TV is one of the main objects in every apartment. When purchasing it, you can find obscure letters on the case, like DVB-T2 and others. Many people have different thoughts on this matter. It just so happens that people in the CIS learn about such new products after some time. This is due to the fact that they are developed and tested in the West. Today you can find out what DVB-C, DVB-T2, DVB-T, DVB-S2 are.
What are the little-known letters DVB?
“DVB” is the first letter of a consortium of European countries that have invented digital TV standards in a row. In English, these three letters have the following meaning: project: digital video broadcasting. The main difference between regular TV and digital TV is the clarity and stable image picture. Older generations of TV viewers remember analog antennas and channels with ripples that were almost impossible to get rid of.
Everything changed with the advent of a new type of video delivery to TV screens. The DVB project is developing in all directions and types of image delivery: terrestrial, cable, airborne and others. Today, such data is transported using signal encoding. A newly designed type of data transmission allows us to encode not only the image signal to our televisions, but also additional data. Such as, for example, a TV program guide.
Due to the fact that there are essentially several different methods of transmitting information (via cable, satellite, etc.), additional technology abbreviations have appeared (DVB-T, DVB-C, etc.). Which will be discussed further. If your new TV supports one or more of these standards, this is definitely a plus for you. Since other TV viewers need to purchase a separate set-top box to connect the corresponding television. Therefore, the price of a TV if it has DVB abbreviations on its body will be higher than others.
More about DVB-T2 and DVB-T
DVB-T2 is another digital European standard for terrestrial television. As in the first description of the standard, DVB-T2 is the second generation of the DVB-T standard. Its newer version is designed to increase the throughput of broadcast data by up to 50%. The notable thing about these two versions is that one is not compatible with the other. The second generation standard has been developed and expanded to a new level: OFDM modes have been increased, modulation capabilities have been added, etc.
DVB-T could only transmit MPEG-TS stream. Whereas its new version allows you to transport different data by its nature, as well as by structure. Any of the streams is transmitted only at the level of the same streams, called the main line (PLP). A device supporting DVB-T2 (as well as others: DVB-C, DVB-T, DVB-S2) has a decoder that processes all input data. Here are the main main input streams:
- GFPS - Generalized Fixed Packet Stream - is supported by DVB-S2, and can also be replaced by GSE;
- GSE - encapsulated streams - these are packets whose headers indicate their length and other additional information for the decoder;
- TS - a number of sequential packets with one specific length;
- GSC - Continuous Signal Stream - is a sequence of data that has no self-size information and can have a maximum packet size of 64 kilobits.
To make it a little easier to understand DVB-T - terrestrial television, which is broadcast over conventional antennas. A few years ago you could see them on all the balconies or on the roofs of village houses. But DVB-T2 is a newer satellite television format. It is still in development and today is not able to broadcast as many channels as other standards. But in the future, it is expected to broadcast in 3D format.
What is DVB-C?
The method of transmitting digital streams from DVB-C requires the presence of a cable. This is a wired TV that is supplied by the provider. Almost all new devices are capable of working with this technology. If yours is not marked DVB-C, you can purchase the appropriate tuner and order the connection of certain software packages from your provider. Such services are the most common and, as a rule, are not expensive compared to other types of connection.
This system uses MPEG-2 codecs when transmitting video and audio. DVB-C can also often be found in large television network organizations. They are also used in conjunction with satellite antennas. You can also watch broadcasts with DVB-C technology via a PC or laptop. But for this you need separate equipment - a TV tuner. It connects to the motherboard in the system unit.
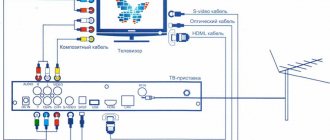
A device that can decode the signal from DVB-C switching stations processes the data quite well. Usually the quality of the broadcast image does not cause any complaints. Often providers offer to buy receivers from them at a discount if your device cannot receive a signal in this format. The TV set-top box is connected to the TV with a cable of three connectors. After that, you can buy special cards to watch TV shows for the entire period (payment period).
