We strengthen the 2G/3G/4G LTE cellular signal Mobile communications and the Internet are something that modern people cannot do without today. Base stations are installed in the most remote regions of Russia, thereby expanding the coverage area and increasing the number of subscribers in the network. Coverage areas are constantly increasing, expanding, improving, covering not only large cities, but also small settlements, roads of regional and local importance. Operators are doing a tremendous job, trying to ensure the continuity of networks and enable subscribers to use cellular communications almost anywhere and at any time.
- The greatest coverage is on 2G networks (900 and 1800 MHz). The network is quite weak, but quite relevant for most regions of the Russian Federation; it provides voice communications and Internet access at a low frequency. 2G network coverage covers almost the entire territory of Russia.
- The next network in terms of importance and coverage is 3G UMTS/WCDMA/HSPA/HSPA+. Its coverage is about 2/3 of the entire country.
- The smallest coverage (2021 data) is for 4G LTE networks. About 50% of the country's territory.
You can only talk about truly high-quality mobile communications and the Internet in large cities. This is due to the large number of BSs of mobile operators. In cities you can use both high-quality mobile communications and equally high-quality Internet. The same cannot be said about the countryside, villages, and cottage communities. Even in the suburbs of large cities, according to statistics, communication is worse than in the city itself, which forces subscribers to resort to various tricks to improve the cellular signal and mobile Internet.
Why can’t communication in the 21st century please us with its quality?
It seems that there are a lot of towers, and there are already more than five mobile operators throughout the country, and users are forced to “catch” the network by climbing onto heights outside the city or identifying for themselves “that very” place in an apartment or office where they “catch more or less normally” . There is no point in blaming mobile operators for poor communications - companies are doing everything possible to improve the quality of the signal, expanding their coverage area, installing dozens of towers every month. However, their work is more than covered by hundreds of new network subscribers every day. The concentration of users is growing exponentially, so the network simply cannot cope with their influx.
In urban environments, achieving an ideal signal is not always possible. High-rise buildings, reinforced concrete, glass structures are the main obstacles to the movement of radio waves. In rural areas, these “silencers” are forest belts, hills, lowlands and other geological features of the area.
Even the presence of any military facility near the subscriber can affect the quality of the mobile communication signal.
The “pain points” for any mobile operator are parking lots, office and industrial premises located below ground level. Even the presence of a base station in close proximity to such an object does not guarantee stable communications and mobile Internet.
Progress does not stand still: we are strengthening the mobile signal
To achieve high-quality communication, it is not necessary to change your mobile operator, what do you think about strengthening the signal yourself? To do this, you need to think about purchasing a special antenna or a set of equipment to amplify the 2G/3G/4G LTE signal. Do it yourself signal amplification
Determining the signal level
To resolve the issue of the quality of cellular communications and mobile Internet, it is first necessary to determine the signal level that is relevant for a particular area. There is no need to talk about 100% lack of signal even in the most remote villages and settlements. Usually there is a signal, but it is very weak, preventing full use of mobile communications. To know exactly which direction to move next, you should determine the signal level, monitor the premises and find out where the signal is worse, where it is better, establish the types of networks relevant to your facility and the available frequencies. The choice of equipment that needs to be purchased and installed in order to finally solve the existing problem related to either improving the signal level of mobile or Internet, or both.
To determine the level of a cellular signal, a spectrum analyzer and special programs are used that are installed on a smartphone or tablet. You can also install a similar program on your computer.
Attention!
To use the program on a PC, you must additionally connect a USB modem to the computer, into which a SIM card from a cellular operator must first be inserted.
Using such applications via a smartphone is much easier than via a PC. Installation takes literally a few minutes, after which you can immediately start using the program. There is no point in talking about any one application - there are a lot of them, they differ from each other only in their interfaces and some of their “tricks”, but their purpose is the same - to measure the current signal level of a particular mobile operator, as well as determine the parameters , affecting the quality of communication.
Most programs can be easily found in the public domain on the Internet and are available for free download. Let's look at several indicators that you need to pay priority attention to when working with special programs.
RSSI is an indicator of the received signal strength, the values of which are measured in dBm (the value will be preceded by a minus sign). The smaller the minus, the higher the power indicator. For example, a signal of -50 dBm is better than -90 dBm.
| RSSI signal quality | |
| Excellent | -30 dBm to -50 dBm |
| good | -50 dBm to -70 dBm |
| Satisfactory | -70 dBm to -85 dBm |
| Bad | -85 dBm to -110 dBm |
Note: if the RSSI indicator is more than -110 dBm, the signal may be completely absent, interrupted, or unstable.
