For those of us who have a TV tuner in our computer, we offer you the frequencies of television channels in Moscow
| 059 MHz | Russia | 517 MHz | News |
| 085 MHz | NTV | 543 MHz | 2x2 |
| 111 MHz | RBC | 591 MHz | Home |
| 119 MHz | NTV (Double) | 599 MHz | Phoenix+Kino |
| 127 MHz | MTV | 615 MHz | 7-TV |
| 135 MHz | TNT | 631 MHz | Star |
| 143 MHz | STS | 647 MHz | Channel 5 St. Petersburg - television channel |
| 151 MHz | TV3 | 663 MHz | EURONEWS |
| 159 MHz | RENTV | 703 MHz | Discovery |
| 175 MHz | Sport | 719 MHz | Animal Planet |
| 183 MHz | Culture | 735 MHz | EUROSPORT |
| 199 MHz | TV Center | 751 MHz | EUROSPORT 2 |
| 207 MHz | Capital | 767 MHz | TV 1000 Russian Cinema |
| 223 MHz | ORT | 791 MHz | TV 1000 - television channel in Moscow |
| 231 MHz | Confidence | 807 MHz | Bibigon |
| 239 MHz | Muz TV | 823 MHz | Amusement park |
| 495 MHz | NKS | 839 MHz | Top secret |
| 511 MHz | DTV |
Digital terrestrial television is a technology for encoding and transmitting sound and video over digital channels. The signal is in DVB-T2 format, which allows you to watch TV channels in good quality for free, even in populated areas at a great distance from Moscow.
At the moment, about 30 channels are available to residents of Moscow and the Moscow region, they are divided into three multiplexes.
First multiplex (RTRS-1)
Launched in 2011. 10 federal channels.
In Moscow, RTRS-1 broadcasts on frequency 546; in other regions the frequency may be different. You can find out more on the broadcast coverage map
| TV channel | Frequency, MHz |
| First channel | 546 |
| Radio Russia | 546 |
| Match TV | 546 |
| Russia 1 | 546 |
| Channel 5 (St. Petersburg) | 546 |
| Lighthouse | 546 |
| Russia 24 | 546 |
| Carousel | 546 |
| OTR | 546 |
| TVC (TV Center) | 546 |
| Vesti FM | 546 |
| Russia K (Culture) | 546 |
| NTV | 546 |
List of on-air analogue channels Moscow and region
Currently, 19 on-air television channels are broadcast from Ostankino in analogue format. In the future, with a complete transition to digital broadcasting, these channels will be disabled.
| Channel | Frequency | Channel | Name | Genre | Range |
| 49.75 | 1 | First | Public Russian Television | Meter | |
| 77.25 | 3 | TVC | All-Russian channel | Meter | |
| 175.25 | 6 | Russia 2 | Sports channel | Meter | |
| 191.25 | 8 | NTV | All-Russian channel | Meter | |
| 215.25 | 11 | Russia 1 | All-Russian channel | Meter | |
| 487.25 | 23 | Pepper | Films, programs | decimeter | |
| 503.25 | 25 | Moscow region | Regional channel | decimeter | |
| 519.25 | 27 | STS | Films, TV series, cartoons | decimeter | |
| 535.25 | 29 | Disney | Children's | decimeter | |
| 551.25 | 31 | Home | Family channel | decimeter | |
| 567.25 | 33 | Culture/Euronews | TV shows, movies/news | decimeter | |
| 583.25 | 35 | TNT | Entertainment channel | decimeter | |
| 607.25 | 38 | Friday | Entertaining | decimeter | |
| 655.25 | 44 | Petersburg 5 | Federal channel | decimeter | |
| 671.25 | 46 | TV-3 | Movies | decimeter | |
| 695.25 | 49 | REN-TV | Movies, TV series, news | decimeter | |
| 711.25 | 51 | Yu-TV | Entertaining | decimeter | |
| 759.25 | 57 | Star | Military Patriotic Channel | decimeter | |
| 783.25 | 60 | Channel Super | Romantic Comedy Channel | decimeter |
Second multiplex (RTRS-2)
Added recently, not yet available (as of September 21, 2019) in all regions, but is being gradually implemented. Connection schedule.