DVB-C is in many ways different from DVB-T2, DVB-S2, DVB-T. First of all, the architecture of the signal receiving device. Such set-top boxes can show up to 150 programs. Setting up other channels that are not in the package yourself is not possible. The quality of the picture on the screen will not depend on the distance of your TV or set-top box from the source itself.
DVB-T2 in Europe and Russia
The transition to the DVB-T2 standard in Europe began in 2009, in Russia - in 2012. The “State Commission on Radio Frequencies” has adopted the technology as the main one throughout the country. The transition ended at the end of 2021. Since then, a couple of multiplexes (packages of channels combined into a stream and operating on the same frequency) have been operating in the Russian Federation, including state channels in 16:9 or 4:3 format.
For example: “Channel One”, “Russia-1”, “Match TV”, “NTV”, “Channel Five”. Additionally, viewers have access to digital radio stations - “Vesti FM”, “Radio Mayak”, “Radio Russia” (the stations belong to VGTRK and its branches).
The second multiplex appeared at the end of 2015 and is focused mainly around entertainment channels and programs: “STS”, “TV-3”, “Friday!”, “Mir”, “Muz-TV”. Some of the content is delivered in a ratio of 4 to 3, the rest - in a ratio of 16 to 9. Combined and experimental multiplexes have appeared in the Crimea (First Crimean, First Sevastopol and STV operate there) and Moscow. In the latter case, broadcasting is in 4K resolution (3840×2160) with a bitrate of 30 Mbit/s and via the HEVC codec.
The DVB-T2 standard, already familiar to European and Russian viewers, eliminates problems when finding compatible equipment: the technology is in demand, and therefore is supported by default by televisions (produced from 2010-2012) and set-top boxes of providers. If the TV receiver is purchased separately, then the manufacturer will definitely write about the DVB-T2 format in the specifications.
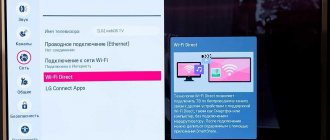
If the details are not described in text, you will have to look for stickers on the front side of the case - even on budget models of digital tuners and set-top boxes, the DVB-T2 label is impossible not to notice. How to proceed? – depends on the type of TV. New television equipment is first plugged into a power outlet, and then connected via HDMI or standard “tulips” to the TV. The search for channels occurs in a semi-automatic mode, but through a separate broadcasting platform (usually selected through the Source button on the remote control).
What do the letters DVB-T on the TV case mean?
DVB-T is another technology that has similarities with the analog signal transport method. Television towers are taken as the source. But, as is the case with other digital standards, a special decoder is needed to display channels on the screen with this type of data transmission. Essentially, DVB-T is the same as analog television from the viewer’s point of view. But in technical terms, the structure and type of signal from the source to your TV have changed.
DVB-T today is more noise-resistant than analog TV. For example, many can remember how other turned on electrical appliances in the house could cause interference on the TV. You won't see this phenomenon in digital TV. Although here there are some factors that can worsen the signal quality - low voltage in the network. Or a poor quality receiver.
The location of the TV tower is important for signal reception. The closer you are to the source, the more consistently good quality TV shows will be displayed. Various buildings along the path to the signal can also affect the picture displayed. Mobile phone developers even tried to use DVB-T technology. It was built into the ASUS ZenFon Go TV smartphone, LG-HB620T and a number of other devices. But users, apparently, did not appreciate it.
At the moment, DVB-T in relation to DVB-C, DVB-T2, DVB-S2 can be considered the last century. But this does not mean that it is not used. This type of TV is spreading in the Russian Federation, despite its age, slowly. This depends on the short range of the signal. And also with other difficulties.
History of DVB-T2: when and why
At the end of the 20th century, conferences were held for the first time on the international transition to new digital broadcasting standards that could replace low-quality analog signals. The consortium that took place in 1991 led to the emergence of DVB technology, which became the basic format in Europe (including the Russian Federation). A little later, there was a global transition to the ISDB standard in Japan and ATSC in the USA.
