GSM-Repeters.RU » How to determine the cellular frequency using a smartphone
When choosing an amplification system, it is extremely important to know two parameters: the generation of the mobile network (2G, 3G or 4G) whose quality you want to improve, and the frequency at which it operates.
The fact is that all the main components of amplification systems - antennas, repeaters, modems and routers - are created for specific frequency ranges and very rarely support all existing standards in the world at once. In other words, you can buy a booster kit “for 4G Internet,” but if it includes an antenna designed for a frequency range that your operator does not operate in, the money will be wasted.
Let's give an example. Most often, 4G Internet is provided at a frequency of 2600 MHz, and most 4G booster kits are designed for this frequency. However, increasingly, domestic operators are starting to use additional frequencies of 1800 and 800 MHz. If this is the network in your location, then a kit designed for a frequency of 2600 MHz will be useless.
So, to choose a kit, you need to know which technologies you want to amplify and in which frequency ranges they operate. The easiest way to do this is using a smartphone running the Android or iOS (iPhone) operating system.
5G frequency bands
| Band | Uplink | Downlink | Duplex |
| n1 | 1920 – 1980 MHz | 2110 – 2170 MHz | FDD |
| n2 | 1850 – 1910 MHz | 1930 – 1990 MHz | FDD |
| n3 | 1710 – 1785 MHz | 1805 – 1880 MHz | FDD |
| n5 | 824 – 849 MHz | 869 – 894 MHz | FDD |
| n7 | 2500 – 2570 MHz | 2620 – 2690 MHz | FDD |
| n8 | 880 – 915 MHz | 925 – 960 MHz | FDD |
| n20 | 832 – 862 MHz | 791 – 821 MHz | FDD |
| n28 | 703 – 748 MHz | 758 – 803 MHz | FDD |
| n38 | 2570 – 2620 MHz | 2570 – 2620 MHz | TDD |
| n41 | 2496 – 2690 MHz | 2496 – 2690 MHz | TDD |
| n50 | 1432 – 1517 MHz | 1432 – 1517 MHz | TDD |
| n51 | 1427 – 1432 MHz | 1427 – 1432 MHz | TDD |
| n66 | 1710 – 1780 MHz | 2110 – 2200 MHz | FDD |
| n70 | 1695 – 1710 MHz | 1995 – 2021 MHz | FDD |
| n71 | 663 – 698 MHz | 617 – 652 MHz | FDD |
| n74 | 1427 – 1470 MHz | 1475 – 1518 MHz | FDD |
| n75 | N/A | 1432 – 1517 MHz | SDL |
| n76 | N/A | 1427 – 1432 MHz | SDL |
| n77 | 3.3 – 4.2 GHz | 3.3 – 4.2 GHz | TDD |
| n78 | 3.3 – 3.8 GHz | 3.3 – 3.8 GHz | TDD |
| n79 | 4.4 – 5.0 GHz | 4.4 – 5.0 GHz | TDD |
| n80 | 1710 – 1785 MHz | N/A | SUL |
| n81 | 880 – 915 MHz | N/A | SUL |
| n82 | 832 – 862 MHz | N/A | SUL |
| n83 | 703 – 748 MHz | N/A | SUL |
| n84 | 1920 – 1980 MHz | N/A | SUL |
| n85 | 2496 – 2690 MHz | N/A | SUL |
| n257 | 26.5 – 29.5 GHz | 26.5 – 29.5 GHz | TDD |
| n258 | 24.25 – 27.5 GHz | 24.25 – 27.5 GHz | TDD |
| n260 | 37 – 40 GHz | 37 – 40 GHz | TDD |
At what frequencies does 4G, LTE Beeline operate?
Since Beeline is one of the first domestic cellular network providers, it provides its customers with a competitive and widely popular 4G telephony service.
The operator is actively developing and improving its working methods, for example:
- annually places relay towers in new regions;
- controls and implements modern mobile communication formats;
- provides clients with flexible tariff plans.
At the beginning of 2021, the company provides 4G communication coverage (“G”):
- all regional centers of the European part of the Russian Federation;
- most of the Central European regions of Russia;
- large administrative centers in Siberia and the Trans-Ural region.