| TV channel | Frequency, MHz |
| Saved | 498 |
| TNT | 498 |
| STS | 498 |
| Home | 498 |
| World | 498 |
| Friday! | 498 |
| Star | 498 |
| TV3 | 498 |
| REN TV | 498 |
| Muz TV | 498 |
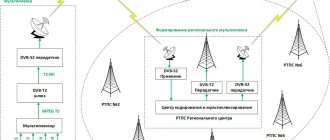
Methods for receiving digital broadcasts
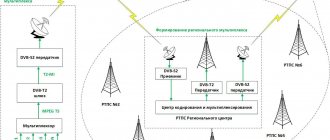
The earliest method of transmitting video in digital format was satellite television, broadcasting mainly foreign channels. Today, three options for receiving digital television are available:
- Satellite. At the moment, you can use it to view all foreign and domestic TV channels broadcasting in Russia in the gigahertz frequency range.
- Cable. It is the most advanced and provides the user with the desired programs to choose from.
- Essential. This option repeats the principle of broadcasting and digital television channels are provided free of charge.
To figure out which method is more suitable, it is better to consider each type of broadcasting separately.
Satellite TV
Despite the high cost of the equipment, it still remains the most popular, but over time it is losing its position. This is due to the fact that digital and cable broadcasting appeared relatively recently.
An important advantage of a satellite dish is that television is independent of weather conditions. For reliable reception, all that is required is the correct direction of the dish towards the satellite. The signal is transmitted from the satellite in the gigahertz frequency range. You can also use it to watch all foreign channels that the receiver can pick up.
Cable TV
This type of broadcasting involves the complete absence of receiving equipment. The entire responsibility for organizing signal transmission (installation of wired and wireless sensors, signal sources and other components) is assumed by the provider. Basically this is installing a tuner on a repeater, sometimes a direct cable from a TV tower. At the exit, residents have only a cable.
Cable TV has two advantages:
- Versatility. It provides both digital and analogue broadcasting.
- Large selection of channels. With it, a set of any free and paid channels is available.
Also, cable television does not require an antenna, i.e. when connected, the user receives turnkey broadcasting.
Terrestrial TV
It works on the same principle as analog. To view it, you only need an over-the-air analogue television antenna and support for receiving a DVB-T2 signal. Broadcasting is provided by multiplex repeaters.
This type of digital reception is currently poorly developed and has a small coverage (only the first multiplex operates throughout the entire territory), but over time the broadcast area is only expanding.
Third multiplex (RTRS-3)
Operates in test mode in Moscow and the Moscow region. About 40 channels. Broadcasts on frequency 578.
| TV channel | Frequency, MHz | Broadcasting time, h/week |
| Sports 1 | 578 | Around the clock |
| Sports 2 | 578 | 00:00-06:00 (42) |
| Fight club | 578 | 06:00-12:00 (42) |
| My planet | 578 | 12:00-18:00 (42) |
| Science 2.0 | 578 | 18:00-00:00 (42) |
| Russian novel | 578 | 00:00-05:00 (35) |
| Russian bestseller | 578 | 05:00-10:00 (35) |
| Russian detective | 578 | 10:00-15:00 (35) |
| Story | 578 | 15:00-20:00 (35) |
| Cartoon | 578 | 20:00-00:00 (35) |
| Sundress | 578 | 00:00-12:00 (84) |
| A country | 578 | 12:00-00:00 (84) |
| Living Planet | 578 | 00:00-06:00 (42) |
| IQ HD (SD quality) | 578 | 06:00-09:00 (21) |
| 24 Doc | 578 | 09:00-12:00 (21) |
| Techno 24 | 578 | 12:00-15:00 (21) |
| Mother | 578 | 15:00-18:00 (21) |
| NST | 578 | 18:00-21:00 (21) |
| Amusement park | 578 | 21:00-00:00 (21) |
| Moscow. Confidence | 578 | 00:00-12:00 (84) |
| euronews | 578 | 12:00-00:00 (84) |
| Music of the First | 578 | 08:30-01:30 (119) |
| Home Cinema | 578 | 01:30-02:30 (7) |
| Time | 578 | 02:30-04:30 (14) |
| TV cafe | 578 | 04:30-06:30 (14) |
| Beaver | 578 | 06:30-08:30 (14) |
| 365 days of TV | 578 | 00:00-02:00 (14) |
| TNT-Comedy | 578 | 02:00-04:00 (14) |
| Lots of TV | 578 | 04:00-06:00 (14) |
| HD Life (SD quality) | 578 | 06:00-08:00 (14) |
| STV | 578 | 08:00-10:00 (14) |
| India TV | 578 | 10:00-12:00 (14) |
| Fighter | 578 | 12:00-14:00 (14) |
