to Internet data banks evolution of WEB
Just as a photocopier and a printer turned a person with a carbon copy into a full-fledged publisher, the Internet, from the first days of the 21st century, turned the average network user into a full-fledged broadcaster. Admittedly, every viewer has had the freedom to choose television programs since the mid-20th century - the boundaries of freedom were limited only by the set of buttons on the receiver and the number of state-owned broadcasting companies, which you didn’t even have to count on your fingers. The new century brought an unprecedented set of freedoms that, as in the Renaissance, placed man at the center of the Internet universe. Freedom of authorship, freedom of creativity, freedom of distribution have become the driving forces of the Internet community. The Internet has rapidly taken the position of not so much a means
exchange of information, as much as
the media environment
, gaining a foothold in all areas of life, and then - more, creating virtual worlds where everyone answers the question not, but.
Internet television is winning the war for attention with conventionally traditional media (terrestrial, cable and satellite TV, radio, newspapers and magazines). According to a 2007 study by eMarketer (www.emarketer.com), in the United States, 70 percent of users watch videos online, and 20 percent do so daily. The audience of broadcast television in Russia has also decreased significantly due to the Internet. According to analysts, in 2008 the growth rate of video on the Internet will be 74 percent.
TERMINOLOGY
The capabilities of the Internet as a means and as a media environment often mislead not only researchers, but also users. The open environment of the Internet has become simultaneously accessible to both major global television broadcasters and ordinary creative users. Both of them were interested in creating their own unique television using the Internet. Different possibilities have led to different approaches to television broadcasting on the Internet - Internet-TV and IPTV.
Internet television
(internet-TV) is an open, constantly growing network in which many small and medium-sized video producers offer original content. It is a whole world of diverse and diverse video material created by independent studios, groups and people in all corners of the globe.
IPTV
appears to be a set of closed proprietary television systems that are used by cable network operators that deliver video using secure IP channels. In most cases, video materials produced by professional studios and channels are distributed via IPTV. “IP” in the case of IPTV refers to a method of transmitting information over a secure, managed network.
As part of this material, we will consider the specifics of Internet television, since Internet-TV is the closest model of a modern network: anyone can publish information that is globally accessible; a television or film company, or an amateur can become a broadcaster.
Various types of resources that provide video materials exist and are being developed on the Internet. These include video hosting sites, independent Internet television channels, and traditional (terrestrial) television channels that duplicate broadcasts to the network. All these types of resources are often classified as Internet television, although each has its own characteristics and capabilities. Let's try to agree on terms.
Internet broadcasting concept
(internet-broadcasting) includes the transmission of video and audio information over the Internet. Broadcasting can be carried out in streaming, which is a kind of live broadcast on terrestrial, cable and satellite television. In addition, broadcasting can be carried out on demand, which can be roughly compared to watching a previously recorded program. It should be noted that the Internet often uses a combination of two types of broadcasting - streaming and on demand. In addition, many sites use television and radio Internet broadcasting along with the publication of text and photographic materials, which is a product of convergence. It is proposed to designate such sites as Internet channels.
Internet channel
is an online media that disseminates mass information through Internet broadcasting using audiovisual means.
Video hosting
— an Internet service that provides video hosting services. Video hosting users can add, view on demand and comment on videos. Video hosting sites can also do streaming.
Traditional (terrestrial) Internet channel
— Internet channels that duplicate or modify their broadcasts on the Internet.
Independent (network) Internet channel
— Internet channels that broadcast only on the Internet and do not have an on-air analogue.
PRINCIPLES AND TECHNOLOGY
Internet television, by definition, provides a wider selection of media products, programs and programs than viewers are accustomed to seeing on regular TV. Internet-TV uses open standards and formats that allow every user to become a broadcaster. The open platform guarantees, along with broadcast channels, a virtually unlimited number of original or independent Internet channels.
The broadcaster immediately receives a direct communication channel with the viewer, regardless of the Internet provider or cable operator. Any technical solution for Internet television turns out to be as independent as possible from user equipment. Broadcasting of Internet television is cross-border, designed for a global audience, if this does not contradict the right to distribute content.
Internet television is integrated into the lives of users in the same way as most services are integrated into the web: mail, text and graphic editors, diaries. Today, video is an integral part of the Internet, just as graphics were during the formation of the Internet. And the mechanisms for working with video - shooting, editing, broadcasting - are maximally accessible to users who, in a matter of days, become authors, reporters, directors, and broadcasters of the new television.