Table 1. 4G and Beeline Internet coverage in the European part of Russia.
| № | Region | Number of repeaters (base stations) |
| 1 | Moscow | 460 |
| 2 | Moscow region | 185 |
| 3 | Tver | 19 |
| 4 | Kaluga | 21 |
| 5 | Tula | 22 |
| 6 | Ryazan | 19 |
| 7 | Yaroslavl | 25 |
| 8 | Rostov | 6 |
| 9 | Ivanovo | 31 |
| 10 | Arzamas | 4 |
| 11 | Saransk | 12 |
| 12 | Nizhny Novgorod | 44 |
2G/3G/4G frequencies in Russia
This picture shows the distribution of frequencies from 450 to 2700 MHz by operators with the designation ARFCN. The distribution of 900 and 1800 MHz is indicated for the Moscow region, the remaining ranges are federal, i.e. the same for all regions.
Individual distribution of the 900 MHz range between operators in Russian regions.
Individual distribution of the 1800 MHz range between operators in Russian regions.
| Standard name | Frequency ranges | Icon on the phone | Possible designations of operating ranges in phones and programs | Range of values for ARFCN, UARFCN or EARFCN |
| GSM-900 (2G) | 900 MHz (Band  | E, G, no icon | GSM900, EGSM900, Band 8 | 0.. 124 |
| GSM-1800 (2G) | 1800 MHz (Band 3) | E, G, no icon | GSM1800, DCS, DCS1800, Band 3, Band 4 | 512.. 885 |
| UMTS-900 (3G) | 900 MHz (Band  | 3G, H, H+ | UMTS900, Band 8 | 2937.. 2712 |
| UMTS-2100 (3G) | 2100 MHz (Band 1) | 3G, H, H+ | UMTS2100, WCDMA2100, Band 1 | 10562.. 10838 |
| LTE-800 (4G, LTE) | 800 MHz (Band 20) | 4G, LTE | 800MHz, Band 20 | 6150.. 6449 |
| LTE-1800 (4G, LTE) | 1800 MHz (Band 3) | 4G, LTE | LTE1800, DCS, DCS1800, Band 3, Band 4 | 1200.. 1949 |
| LTE2600 FDD (4G, LTE) | 2600 MHz (Band 7) | 4G, LTE | LTE2600, Band 7 | 2750.. 3449 |
| LTE2600 TDD (4G, LTE)** | 2600 MHz (Band 38) | 4G, LTE | Band 38 | 37750.. 38249 |
You can read how to choose a cellular amplifier HERE.
Measuring signal levels and frequencies of GSM, 3G, 4G using an IPhone.
Measuring signal levels and frequencies of GSM, 3G, 4G using Android version 7.0 and higher.
Determining the generation of the cellular network
Determining the generation of a cellular network using a smartphone is usually very easy. In most modern operating systems, the data technology is indicated in the status bar next to the cellular signal strength. The technology can be specified directly (2G, 3G or 4G) or using one of the abbreviations. The most common designations are:
- 2G, GPRS (G), EDGE (E) - traditional 2G technology, which runs standard GSM voice communications and slow mobile Internet;
- 3G, UMTS, HSDPA (H), HSPA+ (H+) - the third generation of cellular communications used for calls and access to broadband mobile Internet;
- 4G, LTE (L) is the fourth generation of cellular communications, currently used by domestic operators only for access to high-speed mobile Internet.
For example, on Xiaomi smartphones with dual SIM cards, the status bar looks like this:
It is easy to determine that the first SIM card of the MTS operator is currently operating in 4G mode, and the second SIM card of Tele2 is in 3G mode.
Comments
- 4G potentially operates in all frequency ranges - 800, 900, 1800, 2100, 2600 MHz.
- LTE Band 38 (2600 TDD) is used by Megafon and MTS operators only in Moscow. Repeaters for it exist, but in fact, there is no point in it.
- Yota is the virtual operator Megafon, i.e. Where there is Megafon, there is also Yota.
- LTE Band 7 (2600 MHz) is used only in cities.
- LTE Band 3 (1800 MHz) has the fastest Internet in rural areas.
- LTE Band 20 (800 MHz) – low speed, but the longest range from the base station. This picture at the top of the page shows the distribution of frequencies from 450 to 2700 MHz by operators with the designation ARFCN. The distribution of 900 and 1800 MHz is indicated for the Moscow region, the remaining ranges are federal, i.e. the same for all regions.
What is LTE
Many subscribers of the company often have a question about what LTE means for Beeline. This is regular 4G Internet, which is five times faster than 3G. In terms of quality, it is not inferior to wired Internet or Wi-Fi. With this connection, you can load games, videos, files or pages at a faster speed.