| Comedy TV | 578 | 14:00-16:00 (14) |
| La Minor | 578 | 16:00-18:00 (14) |
| Men's cinema | 578 | 18:00-20:00 (14) |
| Kitchen TV | 578 | 20:00-22:00 (14) |
| Auto Plus | 578 | 22:00-00:00 (14) |
| LifeNews | 578 | Around the clock |
| Our football | 578 | Blocked |
Characteristics of the broadcast standard
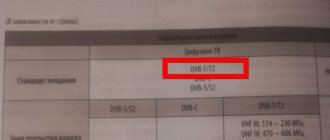
Digital terrestrial television works by encoding and sending the signal to repeaters for further transmission to end consumers. To obtain an image in digital format, the user needs to decode the signal. This function is performed by the TV tuner, which is present on the digital set-top box and on all televisions. Today in Russia the DVB-T2 format is used, which belongs to the second generation of the European digital broadcasting standard.
This signal is transmitted in the decimeter range. It is called that because a signal propagates with a wavelength from 10 to 100 cm, which corresponds to a frequency range of 300 MHz - 3 GHz. Up to 800 MHz are the frequencies of digital channels broadcast from terrestrial stations. Satellite television operates at gigahertz values, which broadcasts in a separate direction and the signal is transmitted according to the DVB-S2 standard.
Frequencies of DVB-T2 digital channels
| TVK | Frequency, MHz |
| 21 | 474 |
| 22 | 482 |
| 23 | 490 |
| 24 | 498 |
| 25 | 506 |
| 26 | 514 |
| 27 | 522 |
| 28 | 530 |
| 29 | 538 |
| 30 | 546 |
| 31 | 554 |
| 32 | 562 |
| 33 | 570 |
| 34 | 578 |
| 35 | 586 |
| 36 | 594 |
| 37 | 602 |
| 38 | 610 |
| 39 | 618 |
| 40 | 626 |
| 41 | 634 |
| 42 | 642 |
| 43 | 650 |
| 44 | 658 |
| 45 | 666 |
| 46 | 674 |
| 47 | 682 |
| 48 | 690 |
| 49 | 698 |
| 50 | 706 |
| 51 | 714 |
| 52 | 722 |
| 53 | 730 |
| 54 | 738 |
| 55 | 746 |
| 56 | 754 |
| 57 | 762 |
| 58 | 770 |
| 59 | 778 |
| 60 | 786 |
| 61 | 794 |
| 62 | 802 |
| 63 | 810 |
| 64 | 818 |
| 65 | 826 |
| 66 | 834 |
| 67 | 842 |
| 68 | 850 |
| 69 | 858 |
What you need to view
Depending on the type of broadcasting, different equipment will be required, but in all cases, support for receiving a DVB-T2 signal is required. The easiest way to organize a digital format will be for cable TV users. To watch you need a modern TV; reception and broadcasting of channels is provided by the provider.
Terrestrial TV will cost a little more, because... You also need to buy an antenna for installation in a private house, or pay for a connection to a collective one. Given the incomplete coverage throughout the country, in addition you will need to buy an amplifier.
To use satellite TV you need to go broke even more. Often it comes complete with a satellite and a receiver, and when purchasing satellite TV you do not need to buy anything else, but the cost of the kit may force you to abandon it. Unfortunately, one plate is not enough, because... The receiver is needed to unblock paid channels.
List of digital TV frequencies for setting up TVs and set-top boxes
| № | frequency, kHz | Modulation | Symbol rate, MS/s |
| 1 | 386000 (SK30) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 2 | 394000 (SK31) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 3 | 402000 (SK32) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 4 | 410000 (SK33) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 5 | 418000 (SK34) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 6 | 426000 (SK35) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 7 | 434000 (SK36) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 8 | 442000 (SK37) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 9 | 554000 (31TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 10 | 546000 (30TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 11 | 562000 (32TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 12 | 570000 (33TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 13 | 578000 (34TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 14 | 610000 (38TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 15 | 618000 (39TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 16 | 634000 (41TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
| 17 | 642000 (42TVK) | 256 QAM | 6750 |
Price: free or paid?
