Progress does not stand still and now you don’t need to be a millionaire to buy a 40-inch flat-screen TV (although you will have to shell out a fairly large sum). Such devices are usually called “plasma”. The main advantage of a plasma display is the low cost of a large-diameter matrix.
Here the situation repeats the case with LCD monitors exactly the opposite: the larger the matrix size, the more profitable it is for the manufacturer to create it. In this case, the price is determined by the contents of each specific model, the ability to connect to a computer, and the presence of not only a digital, but also an analog connector.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of any plasma screen (PDP - Plasma Display Panel) is a controlled cold discharge of a discharged gas (usually xenon or neon) in an ionized state. All this is called “cold plasma” - hence the name.
The ability of certain gases to glow when an electric current is passed through them is still widely used in so-called neon signs. To do this, sealed containers of a certain shape are created (usually depicting the advertised product or in the form of letters), after which the container is filled with gas. If you apply electric current to the contacts, the gas inside the advertisement begins to glow. When the current supply is stopped, the gas stops glowing. The color of the sign's glow depends on the proportion in which certain gases will be mixed.
A similar principle is used in the creation of plasma displays for computers and large-diagonal televisions. Only the dimensions of the vessel in which the gas is stored are thousands of times smaller, and the vessels themselves, of which there are tens of millions, form a matrix that forms the image on the screen.
Disadvantages of Plasma
Disadvantages of plasma TVs:
- lack of models with small diagonals;
- heating during prolonged viewing;
- high energy intensity: power consumption of a 42-inch plasma TV is approximately 160 - 190 W/hour and 0.5 W in standby mode;
- the appearance of afterimages on static elements;
- Brightness is inferior to LCD TVs.
A lot of electricity is spent converting inert gas into plasma. For cooling, fans are provided, which further increase the energy consumption of plasma TVs.
The contrast of the plasma decreases over time, and after several years of use the image becomes less colorful than at first.
Plasma pixel burnout can occur when a static image is presented on the screen, for example, when connected to a computer. During normal viewing, this phenomenon may not occur at all. New TV models have practically no problems with pixel burnout.
Main characteristics of plasma panels:
Like ordinary monitors, plasma panels have five resolution formats - VGA (the simplest, supported by all plasma panels - 640x480), SVGA (800x600), the most common and convenient to use - XGA (1024x768), SXGA (1280×1024), UXGA (1600×1200) are also common. Resolution is measured in pixels. Plasma panels are designed in such a way that the resolution may differ from the format generally accepted in the computer community, for example, there is a resolution of 1280x768, however, as you might guess, a plasma panel with this resolution will support the XGA format. Despite the discrepancy in physical resolution in some cases, manufacturers modify the image, “adjusting” it to the parameters listed above using special converters.
Another important characteristic of plasma panels is the aspect ratio, that is, the ratio of the width of the screen to its height. In total, two formats are used - 4:3 and 16:9. Most plasma panels use the 16:9 format - this was done by manufacturers with the expectation of using a plasma panel for a home theater, since a movie is initially recorded on wide-format film and it is while watching wide-format versions of movies that the “idea” of the film director is most fully revealed. However, if you use a plasma panel as a TV to watch broadcast programs that are transmitted in 4:3 format, you should pay attention to the possibility of scaling it so as to fill the empty screen space as much as possible.
Many people would like to use a plasma panel instead of a traditional TV. To do this, the panel must have at least two functions: a built-in tuner (in this case the name plasma TV is used) and speakers. As for the tuner (TV receiver), it is built into a very limited number of plasma panels; all others use an external tuner. This can be either a special TV tuner, or a VCR, or a satellite receiver, or a cable TV receiver.
Built-in speakers are also very rare, but most models have a built-in stereo amplifier (usually no more than 7 W per channel), and external speakers are sold as an option. But for a home theater, the lack of built-in speakers is usually not a big disadvantage: in systems of this class, where a plasma TV is present, as a rule, a high-quality external speaker system with a receiver is used.
In addition to all of the above, each of the plasma panels can have functions such as adjusting the size and position of the image, picture-in-picture, digital freeze-frame, rotating the image 90 degrees (portrait position), Russian-language menu, as well as various enhancement technologies video image quality, increasing image contrast, smoother moving objects and achieving more realistic color rendition.