Considering the features of Beeline LTE, what it is, it is worth noting the emergence of a new network - 4G+. Its feature is six times faster speeds than 4G and 30 times faster than 3G. It is not surprising that 4G and 4G+ from Beeline are in demand, and the number of people wishing to connect to it is only growing.
Range system
In each country, LTE operates on different frequencies. Currently, there are more than 44 frequency bands for 4G. To determine them, use the English value 4G band, which is marked with the symbol b with a digital prefix. One country may use one or more of these frequency ranges, divided into two categories:
- TDD;
- FDD
The first group provides sequential reception and transmission of the Internet signal. The second category FDD LTE is called the best option for high-speed Internet. This is explained by the possibility of simultaneous reception and delivery of an impulse. Such a system divides the FDD LTE channel into 2 separate parts.
4G speed
It is worth understanding that the actual connection speed almost always differs from the nominal one. The theory does not take into account factors such as landscape, remoteness of cell sites, or the presence of the user in the building - such conditions interfere with the connection and significantly reduce its quality.
The speed of data transfer also depends on the operator’s workload: the more users have access to fourth-generation networks, the lower the speed indicators. The speed of the Internet connection in wireless networks is determined by the width of the frequency range, as well as the implementation of the communication duplex.
These specifications vary by operator. Although some providers guarantee 300 Mbit/s, the average actual speed is only 75 Mbit/s (Tele2, MTS and Beeline).
The already mentioned tandem of Beeline and Megafon recently began the transition to the LTE-advanced standard, which made it possible to increase speed to 160 Mbit/s in some coverage points.
Now such a standard is presented in Moscow and St. Petersburg, but the regions will have to wait a long time for it: the total distribution of 4G+ throughout Russia is now impossible for two reasons.
The first is the cost of the required equipment, and the second (follows from the previous one) is that as the coverage area increases, the load on existing cell towers will increase, that is, the average speed will only decrease.
Since the speed of the connection depends on the width of the frequency range, we can say that today Megafon is in the most advantageous position, which, after absorbing Yota, added channels of the acquired company to its own frequencies.
Theoretically, the Megafon network can operate on a 40 MHz channel and accelerate in FDD mode to 300 Mbit/s, but since part of the channel is given to subscribers of the subsidiary Iota, the actual speed is approximately 100 Mbit/s.
If we compare networks of the third and fourth generations, the latter have several times higher speeds: an average of 80 Mbit/s versus a maximum of 3 Mbit/s. HSPA+ was able to overclock 3G to 45 Mbps, but these figures still lag behind 4G.
Mobile applications for checking used frequencies
Specialized software, in addition to a convenient interface, provides the user with extensive help information. For example, we can take a closer look at the popular Android application CellMapper.
The following options are available when working with this tool:
- displaying a map of the location of base stations, frequency and other signal parameters;
- support for LTE, GSM and UMTS modes;
- editing and recording of individual data.
In the application, all useful tabs are highlighted in a separate drop-down menu.
Operations can be performed without an Internet connection, but with the GPS module activated; the collected data is subsequently uploaded to the server to create a correct coverage map.
The application operates on any of the 2 SIM cards after registration on the developer’s website.
During the installation process, you must give several permissions to ensure that you receive the following information:
- CellID;
- Cellular network information;
- Samsung Field Test Mode.
The following functions are available:
- writing a CSV file when the Internet connection is disconnected;
- start on boot;
- connection to the duty server;
- obtaining location using GPS signals;
- downloading information for a card from a common database.
On some mobile devices, the application works correctly only if you have root rights. Additional information about CellMapper is published in the Google Play store and on the developer's website.
Is 4G Beeline connected on your mobile phone?
To answer this question and determine the bands number of your operator, the user of a device with mobile communications needs to use the technical menu.
Necessary conditions for receiving 4G format from a Beeline client:
- Have a modern model of smartphone or other mobile device with Internet access.
- Connect at the company office to a Beeline number with high-speed (you can have unlimited) Internet (for example, “Everything” from a mobile operator).
- Exchange your old SIM card for a modern one when connecting to a new tariff.
Expert opinion
Andrey
Beeline salon employee. 5 years in the company. Knows everything about Beeline services and tariffs.
As soon as the subscriber makes a purchase and inserts a SIM card into the device, the Beeline system will immediately register it in its network and automatically configure the 4G format.
The client needs to respond positively to the system’s connection request, and he can use high-speed Internet.
If during the operation of smartphones on the Android or iOS platforms the settings have failed, you can restore them:
- independently, manually specifying the required positions in the phone;
- by coming to any of the Beeline offices, where qualified assistance will be provided by managers.