The Internet television model does not focus on a mass audience, but on an infinite number of channels that are as close as possible to the interests of the target audience. As a result, Internet broadcasting is segmented, which leads to the emergence of highly specialized channels, for example, a channel for lawyers dealing only with arbitration cases. Thus, the DanceJam website was opened on the Internet, created specifically for dancers who can post their dance videos, grouped by headings. Chelsea Football Club provides connection services to its own broadband broadcasting system. In addition to Internet broadcasts, subscribers will be the first to receive club news, and will also be able to enter into correspondence by e-mail with players of their favorite team.
The model of Internet television can be presented as follows: global distribution, convergence, multichannel and multilingual within one broadcaster, unlimited archive of information, additional services, personalization of broadcasting, low-cost technological chain, interactivity.
NEAR FUTURE
The speed of development of Internet technologies usually outstrips the evolution of theoretical ideas about them. However, some trends are obvious. In 2008, according to eMarketer's forecast, the supply of video content on the Internet will significantly increase, both from professional market players, such as television channels, and from numerous amateurs. The largest players in the online video market, such as Google, Microsoft
and TV channels will support their services and video content by purchasing small companies that will engage in advertising in this area. In Russia, the Gazprom Media holding is also preparing to launch an Internet channel, whose users will be able to watch original programs commissioned by the channel, including on NTV and TNT. The opening of the Internet channel is expected in September.
Globally, YouTube is expected to become an important political tool. YouTube already attracts the most traffic on the Internet and consistently ranks high on the list of social media favorites among American Internet users. YouTube is already playing an important role during the presidential election campaign. Thus, the election campaign of one of the US presidential candidates, Barack Obama, was in jeopardy after it turned out that one of his employees posted a video on YouTube that humiliated Obama’s opponent Hillary Clinton.
Video technologies are also spreading into virtual worlds. In one of the most popular three-dimensional worlds - Second Life, with more than 7.5 million accounts, an official Reuters office has already been opened. It is more than logical to expect a surge of new forms of Internet-virtual television in these worlds.
© Garmatin Alexey Alekseevich
to Internet data banks evolution of WEB
STORY
Sharing the views of one of the ideologists of Web 2.0, Tim O'Reilly, the development of Internet television can be divided into two periods - before 2000-2001 () and after 2001 (arming broadcasters with Web 2.0 tools). If the first stage was characterized by experiments with video broadcasts, as well as attempts by large corporations to use the Internet for broadcasting, then in the second stage Internet television is experiencing a new birth due to socialization, the emergence of video communities, as well as the increasing availability of video equipment, for example, the convergence of the telephone and video camera.
At the first stage, the process of developing broadcast sites was a series of experiments. The first mention of test Internet broadcasts of video streaming in the United States is contained in Internet Timeline and dates back to November 1992. One of the first experiments in Internet broadcasting was carried out by students of the Faculty of Journalism of the University of Maine at an exhibition in Hanover, USA. About 16 thousand people watched the programs organized by the students. Every day 5 programs were broadcast. Two of them were 10-minute news blocks, the rest were entirely devoted to analysis of the exposure of a particular company.
In September 1999, an Internet project was created specifically for broadcasting several concerts of world pop stars online. In 1999, the Canadian Internet Project began broadcasting 17 American television channels on the Internet. Management was not involved in the production or procurement of video content. By and large, the business model was very close to the business model of underground television networks. In February 2000, management was forced to close the site in order to comply with current Canadian legislation.
In parallel with the experiments, Internet broadcasting began to be of commercial interest. In 1998, American billionaire Mark Cuban launched the multimedia Internet project Broadcast.com,
on which he posted video and audio files, with a special emphasis on sporting events. Broadcast.com offered visitors a one-stop portal to access breaking news, sports matches and court hearings. At the same time, the company sold advertising videos, attracting advertisers by the fact that the site was visited by smart, educated and rich people. It is worth noting that in 1998, only a rich person could afford an Internet connection sufficient to watch videos on the Internet. Broadcast.com allowed 500 radio and 65 television stations to be received via Internet programming. In 1999, company owner Mark sold Broadcast.com to the company for $5.7 billion.