TVs. Part 2. Plasma or LCD, chassis, diagonal, motion transmission, color, effect on vision
Hello again, dear habra-people. The first part aroused some interest, so it was decided to continue this topic. I would like to say a special thank you to those who paid attention to the first part. I did not think that my modest article would arouse such considerable interest.
We can continue. In the second part, I would like to share my thoughts on the choice of TV diagonal for various applications, the choice of technology, as well as how frame interpolation affects the smoothness of movement and try to debunk some myths regarding modern TVs. Also, I want to touch on the topic of the influence of various TV parameters on vision.
After I figured out the hardware, I decided that now I need to find out what affects the image in practice and how, knowing this, you can choose a TV.
Chassis
We need to remember such a concept as the chassis. Roughly speaking, this is all the electronics inside the TV. TVs on the same chassis have exactly the same video path. TVs with the same chassis necessarily carry the same set of inputs and have exactly the same signal processing. Chassis models are most often described in service instructions, but they cannot be compared directly: the chassis does not have characteristics by which comparisons could be made. When LCD matrices are produced by only a few players in the market (these are Samsung, Sharp and LG), the chassis is developed by almost every TV manufacturer. Of the major players, only Sharp is not doing this (oddly enough, it produces the best matrices on the market and is unable to develop a chassis), which buys the chassis from Philips. Basically, the chassis differs from series to series (the lower the series, the simpler the chassis), one chassis model can cover several series (then TVs from different series will be similar). Philips, if I may say so, created an interesting incident this year - it built all TVs from the 6th to the 9th series on one chassis, which means that, among other things, all these TVs have one image processing processor that responds for frame interpolation. Philips calls different types of processing with beautiful marketing names “Perfect Pixel HD”, “Pixel Precise HD”, and if previously there were real differences in processing between these names, now all the differences have been erased. I understand why Philips left different names for essentially the same treatment - older series TVs should feel superior. But it's not fair.
LCD, Plasma - what to choose?
If you haven’t read part 1 of the article and don’t know the main differences between different image output technologies, matrices and different types of LCD backlighting, I advise you to read it.
If you are choosing a TV, you should first decide which technology to choose. And this is the hardest part. The sellers unanimously said that there was nothing other than LCD; on “advanced” video forums they only recommended plasma. Everything turned out to be a little simpler - everything has its own purpose and each technology is suitable for its task.
What factors influence the choice in favor of LCD
— You are watching TV in a bright room.
Plasma is essentially glass, and no matter how “cool” the anti-glare filter is, plasma behaves worse in bright light. Add to this the high brightness of LCD LED and you get the answer - if you watch TV in a bright room, you should pay attention to LCD.
— You want to use the TV as a monitor (Internet, image processing)
As you know, LCD has virtually no memory effect when the image “freezes” on the screen, so it is ideal as a technology for monitors. Plasma has a residual image effect. In addition, gradations on a plasma display occur using dithering, so near a clear grid of pixels you can’t see everything “moves.” Plasma is not suitable as a monitor.
— Do you want a small diagonal TV?
Small diagonals are where LCD reigns supreme. FullHD plasma starts only at 42″.
— Your eyes do not perceive the imaging technology of plasma TV
There are people (only a few percent) who are not suitable for plasma because they see flickering. If you see flickering, set the mode to 96 Hz, turn off all the lights (“energy-saving” lamps also have their own frequency and it can interfere with the plasma), change the settings if you are using a PC. Only then will it be possible to talk about “flickering”.
- Do you like oversaturated colors?
I do not belong to this category of people, but there are such people.
What factors influence the choice in favor of Plasma
— You want to watch mostly HD
Blu-Ray content, BD rips - it's all about plasma. These are her best friends and she brings out quality content the most.
- You often watch TV with the lights dimmed or in the dark
If light is plasma's main enemy, then darkness is its best friend. It is in the dark that the image reveals itself in full force.
— You choose a TV for home cinema
Cinema is what people buy plasma for. It is this that creates the “volume” effect of a 2D image, has a deep black level, is famous for its lack of flare, and has excellent contrast transitions.