To configure it yourself, the subscriber needs to know all the details of his cellular operator.
Example of settings by graphs:
- Enter the “Network name” (in English): Beeline Internet.
- Fill in (or select from the list) the “APN” column: internet.beeline.ru.
- The next one is “Username” (in Latin): Beeline.
- “Password” (in Latin): Beeline.
- Select from the proposed “Authentication Type”: PAP.
- Next – “APN Type”: default.
- The last one is “APN Protocol”: IPv4.
Then in the device settings you need to find the section regarding mobile communications:
- On Android: in Settings, select Mobile Network.
- If the subscriber has iOS, then “Cellular”.
- In the subsections, choose from a list of proposed formats: LTE or 4G.
How to check if LTE is connected
To search for information, open the thematic section “Network mode” in the “Settings” menu.
Checking the LTE connection - when you enter the number, a menu with data opens immediately on the smartphone screen.
In certain versions of the Android shell, the user can set the preferred option:
- LTE;
- GSM;
- WSDMA.
By fixing the mode, channel switching is eliminated to stabilize communication in difficult conditions.
You can clarify the data using the engineering menu using the following algorithm (example of actions with a Samsung smartphone):
- turn off the Wi-Fi connection in the “curtain” or in “Settings”;
- indicate the network mode “LTE only”;
- dial the code *#0011#.
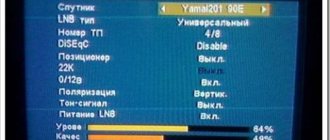
In the window that opens, the frequency band value is indicated in the Frequency position.
Additional information on the screen helps you evaluate the quality of the connection. At low signal strength (worse than 120 dB), the stability of the connection is disrupted. Similar disadvantages appear if the noise level exceeds the amplitude of the useful signal (CINR<0).
How to check the signal on a PC
The necessary information can be found using a laptop or PC by connecting a GSM modem to the USB port.
Algorithm of actions when working with a specialized MDMA program:
- before the first start, close the modem service applications;
- in the main menu select the Band Configuration item;
- mark the Custom position and band (Band 7 or 20);
- click OK.
The communication channel parameters are automatically displayed in the window that opens.
Content
Many owners of mobile devices who use Internet services from various providers are aware of the existence of outdated and new technologies for transmitting data over a wireless network. Thanks to constant improvement, older technologies are being used less and less, giving way to LTE. This new communication standard provides users with high Internet connection speed and signal quality. Internet in the village is the best option, Moscow region.
For successful operation, a certain 4G frequency is used in the Russian Federation. Information about your operator's frequency band may be useful when choosing smartphones and mobile modems, some models of which may not operate in the entire LTE frequency range.
Upper and lower frequencies
From a financial point of view, the development of LTE networks at lower frequencies (less than 2000 MHz) is most profitable for operators. Such frequencies penetrate buildings better, but are not able to provide high-speed connections to areas with high population density.
The functions of the upper frequencies are opposite to the functions of the lower ones, so the best option for a high-quality connection is a combination of both frequency channels, which allows you to get rid of “shadow” areas over large spaces.
Also in megacities, there is a tendency to install special devices on the roofs of office buildings to facilitate the spread of high-speed networks indoors.
Which ranges are better - high-frequency or low-frequency
The lower the frequency, the wider its coverage and better cross-country ability. This gives the user the opportunity to connect to the Internet with a high-quality connection in various remote corners or surrounded by high-rise buildings (and even in the high-rise buildings themselves) in megacities. But such a connection has a lower data transfer rate than high-frequency bands.
For cellular operators, low frequencies (up to 2,000 MHz) are a more profitable solution due to the opportunity to save on equipment. In large cities they are usually used. For the best coverage, the most sophisticated operators combine high and low frequencies. These include, for example, Megafon, MTS, Beeline.
High-frequency bands have higher data transfer speeds, but such towers have a smaller coverage area and wave penetration. They are better suited for open spaces such as suburbs.
Cost and additional conditions
The “Unlimited 4G” option is suitable for computers and tablets, USB modems and smartphones. Connection is free, the subscription fee is 5 rubles per day. After activation, the speed will not be inferior to the wi-fi connection. If the subscriber decides to use the traffic package provided by the tariff plan, then after the limit is exhausted, the volume will be extended automatically, thanks to.
With Unlimited you have unlimited access to the network even when traveling around the country at speeds of up to 75 Mbit/sec.