RSRP is the signal level that is received by the Subscriber from the Base Station. This indicator is measured in dBm. With a value of -120 dBm and below, there is no need to talk about a stable LTE connection; it is often completely absent. The higher the RSRP, the higher the signal strength and internet speed will be noted. Indicators from -50 dBm to -95 dBm are considered optimal. Indicators from 110 dBm and below are considered unsatisfactory.
SINR (CINR) is the ratio of the signal level to the noise level. Measured in decibels (dB). We can talk about a good ratio if this value is high. With SINR values below zero, the connection speed will be low or there will be no connection at all. In other words, this indicator will mean that the signal is dominated by noise. In this case, there is a high probability of complete loss of LTE connection. A good signal will be indicated by the SINR with a plus sign. It is important that the positive indicator is high, in which case the connection will be of high quality, there will be practically no noise, and the Internet connection will be stable.
Example: SINR 20+ dB is a very good indicator, from 10 to 20 dB is good, from 0 dB to 5 dB is satisfactory, from -1 dB and below is bad.
RSRQ —Indicates the quality of the received pilot signals (measured in dB). The indicator shows the noise level (ideally, there should be as little noise as possible). With good signal quality, the RSRQ indicator should be either zero or have a minimal positive value.
CQI is an indicator of signal quality, generated individually for each subscriber station UE and each frequency block.
The values of this parameter range from 0 to 15. With high values, we can talk about good speed provided by the LTE operator’s base station.
Ways to boost a cellular signal
In order to strengthen cellular communications with your own hands (regardless of the operator whose services the Subscriber uses), numerous antennas and special devices are used - namely, signal amplifiers. Let's figure out which ones:
Antennas
External antennas are widely used by users to strengthen the cellular signal. The choice in favor of this equipment will largely be determined by the conditions of use, the current distance from the network subscriber to the Base Station and other parameters. The main difference between antennas is not their cost and design features, but the gain. It is recommended to select an installation taking into account the level of the current signal, which is noted without connecting any amplifying systems. If the signal is more or less good and stable, you can give preference to antennas with a gain of 5 to 14 dB. If the signal level is average, you need to choose among models with a gain from 9 dB to 19 dB; if the signal is poor, you will need to install antennas with a gain of 17-30 dB.
Choosing an antenna for urban conditions
For urban conditions, there are several basic principles of choice: you can purchase an omnidirectional antenna or give preference to a wide-angle (MIMO). What does the choice depend on? Typically, this type of antenna is chosen by users who do not complain about poor communication and low-quality mobile Internet, but at the same time would like to achieve maximum signal performance. The location of the cellular operator's BS to the reinforcement site is of no small importance. In what cases will wide-angle and omnidirectional antennas be effective? Firstly, if the distance to the BS is short, not exceeding 5 km, secondly, the object where amplification of the cellular signal and mobile Internet is required is surrounded by neighboring high-rise buildings (such devices perfectly pick up the signal reflected by neighboring buildings). Some craftsmen construct homemade antennas to enhance cellular communications; a lot of material can be found on this topic on the Internet.
To normalize the signal level (provided that it is initially good), an antenna with a gain of 9 to 15 dB is sufficient.
Selecting an antenna for a vehicle
Car owners interested in constant availability of stable mobile communications are recommended to consider the option of installing an omnidirectional antenna. There is no point in buying a directional model - the constant movement of the vehicle, different distances from base stations, landscape features and other factors affect the signal quality and make the purchase of a directional antenna, which is no longer considered stationary, absolutely impractical.
It should also be understood that directional antennas are bulky and it is illogical to install them on a car - there is no way to properly secure the system and create all the conditions for its normal use.
The peculiarity and advantages of omnidirectional models in this case are high sensitivity and the ability to pick up signals from all towers located in maximum proximity to the car (even while it is moving). Despite the fact that the gain of omnidirectional car antennas is small and does not exceed 12 dB, this will be quite enough to improve the quality of the mobile signal and increase the speed of data transfer via the mobile Internet.
Antennas for rural areas
Rural areas include not only holiday villages and villages, but also warehouses and production facilities located both far from the city and away from the base stations of cellular operators. Rural areas are the most popular segments for strengthening cellular communications, where the majority of the country's population is concentrated, equally interested in the opportunity to use full-fledged mobile communications and the Internet.
A similar problem arises among residents of private cottage communities, as well as among residents of the suburbs, especially near large cities, where there is an increased density of subscribers per base station.
At a significant distance from the base station (more than ten kilometers), directional antennas (regardless of their type) have good efficiency. The most important selection criterion is a good gain (from 15 dB and above). The choice of antenna depends on the terrain, distance from the BS, current signal level, and the presence of obstacles (forest belt, buildings, etc.) that affect the passage of radio waves.