— You need a large diagonal TV:
50″—65″ these are exactly the diagonals in which you should choose plasma. A 65″ LCD TV for home theater is a very strange choice.
- Do you like natural colors?
I do a little photography and have an idea of what reference colors are. These are not at all dull, as you might think, but bright, rich and deep colors.
Diagonal selection:
It's time to choose the diagonal for your TV.
The choice of this diagonal is influenced by the following factors: - Distance to the TV. Attention - only distance, the size of the room does not affect the choice of diagonal. — Content permission. It is absolutely clear that the higher the clarity of the content, the closer you can watch TV. - Purpose. If you choose a TV for a home theater, this is one diagonal, a TV for the dacha is another. - Budget. If, as often happens, the budget is limited, it is not necessary to buy the recommended diagonal; you can buy a smaller one. There is such an organization: George Lucas's THX, which gives out picture certificates and sets standards in the field of television. It is her recommendations that I propose to use (especially since these are recommendations not of just THX, but of many, many companies and experts.
I present for your consideration a table of diagonals:
When I bought my first modern 42″ TV for viewing from 3 meters, this table would have shocked me, but not now. Now I realized that the diagonal tends to “shrink out” (when the TV appears large at first). Please note that the table is relevant when choosing a TV for a home theater. If you are not such a “gourmet” and choose a TV for a pleasant viewing of programs in the evening, you can pay attention to smaller diagonals. When choosing the THX-designated diagonal for 1080, the diagonal does not seem large, the eyes do not run around the screen and do not get tired at all.
One simple rule applies here: there can never be too many diagonals. If you are choosing a TV for a home theater and are not limited by budget, take the diagonal from the table.
What about the eyes?
So we come to the most common myth that has remained in our memory since the days of CRT.
This is due to the radiation generated by this type of TV. Modern TV lacks this. The myth says that the larger the diagonal of the TV, the more harmful it is to the eyes in the long run. It is mainly the accommodative muscle, which is responsible for focusing, that “breaks”. She stretches the lens so that the rays converge at the desired point. When the functions of the accommodative muscle are disrupted, a spasm of accommodation occurs and it becomes increasingly difficult for the eye to focus on distant objects. School-age children are at high risk of developing myopia. What causes vision damage when watching TV? In general, due to the same thing that causes it to deteriorate when reading a book, especially in dim light - the eye focuses at one distance, tenses, and the ability of the accommodative muscle is impaired. The muscle tenses the more, the closer and smaller the object on which you need to focus. What conclusions can be drawn from this? — The closer the distance to the TV, the more tired the eyes are and the higher the likelihood of visual impairment. But the dependence is not linear (that is, 2 meters is not 2 times more harmful than 1 meter), but rather exponential or close to it, and there is no big difference between 2 and 3 meters. — The smaller the object on which you need to focus, the more tired your eyes are and the greater the likelihood of disruption of accommodation functions. That is, in theory, a small diagonal is more harmful than a large one. I was unable to find research on this matter, but we can say with confidence that, all other things being equal, a large diagonal of an LCD or plasma TV is no more harmful than a small one.
Frame interpolation
Many users ask why fast movement of objects or panning looks smooth on some TVs, but not on others.
It’s worth starting with the fact that the 24 frames per second standard for the film industry was adopted in the first half of the 20th century, when the requirements for cinema were somewhat different and excessive waste of film was not welcomed. This “jerking” of the image is called a strobe. It is an absolute fact that 24 fps is not enough to convey fast-moving objects or panoramic camera movement. This means that if software processing is turned off, all televisions without exception will display this type of motion not in the best images. We are hostages of the standard. There are several real solutions to this problem, but they all boil down to increased frame rates. 1) Frame interpolation. Something that all modern TVs in the mid-price category can do to varying degrees of success. The TV analyzes 2 adjacent frames on the fly and draws another one or even 2 at its discretion. 2) HFR (high frame rate). Shooting initially in high frame format. It eliminates image processing artifacts by the TV processor, but requires special shooting, and most importantly, the media. The first and only film produced by HFR was The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey. It is not yet clear to me what media it will be distributed on or whether it will be distributed in HFR at all. All methods of increasing the frame rate carry one serious drawback - the loss of the “cinema” quality of the image. The film looks unnatural and unusual. While the film world is at a crossroads - to shoot and watch in HFR or the usual frame rate. No one knows which path will be chosen. Personally, I watch documentaries and cartoons with frame interpolation, but turn it off for feature films.