All the availability of digital television is rather conditional. Because you can only enjoy it when you connect the TV to an individual or collective antenna. And if the cost of the first depends on its model and technical capabilities, then the second costs a metropolitan resident approximately 230 rubles/month.
It is also worth understanding that digital quality TV is a new branch of its development. This type began to actively displace analogue, due to the quality of its image and sound. However, since this is a new technology, to use it you must have a TV with a built-in DVB-C tuner. But older generation TVs are capable of receiving exclusively analog TV.
Thus, in order to be able to enjoy a high-quality picture, a Moscow resident must connect to an antenna, as well as purchase a new generation TV, or equip his or her set-top box for receiving digital TV, the cost of which can range from 900 to 5 thousand rubles.
DVB-T
This standard has not become the main one in our country, giving way to the second version, but it is quite suitable for use by the operator for the reason that DVB-T2 receivers are backward compatible with the first generation standard, which means the subscriber can receive such a signal on almost any digital TV without additional consoles.
In addition, the standard intended for transmission over the air (the letter T stands for Terrestrial, ether) has such good noise immunity and redundancy that it sometimes works where, for some reason, an analog signal cannot penetrate. On the device screen we can observe how the 64QAM constellation is being built (the standard supports QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM). It can be seen that in real conditions the points do not add up into one, but come with some scattering. This is normal as long as the decoder can determine which square the arriving point belongs to, but even in the above image there are areas where they are located on the border or close to it. From this picture you can quickly determine the quality of the signal “by eye”: if the amplifier is not working well, for example, the dots are located chaotically, and the TV cannot assemble a picture from the received data: it “pixelates”, or even freezes completely. There are times when the amplifier processor “forgets” to add one of the components (amplitude or phase) to the signal. In such cases, on the device screen you can see a circle or ring the size of the entire field. Two points outside the main field are reference points for the receiver and do not carry information.
On the left side of the screen, under the channel number, we see quantitative parameters:
Signal level ( P
) in the same dBµV as for analogue, however, for a digital signal GOST regulates only 50 dBµV at the input to the receiver. That is, in areas with greater attenuation, the “digital” will work better than the analogue.
Modulation error value ( MER
) shows how distorted the signal we are receiving, that is, how far the arriving point can be from the center of the square. This parameter is similar to the signal-to-noise ratio from an analog system; the normal value for 64QAM is from 28 dB. It can be clearly seen that significant deviations in the above image correspond to a quality above the norm: this is the noise immunity of the digital signal.
Number of errors in the received signal ( CBER
) — the number of errors in the signal before processing by any correction algorithms.
Number of errors after operation of the Viterbi decoder ( VBER
) is the result of a decoder that uses redundant information to recover errors in the signal. Both of these parameters are measured in “pieces per quantity taken.” In order for the device to show the number of errors less than one in one hundred thousand or ten million (as in the above image), it needs to accept these ten million bits, which takes some time on one channel, so the measurement result does not appear immediately, and may even be bad at first (E -03, for example), but after a couple of seconds you reach an excellent parameter.
Settings for Philips and Sony TVs
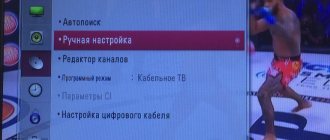
You can set up cable and digital TV on both TVs using the general guide, which will be discussed together. At the first stages, everything is according to the standard - language, region and PIN code. The frequency is set manually only when connecting a satellite dish; in other cases it is determined automatically based on the characteristics of the connected receiver.
Next will be the choice of provider. All major Russian operators (Rostelecom and MTS) are present, but the little-known regional provider will be conspicuously absent. In order not to make a mistake, it is better to select the “Other” item. This must be done in order to connect digital television and not return to the settings after changing providers.
The latest versions of Philips with Smart TV function have “Home” and “Shop” operating modes. The first one is selected, because only it opens all the functionality. The second is used by sellers so that they can let the buyer use the TV before purchasing.