Antenna selection criteria
Directional antennas.
A directional antenna (for example, “Wave Channel”) is ideal for flat terrain. The modifications are distinguished by a good gain (more than 15 dB) and efficient operation at a distance of no more than 20 km from the base station. Capabilities of directional antennas: amplification of the signal and data transmission speed by one and a half to two times.
Panel MIMO
The gain of these models varies from 17 to 24 dB. Their peculiarity is the minimum requirements for directional accuracy, the presence of two antennas operating simultaneously to receive and transmit the incoming signal. Thanks to this specificity, it is possible to completely stabilize the connection and increase the data transfer speed. Panel MIMO with a gain of 24 dB can increase the speed of mobile Internet by a factor of two or more at a distance of 20-23 km to the base station. The shorter the distance to the BS, the greater the increase in transmission speed.
Parabolic MIMO
It is advisable to use this type of antenna in the case of a significant distance between the Subscriber and the base station of the cellular operator, at a distance of 25 km or more. MIMO parabolic antennas have a gain of about 30 dB.
If mounted on the roof of a house and directed to a base station, the antenna can amplify a practically absent signal and increase the speed of mobile data transmission.
Automatic Interference Cancellation (ALC)
As already mentioned, by increasing the signal power, the repeater also increases the interference that enters the street antenna. Thus, the loud sound of voice communication is accompanied by extraneous noise, which causes its quality to sharply decrease. But many repeater models are equipped with an auxiliary option - automatic interference suppression.
This feature not only increases the signal strength, but also removes noise, making the sound perfectly clear. The owner receives flawless communication without an unpleasant background.
All presented parameters and additional features of the cellular communication amplifier affect its price. The more functional and convenient the device, the less likely it is to damage the equipment, the more expensive it will cost the buyer. In order not to make a bad choice, you need to carefully consider all the indicators and analyze the conditions for using the equipment.
Signal boosters
Strengthening the signal of cellular communications and mobile Internet using an antenna is an ideal option for most subscribers. However, users often encounter a lack of signal even with an installed antenna (with normal gain). The reason lies not in weak equipment or improper installation, but in the terrain features, numerous obstacles in the path of radio waves and other factors. It has already been established that even the material of walls and glass with a special UV layer inside can affect the quality of the signal and the degree of its amplification by the antenna.
In this situation, experts recommend using special devices to amplify the signal - repeaters that work in tandem with antennas (one external and internal antennas, the number of which depends on the area of the building, its number of floors and other criteria).
The “repeater + antenna” set, where the gain is at least 40 dB, allows you to achieve a stable signal for mobile communications and the Internet. The coverage area of these systems is from 100 sq.m. or more (maximum coverage 1500 sq.m.). Thanks to the set of equipment, it is possible to “pull out” the signal (even if it is actually absent), provide a stable connection without failures or interruptions, as well as high-quality mobile Internet. An external antenna is responsible for signal reception, a repeater is responsible for amplification, and internal antennas are responsible for distribution over the coverage area.
Repeaters (mobile signal amplifiers) are devices whose main purpose is to strengthen the signal coming from the base station of a cellular operator without converting the signal strength to indicators sufficient to ensure high-quality communication.
GSM repeaters receive a signal from an external antenna and amplify it, locally expanding the coverage area. This is a complex technical device, the full functioning of which requires a set of antennas and cables.
IMPORTANT!
Repeaters are independent devices, the installation of which does not require coordination with mobile operators.
How repeaters work
The signal from the base station is captured by an external antenna, then it is transmitted via a coaxial cable to a repeater, which amplifies the incoming signal and transmits it further along the cable to the internal antennas. The installation locations of internal antennas are selected by the Subscriber himself before their actual installation. The number of antennas depends entirely on the area of the building and its number of floors. The more internal antennas, the more coverage areas the amplified signal will provide.
It is recommended to purchase a set of equipment in specialized stores. Specialists, taking into account the characteristics of the building, the existing measurement of the current signal level, as well as the geological features of the area, will select the most optimal equipment in terms of technical and operational characteristics. It is important that specialists will be able to advise, provide detailed information about the equipment, and, if necessary, install the system and configure it. Strengthening a GSM signal with your own hands is possible, but sometimes it’s better to turn to professionals, and they have all the necessary equipment and will do all the work in one day and on a turnkey basis!
Before choosing a signal amplification kit, experts recommend paying attention to the following conditions:
1. Decide what communication standard your cellular operator uses. It can be GSM, CDMA, UMTS or LTE. Setting the standard is not difficult - just use special programs for smartphones or PCs.