Frame interpolation is designed not only to combat strobe, but also to increase the dynamic resolution of LCD TVs (only modern Panasonic plasmas are capable of displaying 1080 lines of dynamic resolution with frame interpolation disabled).
So we come to why some TVs show a dynamic picture this way, while others show it differently. To make comparisons, you need to set the interpolation value to one position or turn it off completely (different manufacturers call this item differently). Only then can we talk about different displays of dynamics.
Modes
It seems to me that this is the most important point at the initial stage of choosing a TV.
I have often heard people say that models of the same class from different manufacturers show completely different pictures (for example, the Philips 5-series is much better than the Samsung 6-series, etc.). With a 99% probability this is an error and it's in the details. At this stage, almost everything depends on the selected mode. An incorrectly set mode can create the worst image on the best TV in the world. When choosing a TV, pay close attention to the modes - look through all the candidates, choose the ones you like the most. If something doesn’t suit you, set it to “Custom” mode and adjust the color and contrast settings.
This is where several other myths come from. For example, about the fact that Samsung displays “nuclear” colors. This is true for phones where setup and calibration is nearly impossible or difficult. On TVs, absolutely all parameters are customizable. From here we move smoothly to calibration.
Calibration
This point will be very short, since this is not my environment at all, but a few words are worth saying.
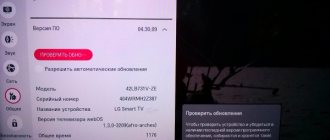
Absolutely everything in our world has permissions. especially in mass production. The parameters of each released TV differ from both the standard and its counterparts. The degree of color deviation from the standard is measured by the complex characteristic DeltaE (this was briefly mentioned in the first part in the “image characteristics” section). The greater the deviation from zero, the greater the color deviation from the standard. As a person who does a little photography, I can say that the standard the colors are very deep, bright and saturated, they do not need any processing. TV calibration is a process when a signal is sent to the input from a reference source, which is measured at the output by a colorimeter. Then the master configures the TV so (only top and pre-top models have full calibration capabilities models) so that it produces colors as close as possible to the standard. On average, it is possible to achieve values of 2-3 Delta E, which is considered indistinguishable from the standard by the human eye.
Instead of a conclusion or brief theses
In a brief form I want to write everything that I wanted to convey for those who do not want to read the whole article: 1) Each technology has its own purpose.
Plasma - for home cinema, large diagonals, viewing in the dark. LCD for viewing in bright rooms, in country houses, when selecting small diagonals, when working with a computer, or if you see plasma flickering. 2) When choosing a TV, pay attention to the modes. They decide a lot. Look at the modes of all candidates for purchase, select the ones you like best, and look at them. Do not compare TVs based on the modes set by store clerks. 3) When choosing a diagonal, start from the task. If you are choosing a TV for a home theater and are not strapped for money, there is never too much diagonal. In this case, for 2.5 m and 1080 content, the ideal diagonal would be 65″. If you are choosing a TV for other purposes, you can, and sometimes need to, choose a smaller diagonal. Don't forget that those TVs that seem huge at first seem much smaller over time. 4) Frame interpolation is a slippery thing. While it helps create smooth movement, it won't be to everyone's taste. It is important to know that there is no universal way to achieve smooth movement of fast-moving objects. There are trade-offs and you have to choose what you want. 5) If you are buying a top-end TV for home theater, it may make sense to have it calibrated. This is especially important for some TVs. In particular for those that have a very large DeltaE deviation out of the box. For example, Samsung ES8000 (8007), Sony HX923. Since the article was much longer than I expected, much of what I wanted to say did not fit here. Let's leave this for the final 3rd part. If you're interested, I'll talk about the types of 3D, their practical differences, pitfalls (complexities and features that sellers don't talk about), sources for playing 2D, and most importantly, 3D content (there are huge difficulties with this), well and about your choice, of course.
Thank you for your attention to my thoughts.
