and what it is needed for.
The number of outputs on the LNB can be judged by its markings:
- SINGLE - one;
- TWIN - two;
- QUAD - four;
- OCTO - eight.
Which is better – a multi-output converter or a splitter?
The price of the converter will directly depend on how many TVs can be connected to it. Obviously, a satellite converter with 4 outputs for Tricolor will cost more than a similar device with two connectors and cheaper than with eight.
In addition, ideally, there should be a separate cable from each F-connector of the head to each TV. This only increases the overall cost of multiple connections, especially when you factor in the additional installation. In this case, craftsmen suggest saving money by installing special cable dividers (splitters) directly on the approach to the receivers.
Selecting a channel list
First of all, you need to decide which channels you would like to watch on your TV. lists of channels broadcasting in Russian and Ukrainian on our website on the page “Lists of channels without a subscription fee.” This page lists only channels broadcast in the public domain or that can be opened using Biss keys, which are supported by any modern receiver. If you are not satisfied with the above lists of channels without a monthly fee, you can familiarize yourself with the lists of paid channels from the Ukrainian providers XTRA TV or Viasat, where the conditions for viewing them are clearly described.
Connecting the diseqc switch to antennas and receiver
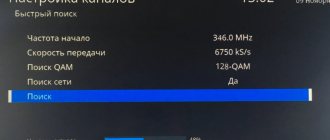
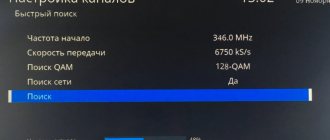
We connect the cables from the converters to the diseqc switch. We write down which switch port (the ports are numbered) each satellite corresponds to. For example, you connected a converter that receives a signal from the HodBird satellite to the first port, Sirius to the second, Amos to the third. Next, connect one end of the cable to the disk drive in the “Reseiver” port, and the other end to the tuner’s “LNB IN” socket and turn on the receiver. In the receiver, go to menu, antenna settings (installation), in the top line in the drop-down list, select a satellite, for example Amos, and in the “diseqc” line select the appropriate port (in this example 3/4, where 3 is the switch port number, 4 – means that our switch has only 4 ports).
In some receivers, the diseqc numbering is not digital, but alphabetic in the English alphabet, for example, LNB “A”, LNB “B”, LNB “C”, etc. We “tie up” the remaining satellites in the same way. We exit the menu with the “EXIT” remote control button and agree to the proposal to save the settings. If connected correctly, channels from all configured satellites should be shown. The second antenna is configured in the same way as the first and is connected to the remaining port of the diseqc switch.
It should be recalled that all connections are made with the receiver disconnected from the power supply.
Types of converters
A feature of satellite systems is the use of different polarizations and frequency ranges. Program transmission occurs in the C and Ku bands, and in the latter - in two subbands. Within individual varieties, there are many LNB options, differing in local oscillator frequency, input and output ranges, and the method of selecting the received polarization.
Most of those used in Europe are so-called universal LNBs or with set values of the so-called LOF (local oscillator frequency) of 9.75 / 10.60 GHz.
Older type heads with a range of 10.7-11.75 GHz and high attenuation are often called "analog" to distinguish them from "digital" ones operating in the 10.7-12.75 GHz range. This is not true. "Analog" and "digital" LNBs will work with both analog and digital satellite receivers, except that the combination of an "analog" LNB and a digital tuner will not be able to receive channels broadcast on frequencies above 11.75 GHz.
For satellite communication
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the satellite signal is distributed in the frequency spectrum C (3.5-4.2 GHz) and Ku (10.7-12.75 GHz). The C-band is used for terrestrial and satellite radio communications, because... has great advantages in operational stability.
Some satellites still broadcast in the C-band, and if they are of interest to you, your antenna will need a C-band converter. It operates in linear polarization, is slightly larger in size than its counterparts and is more suitable for direct-focus mirrors.
For satellite TV broadcasting
The use of broadcasting in the C-band, which is currently overloaded, is declining. The main broadcast occurs in the Ku-band. The transition to broadcasting in a new frequency spectrum makes reception possible with relatively compact dishes.
Regarding the satellite operators popular among Russians, for successful reception and correct operation of the equipment, choose an LNB with the correct parameters:
- converter for telecard – Ku band linear converter;
- converter for Tricolor - Ku band, circular polarization;
- head for NTV plus - Ku band, circular satellite converter.
Number of outputs
The choice of a suitable dish head depends on the number of devices that need to receive the satellite signal.
One way out
LNB with one connector is the simplest type of converter that supports one receiver. The tuner controls the converter depending on what range and polarization it receives. The signal from such an LNB cannot be divided into two tuners with full access to the entire range. The two tuners may provide different control signals to the unit and its operation will become incorrect.
Double output
A satellite circular converter with 2 outputs is suitable for most viewers. It has two independent outputs. Essentially, these are two converters in one housing. This two-port head can support two tuners or a tuner with two signal inputs.
LNB with four outputs
More demanding users will be satisfied with a circular satellite converter with 4 outputs. This quad LNB is equipped with four independent outputs. Its housing contains four individual converters. It can support, for example, four independent tuners or two tuners with PVR function, or two conventional set-top boxes and one with PVR function. A separate antenna cable is supplied to each tuner.
LNB for eight outputs
And for dessert, for those who want to compete with the “cable guys”, a converter with eight outputs. It also has four outputs, but it is a converter designed to work with a signal splitting device called a multiswitch. Each of the outputs of the quattro block has a different range and polarization. The signal from such an LNB, supplied to a multiswitch, can be divided into several tens or even hundreds of satellite set-top boxes. Therefore, eight-port heads are used with a multiswitch in installations where it is necessary to connect more than four satellite receivers to one antenna.
Double monoblock for one output
When using it to receive from two satellites, there is no need to install two separate LNBs complete with double multifeed and a “Dysec” switch to control their operation. The signal from this LNB model is intended for one receiver.
Double monoblock with two outputs
Similar to a single-port monoblock, but with two independent outputs. Allows reception from two satellites. Can support two independent tuners or one PVR tuner.
General characteristics
There is no best LNB, and there is no single parameter that would define this superiority. Converter is different from converter to converter, it cannot be characterized only by color, country of origin or the ill-fated noise indicator, which has been falsified for many years to improve sales.
A really good converter for a satellite dish is distinguished by a solid body that is resistant to weather conditions, especially the sun, because otherwise its body will crumble within a year. What is important is the repeatability of its parameters throughout the entire receiving range from bottom to top, the absence of gaps in frequencies or problems at the beginning of the reception band.
Here are the LNB characteristics that definitely deserve your attention:
| Execution | The converter housing must be made of high quality material that ensures complete sealing. It is good if the case has at least protection for the connectors to protect this area from moisture. |