2. Track the frequencies on which the operator is working and the signal needs to be strengthened.
Rules for choosing a signal amplifier depending on the communication standard
Before choosing an amplifier, you need to decide what exactly needs to be improved - voice communications, mobile Internet, or both. A clear understanding of the tasks is required due to the fact that voice communications and mobile Internet operate at different frequencies.
Amplifiers come in single-band, dual-band, triple-band and even five-band:
- GSM 900, GSM 1800, GSM 900/1800 - designed only to amplify the voice signal;
- GSM/UMTS 900/1800/2100 - enhance mobile communications and 3G mobile Internet;
- GSM/DCS/LTE 800/900/1800/2600 - designed to enhance voice communications and mobile Internet of the 4G generation.
- GSM/UMTS/LTE 900/1800/2100/2600 - used to enhance voice communications and mobile Internet of the 3rd and 4th generations.
Example:
- only voice communication needs to be strengthened - for these purposes, purchasing a repeater operating at frequencies of 900/1800 MHz will be sufficient;
- It is necessary to strengthen voice communications and 3G mobile Internet, in which case it is recommended to buy a GSM/UMTS 900/1800/2100 signal amplifier;
- To improve the quality of voice communications and 4G mobile Internet, you need to purchase an amplifier that supports GSM/DCS/LTE 900/1800/2100/2600 MHz or GSM/UMTS/LTE 900/1800/2100/2600 MHz.
For your information: Voice communications in cities operate mainly at a frequency of 1800/2100/2600 MHz, outside the city, in rural areas - at a frequency of 900/1800 MHz. The standard for 3G Internet is UMTS, with a frequency of 900/2100 MHz.
The new generation 4G LTE operates at different frequencies: in large cities - 900/1800/2100/2600 MHz, outside cities - at 800/1800 MHz.
After determining the required operating frequency and communication standard, you should consider the output power parameters and decide on them. The output power provides a certain coverage area. For a standard apartment or small office space, the figure can vary from 100 to 150 sq.m. The coverage area of a private house or local area usually varies from 200 to 400 sq.m., for large premises, for example, warehouses, production facilities, parking lots, the coverage area should be at least 500 sq.m.
About the main criterion for choosing a repeater
A mandatory selection criterion is the power of the amplifier. On sale you can find options from 10 mW to 2 W or more. The number of internal antennas that can be used in conjunction with the amplifier in accordance with the coverage area stated in the parameters largely depends on the power of the repeater.
Example: A 10 mW amplifier can only operate in tandem with one internal antenna, but a 100 mW model can easily handle up to five internal antennas. 320 mW options can handle loads of up to 15 antennas, etc.
Rules for choosing an external antenna
The main task of the external antenna is to capture and transmit to the repeater via cable the cellular operator signal coming from the base station. Therefore, you should choose an external antenna based on the frequency range at which the repeater operates. This is of fundamental importance, because otherwise the equipment will not work. For the city, you can use two options for external antennas: directional and omnidirectional with an allowable gain of 9-20 dB. In the suburbs and outside the city, in the conditions of holiday villages or cottage developments that are located at a distance from base stations, preference should be given to directional antennas, the gain of which “starts” from 10 dB. Directional models differ from omnidirectional models by a higher gain.
The signal receiving antenna should be installed at the highest possible point and only outside the building. This could be the roof of a house, a mast, a pole specially installed for mounting an antenna, etc.
Why should the installation of an external antenna be carried out exclusively outside the building?
- Firstly, on the street it is possible to “catch” the strongest signal coming from the base station of the cellular operator.
- Secondly, if an external antenna were installed inside a building, its operation would be impaired by interference from internal antennas. And this is not acceptable.
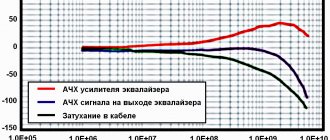
Frequency response of repeaters
Frequency response - amplitude-frequency response - dependence of the repeater gain on frequency. It is always nonlinear, so some channels will be amplified better and some worse. The frequency response has blockages at the boundaries of the ranges of 3-8 dB. Therefore, you need to pay special attention to the channels located on these boundaries.
The cheapest Chinese models cannot provide good signal amplification for all mobile operators due to the large uneven frequency response. Because in the border ranges, a weak signal will be suppressed by a stronger one.
Internal antennas: how to choose the right option
The basic rule for choosing internal antennas is that they must support the same frequency range(s) on which the repeater and external antenna operate. Installation of indoor antennas is always carried out indoors. The number of devices is selected based on the area of the facility, the number of floors and other criteria, for example, the number of rooms, the material of partitions and interior walls. The connection is made through the repeater output connector using a coaxial cable.