Diagonal size
Traditionally, the display size of a plasma panel or TV is measured in inches diagonally. According to this indicator, panels are conventionally divided into three main categories - with a diagonal size of less than 40", with a diagonal of 41 - 49", and more than 50". The largest number of products belongs to the second category, where plasma panels from almost all well-known manufacturers are concentrated (the diagonal size is mainly 42 or 43 "). We will not dwell on the reasons for this distribution. Let’s just say that this is due to the lack of profit in the production of small-format plasma panels and, on the other hand, to insufficient demand for large-format plasmas (60, 61, 63 “) due to their high cost and lack of superiority in resolution over smaller panels.
What to choose
Plasma TVs are significantly inferior to their analogues in terms of brightness. They are suitable for viewing in the darkest possible room. If you want to create a home theater in a separate room, and also want to get maximum image detail, then feel free to buy plasma.
If you are faced with the choice of LED, plasma or LCD for installation in the living room or bedroom, then give preference to the first option. The second choice is LCD. All this is explained by the peculiarities of the impact of external lighting on image quality. The screens of liquid crystal models fade very much when exposed to sunlight. But this problem is not present in expensive models, the screens of which are supplemented with a special coating.
Another disadvantage of plasmas is the appearance of a static image. This situation occurs when the TV channel logo remains on the display after switching to another channel. The effect in question is extremely rare in modern models.
Now you know which TV is better to choose. The final choice will depend on your individual preferences.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KZGpQEgPu8M
Contrast and brightness.
Despite the fact that these indicators are considered one of the most important, their role when choosing a plasma panel should not be overestimated. The fact is that the non-standardized methodology for determining contrast and brightness does not allow comparing real values. As a rule, the maximum possible, or peak, contrast and brightness indicators are recorded in the characteristics of the model. And therefore, they should simply be taken into account, without being guided by these numbers as paramount. Be that as it may, the higher the contrast and brightness values, the better for the plasma panel and, accordingly, the more saturated and bright the reproduced picture.
LED TVs
Roughly speaking, LED TVs are no different from LCD TVs. They simply use more sophisticated, durable, stable light sources - these are semiconductor crystals. They solved all the problems of gas-discharge lamps in LCD TVs, namely:
- do not have high energy consumption;
- show a service life much longer than gas-discharge lamps;
- are characterized by small dimensions;
- work in a wide temperature range;
- form a more intense color flow;
- are distinguished by a pure, uniform white spectrum, allowing for more color tones to be conveyed on the display.
Like LCD, LED TVs use a liquid crystal matrix and backlight. However, the intensity of its radiation, which has increased many times over, has made it possible to simplify and reduce the cost of the overall design as much as possible. This is how Edge LED backlighting appeared. In it, diodes are placed only around the perimeter of the display. Their light is directed along the screen. Refracting at the light filter and reflecting from the back substrate with a mirror surface, it forms a general, uniform light flux over the entire area of the matrix.
Permission.
The number of pixels (short for PICture ELement). The resolution of the plasma panel directly affects the number of pixels on the screen and the “texture” of the image: the higher the resolution, the more pixels, and, accordingly, the more uniform the image will be. However, a picture even with a high resolution may not look ideal, and on the contrary, a plasma panel with a relatively low resolution can show an excellent image. This depends on other important aspects, the combination of which with the resolution parameter gives tangible results. In particular, the method of image formation is important - interlaced or progressive scanning.
Is it worth taking plasma?
Panasonic exhibited its largest plasma TV in 2010 at the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas. Model TH-152UX1: diagonal – 152 inches (386 cm), weight – 580 kg. The plasma panel produces a resolution of 4096 × 2160 pixels and can display 3D content.
Plasma would be a good choice if the user needs a large diagonal screen at a reasonable cost. A plasma with a good anti-reflective coating will look better in a bright room than an LCD with a glossy finish.
At the moment, only Samsung produces plasma panels. So there's not much choice.