Despite the differences in names and wording, the idea behind the transition is the same - to open up a number of significant benefits for viewers, such as interference-free streaming, 3D technologies, teletext and TV guides, Dolby Digital surround sound and even digital radio.
But the last push that turned the industry upside down was access to HD and FullHD broadcasting: while analog television barely produces a picture in 480p format, digital standards are not limited to 720p and even 1080p. And also, due to the new compression technology, high-quality content is transmitted almost at lightning speed and takes up a minimum of “space” in the data stream, opening up the opportunity for providers to fit 10-20 separate channels on one frequency, while the “analog” version takes up the entire stream at once.
DVB-T2 – the next generation of TV
Consider the following type, codenamed DVB-T2. This is terrestrial TV. It will make it possible to spread the popularity of DVB-T by almost half. At the same time, the creators will not have to change almost anything in the old type structure. Most of the infrastructure is useful for the functioning of DVB-T2. Despite the fact that these two types are related, the receivers are practically incompatible. This means that if you connect a receiver with DVB-T, you will not find programs in DVB-T2. And vice versa.
DVB-T2 is also characterized by the fact that on your TV screens you can display images not only in HD quality, but also in 3D. This is a more advanced method of digital-TV transmission, in which a number of additional technologies were used. It is already clear to many people who have an understanding of digital TV that this particular standard will become the main one when analog has completely exhausted itself. The object for receiving radio waves and transmitting them to a TV or set-top box is a regular antenna. The signal, as in the example with DVB-T, is still distributed through television towers.
The full transmission of the signal is carried out according to the already familiar scenario: you connect the set-top box to the TV, the antenna to the set-top box and pay for the corresponding services from the supplier. The decoder can be connected to DVB-T2 using a well-known cable with three connectors. Such networks operate even with a poor signal when you are far from the broadcast source. Due to this, every resident of even remote villages can enjoy their favorite television series.
Most TV tuners have a built-in program for controlling and automatically searching and tuning channels. You can also find a list of radio channels there. Due to this, you can use your TV as a radio receiver with convenient control. The tuners have additional connectors for USB flash drives. So, you can burn music or movies to a flash disk and play them on your blue screen.
What is DVB-S2?
The initial type of TV DVB-S, relative to DVB-C, DVB-T, DVB-T2, is a type of information transmission with a familiar dish. For this scheme to work, any blue screen, TV receiver, as well as a dish (satellite) that picks up the reception will do. If you notice a sticker on the monitor marked DVB-S (or DVB-S2), then it does not need an additional set-top box at all. You can directly connect a dish to it and start automatic channel tuning. It is no coincidence that this technology is found in many popular TV models.
But there is one nuance - foreign TV manufacturers integrate DVB-S technology into their devices in a “pure” form. And the tuners that we often purchase from suppliers are . This allows us to access some paid channels as well. But with built-in technology, you may have problems. They can be resolved by calling a technician to your home. If you can decode the channels yourself, then you can save money.
DVB-S2 is the next standard in the development branch. The previous version has been significantly improved. New features have been introduced both in technical details and in terms of user interface. Added news gathering, which was also implemented on mobile devices. The new digital TV format opens up the possibility of viewing in HD quality. During its development, various types of channel coding and modulation were introduced. DVB-S2 is excellent in many respects for broadcasting programs. It is used:
- Resources for data dissemination;
- In standard signal transmission methods, as well as distribution in high definition (HDTV);
- In professional programs.
Unlike the previous generation, DVB-S2 is quite flexible. It is capable of working with different transponder parameters. Allows you to transfer different formats of input streams. Connection of such television is carried out using distributed cards. They are inserted into special holes in the tuner or TV. After which the channels are opened for viewing. The standard is not without some shortcomings from the previous version. Channels may disappear from time to time. Ask your provider for help by changing the direction of the heads on the cymbal itself.
DVB-S2 transports data in converted form. But the image improves noticeably. At the same time, you may not even feel the differences in colors on flat panels and outdated TVs. Only for old ones without a mark on the case you need an addition in the form of a DVB-S2 set-top box.