The main purpose of internal antennas is to distribute the signal received from the external antenna and amplified by the repeater from the base station inside the building.
Deciding on the number of internal antennas
For small, compact buildings, for example, country houses, where there are no internal partitions or, if there are any, they are made of materials that transmit radio signals well (wood, laminated chipboard, drywall), one internal antenna will be sufficient. For buildings with stationary partitions made of brick, gas silicate, or reinforced concrete, the installation of several antennas is required. The main thing is that the repeater has enough power to install several internal antennas. Therefore, when choosing a set of equipment, experts always ask to provide the most detailed information about the structure and its technical, operational, and architectural characteristics.
Number of channel bands: wideband, single-sideband or selective
Single-band models receive and process signals only from certain bands, and therefore are not able to work with all telecom operators. Such outdated devices are almost never found on the market.
Wideband repeaters work with all bands of a particular channel, providing increased power for both audio and Internet signals.
Selective devices operate on all frequencies of a particular communication standard, but allow the owner to manually select bands and ignore unnecessary signals. This is the most expensive group of devices, as they are effective in difficult radio conditions: they amplify the waves of a certain operator without causing inconvenience to others.
Coaxial cable: why choose it?
Equipment for amplifying a cellular signal works in conjunction with a coaxial cable, the characteristic impedance of which is 50 Ohms. The use of this cable eliminates interference in the operation of the amplification system. The design features of the coaxial cable completely eliminate or minimize signal attenuation and losses along the entire length.
Why can't you use TV cable in amplification systems?
TV cable resistance is 75 Ohms. It is unacceptable to use it in amplification systems, because The characteristic impedance of this type of cable does not completely correspond to the characteristic impedance of the repeater and antennas. The use of a television cable will lead to a mismatch in the operation of the system.
It is important to use high-quality coaxial cable in amplification systems. This way you can be sure of virtually no signal attenuation, and the gain will fully correspond to that declared by the manufacturer. It is especially important to use high-quality coaxial cable if it is necessary to distribute internal antennas at a significant distance from each other. If you give preference to a cheap cable, then all the work of the repeater will be reduced to virtually zero.
Number of frequency bands
Operators distribute signals in different frequency ranges. A few years ago they used separate cellular amplifiers. This method of improving wave power caused a number of inconveniences: all repeaters required their own place and connection to an outlet. To avoid installing several outdoor antennas, a signal combiner was added to the system.
There are currently 2 types of repeaters on sale:
- Devices that are capable of processing waves in only one frequency range are called single-band. In cases where this interval is known, this option may be optimal, since it is considered budgetary.
- For the convenience of users, devices began to be produced that operate in several intervals - multi-band. By design, they represent 2 or more single-band elements connected in a housing and operating from common antennas. Along with the number of frequencies received, the cost of such equipment also increases.
Typically, dual- or tri-band cellular amplifiers are used, configured for 2G, 3G and 4G standards. They provide the user with a reliable sound signal and a high-speed Internet connection.
What are splitters and why are they needed in an amplification system?
For the full functioning of the cellular communication and mobile Internet amplification kit, it is necessary to install additional equipment - splitters (devices are also called signal splitters). Their main purpose is to distribute the signal received from repeaters to internal antennas indoors. Splitters separate high-frequency signals over a wide frequency range and ensure uniform distribution of the signal between all indoor antennas installed in the premises.
There are several types of splitters:
- 1 in – 2 out (one input and two outputs);
- 1 in – 3 out (one input and three outputs);
- 1 in – 4 out (one input and four outputs).
The splitter is selected depending on the number of internal antennas installed in the building.
Types of repeaters
In addition to the amplification characteristics and auxiliary options, you should understand the types of devices. They are suitable for solving various problems and for specific conditions of use. Buyers will have to choose from single-, broadband, or selective cell phone boosters, as well as analog, digital, or optical models.
High frequency connectors
High-frequency connectors are the last “detail” in the system for amplifying the GSM signal and mobile Internet. These connectors are used to connect all equipment into a single chain. Important! There is no point in saving on connectors. It is not recommended to consider cheap options for purchase. Just like coaxial cable, connectors play an important role in the smooth operation of all equipment. Poor quality connectors can cause signal loss on the way from the external antenna to the repeater and internal antennas. We recommend buying connectors with a characteristic impedance of 50 Ohms, type N or SMA, but it is advisable to avoid type F, because In practice, cases of excessive signal loss have already been noted.