About pixels
In a plasma monitor, to form the color of each individual point, a combination of three subpixels is used, each of which is responsible for one of the three primary RGB colors (Red Green Blue - Red, Green, Blue). The cells are located between two glasses, the distance between which is 0.1 mm (100 microns). When an electrical pulse is applied to the electrodes, some of the charged ions begin to emit light quanta in the ultraviolet range. The emission range, in most cases, depends on the gas used in each specific model. Ultraviolet rays act on a special fluorescent coating, which in turn emits light visible to the human eye. By the way, ultraviolet rays are very dangerous for human eyes, but in this case there is nothing to be afraid of - up to 97% of harmful radiation is absorbed by the outer glass. The brightness and saturation of colors can be adjusted by simply changing the value of the control voltage: the higher it is, the more quanta of light the gas emits, the stronger the fluorescent film glows, the brighter we get the picture on the screen.
Tips for choosing a TV
It would seem that if all TV manufacturers used the same imaging system, all models would offer their customers the perfect picture. In practice this is not the case. On some TVs, only calm video content looks good, for example, programs about nature or news. Dynamic images, such as sword fights or modern special effects, look downright dull and lacking in contrast.
This is explained quite simply. Liquid crystal colloids of different quality have different sensitivity to the electric field. Roughly speaking, they are positioned more slowly when pulsed by the imaging system. As a result, the matrix simply cannot keep up with the video sequence. When displaying dynamic scenes, a situation arises when an elementary color point does not yet produce the required level of transparency, and the TV is already sending a command to reorient the crystals. As a result, the image is blurred and a halo appears around moving objects. This feature of the operation of LCD matrices must be taken into account when purchasing a TV. Some manufacturers explicitly indicate the reaction rate of the crystals.
Important! The peculiarity of human vision is such that the eye-brain system has a minimum time for image and color recognition of 2-4 ms, depending on the characteristics of the organism. If your TV has a response time close to this value, dynamic scenes and complex color transitions will look great on it.
Modern normally transparent LCD matrices have a response speed of 5 ms. These are cheap TN-Film displays and solutions of a similar group. The best IPS matrices show about 4 ms. Premium screens have a response speed of 1-2 ms. But what to do if the manufacturer has not indicated such detailed data in the TV’s specifications, but you want to buy a device to enjoy a perfectly clear picture? In this case, you need to focus on another key TV parameter - the progressive scan frequency. This image rendering mode means that the image is transmitted sequentially, and the pixels are activated without skipping rows. A value of 50 Hz will indicate that the matrix refresh rate is 20 Hz.
This seems to be an unacceptable amount for the human eye. However, it is worth considering the mechanics of the LCD pixel. It needs time to orient itself, only after that a shade with the required characteristics is formed. Thus, the screen refresh interval must be divided by 3 (rounded value). At a frequency of 50 Hz, we get a basic matrix response speed of 6.5 ms. It's already very close. And if you consider that today the market offers TVs with progressive scanning at 60, 80, 100 and even 200 Hz from the best Samsung solutions, buying the ideal model that fully satisfies all your needs will not be difficult.
Connectors and ports.
An important parameter that represents the range of devices that can be connected to the panel / TV. Here it is necessary, first of all, to pay attention to the possibility of connecting acoustics, the availability of ports for working with a computer, etc. For example, the presence of a SCART connector with enabled RGB pins and a fast switching signal, or an S-Video connector with separate luminance and chroma signals, or a Y/C output on SCART, as well as an optical audio output, guarantees the best quality video and audio signals .
Typical problems and their probable causes
The most common malfunctions often found in devices equipped with plasma panels are divided into the following types:
- Violation of the screen glow, manifested in the complete or partial disappearance of the previously reproduced image.
- Lack of a clearly visible picture (in this case the glow does not disappear at all, and only moire or characteristic interference is visible on the screen).
- Spontaneous shutdown of the panel when the image-reproducing device is operating.
- Mechanical damage to the working part of the display.
- Malfunction of the connecting strips supplying power supply voltage and control signals to the panel.
Each of the listed malfunctions requires a more detailed consideration.
The cause of irregularities in the display screen glow is either damage to individual cells, or the loss of the control signal generated by the video processor.
Please note: A special case of the malfunction in question is the burnout of individual pixels of the matrix (usually this problem is classified as damage to the phosphor layer).
In a situation where one “white” field is visible (the image is completely absent), the fault may be hidden in the unit for generating and amplifying the signal from the motherboard (see picture below).
Spontaneous shutdown of the panel in most cases occurs due to overloads in the power supply of the device that includes the display (this usually happens due to a sharp surge in current in the power circuits).
Damage to the display or loss of contacts in the supply cable can be eliminated by simply replacing these components of the TV or laptop.
Operating life of a plasma panel/plasma TV.
This value is not an indicator of the time of plasma failure, but the estimated period of loss of the initial brightness of the image. But, despite the apparent importance of this indicator, it is not worth dwelling on it, since the resource of the filling (electronic and technical) that the plasma panel has in large quantities is also important. And each of the elements of this filling has its own “expiration date”. We can only recommend one thing here: you should trust the products of reputable companies.
Basic structural elements of a TV
The TV consists of the same main functional blocks as decades ago. It has a power supply with multiple outputs to supply power to individual modules. There is always a user interaction system. It has changed from round mechanical switches and slide controls to a fully electronic solution with touch keys and a node for receiving signals sent by the remote control.
There are two main blocks of a modern TV - a signal processing system (television or received from an external device) and a display . The latter has a rather complex structure. It includes a color matrix with thousands of elementary dots and a system for their activation. There is backlighting, light filters, control circuits and many other technical solutions.
But if we consider only the familiar formats of a modern flat-panel TV, imaging technologies have changed little over the years. The elements for creating colored dots have become better. The viewing angles and the speed of their response have increased. However, plasma, LCD, and LED displays all function very similarly. The operating principle of a modern class TV is based on processing a huge array of elementary sources of color formation, which are combined into a single bright and clear picture.
Advantages of plasma panels
Why are more and more people choosing plasma panels?
- The bright areas of the image on the plasma panel glow with an even light, and therefore the image does not flicker at all. This distinguishes the image of a plasma panel from the image of traditional picture tubes, in which the brightness of the elements continuously pulsates, which creates a strain on the eyes and causes them to quickly fatigue. This also applies to projection TVs.
- The plasma panel does not have a harmful effect on humans and pets and does not attract dust to the surface of the screen. In addition, which is very important, they do not have X-rays or any other radiation. Plasma panels are universal and can be used as a TV and as a computer display with a large screen size. All panel models have a VGA input
- Most plasma panels have an aspect ratio of 16:9, so their image is very similar to that of a movie theater. Small dimensions with a large screen diagonal. The thickness of panels with a screen diagonal of 1 m is 10–15 cm, and the weight is about 30 kg. This allows you to place plasma panels in any interior. They can also be hung on the wall.
- A normal image can be obtained from a wide horizontal viewing angle (up to 160 degrees). This allows any viewer in the room to fully see everything that is happening on the screen as clearly as someone sitting in front of the screen.
- High brightness. Plasma panels have high brightness, so they can be viewed in any light. For projectors, for example, the brightness of room lighting has always been critical.
- High reliability. The technical life of plasma panels is 30,000 hours. The service life of conventional picture tubes is 15,000–20,000 hours.
- Resistance to strong magnetic and electric fields, which allows the panel to be used with acoustic systems without magnetic shielding. This can be especially useful when using a plasma panel as part of a home theater.
Cleaning the screen
Improper care of the TV will lead to the appearance of various stains on the screen, glare, scratches, which will not contribute to comfortable viewing. Dust on the screen accumulates static electricity. It should be taken into account that the screen of a plasma device consists of several layers, each of which is sensitive to the effects of aggressive chemicals.
General recommendations on how to clean the surface of a plasma TV screen:
- Carry out cleaning in a room with sufficient lighting;
- disconnect the TV from the network - a safety rule, wait until it cools down completely;
- to remove dust, use a soft, lint-free cloth: cotton, fleece or flannel;
- Use recommended cleaning products to remove dirt;
- Do not press on the screen or use scrapers;
- Do not spray chemicals directly onto the screen. A microfiber cloth or soft, lint-free cloth is suitable for this. Make the napkin damp, but not wet;
- Do not turn on the TV until the screen is completely dry.
The TV body must also be regularly wiped with a soft cloth. Specialized stores sell wet wipes for caring for LCD TV screens. Wipes impregnated with a special composition do not contain alcohol or abrasive components and can be used for any type of screen.
How to clean a plasma TV at home. Prepare a soap solution from baby soap. Laundry soap is not recommended for use due to its high alkali content. Use a soft, lint-free cloth soaked in the solution to wipe the screen. Use a well-wrung cloth to remove any remaining soap and wipe the screen dry.
Image source
When purchasing a plasma screen, you should immediately think about the image source. It is not recommended to connect an old VCR to such a TV, but even if you have a large collection of high-quality video cassettes, it is worth remembering that the VCR must play Hi-Fi tracks, be able to play and record video in the NTSC standard, and have several video heads (the more of them quantity, the higher the image quality). Otherwise (when using a cheap VCR, low-quality, pirated recordings) you will not be able to appreciate all the advantages of a home theater. The amount of interference will be unacceptably high, so they often buy not only an audio system, but also a DVD player together with a plasma screen. At the moment, this is perhaps the highest quality source of video and sound. If regular CDs recorded in Video-CD format and expensive video cassettes have sound recorded in Dolby Surround format, but the DVD has full 6-channel audio in Dolby Digital format.
The third option for obtaining high-definition video images is satellite television (DSS - Digital Satellite System). This market segment is one of the fastest growing. There are now several satellite television networks operating in Russia, for example, NTV Plus and Kosmos TV. In this case, there is only the problem of correct installation of the satellite dish: it must constantly “see” the sky, and even the slightest misalignment of half a degree leads to the appearance of a huge amount of interference, various sound and image defects.
As a result, I would like to note that when purchasing a plasma screen, as a rule, they are guided not by technical characteristics, but by the appearance and specific design of the panel. In our opinion, there is nothing wrong with this: most models with the same price have the same number of functions.
How is TV screen plasma formed?
If you take a piece of ice, which represents the solid state of a substance, and heat it, you get water, the liquid state of the substance. By continuing heating it is easy to obtain steam - a gaseous state. The more heat is applied, the more energy is supplied, the more energetically the molecules (atoms) move.
A relatively solid substance, such as water, is characterized by close bonds between molecules. In this case, the molecules have access to a movement phase (that’s why water flows). The state of steam (gaseous water) is marked by greater freedom of molecules - dissipation energy, due to which the steam fills all available space.
However, if you continue to heat the steam, the molecules and atoms begin to disintegrate, followed by the release of some electrons. When atoms disintegrate in this way, positively charged particles - ions - are formed.
The mixing of positively charged ions with negatively charged electrons creates a conductive state of electricity. Matter in this state is plasma, a special type of gas in which some of the atoms become ions (ionized gas).
Processes of changing the state of matter: 1 – solid; 2 – liquid; 3 – vapor; 4 – plasma; A – atom; I am the core; E – electron; T – increasing temperature scale
Summarizing
Thus, it is not so difficult to determine which is better - a plasma or LCD TV. The last option is considered universal. New technologies and developments have brought image quality closer to the level of plasma devices; they are more economical and cost less.
On the other hand, plasma TVs have a number of additional features that LCD TVs do not have. The final decision must be made based on personal preferences and the set of desired characteristics.
Technological features of LCD TVs
Such a display consists of two plates and liquid crystals placed between them. Transparent polished plates have the same transparent electrodes through which voltage is transmitted to the matrix cells.
Liquid crystals between such plates are arranged in a special way. A beam of light passes through a polarizer installed near the plates, which turns at a right angle. This design is complemented by backlighting and a light filter with RGB colors.
To increase the speed of operation in these devices, special thin-film transistors, better known as TFT, are produced. Thanks to them, each cell is controlled separately. Because of this, the response speed can reach 8 milliseconds.
Which TV has a clearer and brighter picture?
If we compare all plasma and LCD screens, we can say that the former have a better picture. Their image quality is better than the most modern LED models. There are darker and deeper blacks, high contrast. This makes dark scenes more enjoyable to watch. LCDs use pixel backlighting at all times. it cannot be disabled. That's why the black here looks greyish.
Other colors also look more natural on a plasma screen. There are more reproducible shades here, although modern advanced models of LCD screens are almost the same in this parameter.
Plasma copes better with dynamic scenes and conveys movement in games and films more naturally.