At the beginning of 2000, the company launched its own network television channel. The channel was a typical example of a financial television channel broadcasting in real time. The channel's staff included professional TV presenters, cameramen, correspondents and other specialists. The editorial teams of the companies , , , took part in the Internet project. In June 2002, the channel was closed. The television channel was supported by advertisers and large financial investments. However, when large players (dot-coms) left the Internet market, financial flows dried up.
Russian broadcasters are faced with a less developed telecommunications infrastructure compared to Western countries. This has increased the country's gap with developed telecommunications countries. In 1995, Telecom Center began its first experiments with Internet television broadcasting. In 1998, Telecom Center presented a project for organizing high-speed Internet connections for central television companies, news agencies and radio stations. This was a time of active introduction of network technologies and multimedia applications into the production processes of newsrooms. In 2000, Telecom Center created a company that began work on organizing specialized Internet projects for television and radio broadcasters. Internet streaming technologies were tested during an interview with S. Kiriyenko at the Space Research Institute in July 1998. Television cameras were not allowed into the hall. It was a successful experiment. Television companies became interested in this technology and expressed a desire to have their broadcasts on the Internet.
Terrestrial TV channels also began to invest money in the Internet. At the end of 1999, Russian oligarch Vladimir Gusinsky implemented the Ntv.Ru project,
offering, along with operational news information, footage and videos of the television company - the first Russian-language media outlet to rely on full multimedia when presenting information.
In 2001, after the reorganization of the TV channel, the site's editorial team separated and continued its activities under the brand and address NTVRu.Com, and then under NEWSRu.Com
.
2001 marked the debut of entertainment broadcasting on the Internet. 24-hour live broadcast via the Internet ensured the success of the channel's online reality show resource. In nine days, the program’s website reached third place in the ranking, thereby setting a record for the speed of growth in the popularity of a resource on the RuNet. This changed the prevailing ideas about broadcasting on the Internet. Online advertising helped TV-6 to interest part of the audience of other channels, attracting the attention of their most active part, which caused. At the moment when the channel's broadcasting was stopped, the show continued to be broadcast on the Internet.
In 2002, an Internet directorate was created under the All-Russian State Television and Radio Company. State Internet Channel
included the creation of regional Internet channels based on local State Television and Radio Broadcasting Company. Each Internet channel provides operational information in real time in text and video formats. And some resources, for example, Dontr.Ru, immediately began broadcasting both video and audio on demand. The most interesting materials appear on the federal news feed - www.vesti.ru.
In 2004, a TV channel began broadcasting online. In 2005, a Moscow Internet provider launched a service called ,
allowing users to record and watch television at any time of the day, at work or at home. Subsequently, the website www.corbina.tv expanded to a full-fledged video hosting, which presents various channels - from collections of advertising and social videos to archives of various television programs.
The history of the development of Internet broadcasting has passed a significant stage from the duplication of broadcast video to original author's projects with rich interactive capabilities. But 2005 brought something more than new non-terrestrial Internet channels; video hosting sites, in particular YouTube, rapidly gained popularity on the Internet. Their technical developments for organizing and popularizing broadcasting have become equally available to both large corporations and home users.
In a 2005 article, Tim O'Reilly linked the emergence of a large number of sites united by certain common principles with the general trend in the development of the Internet community, and called this phenomenon Web 2.0, as opposed to Web 1.0. If the first generation web was built on venture capital investments, large injections of money into Internet projects and minimal user participation in content production, then the second generation web gave everyone all the tools to feel like a publisher or broadcaster.
One of the main principles that has significantly changed the idea of information dissemination is the possibility of socialization
, creating a personal zone - a blog or video blog, which can be used to distribute texts, photos and videos.
Everyone can feel their uniqueness, create their own video channel, and receive feedback from readers and viewers. The second principle is
by Wired editor-in-chief Chris Anderson.
He noted that niche products can generate equal or greater profits for a company than best-selling products. A new technology for distributing information, including video, is web syndication
- the simultaneous publication of the same material on different pages or websites. For this purpose, RSS feeds containing headings of text materials, audio or video materials are used. Initially, this technology was used on news resources and blogs, but gradually the scope of application expanded and is now widely used for the distribution of audio and video podcasts.
The principles of building the Web 2.0 model have led to the following trends:
— a large amount of content is created by the users themselves, for free, but with pleasure (for example, on YouTube);
— horizontal connections are as effective as possible, and everyone can find a colleague, professional friend or friend in a matter of hours with tags or special communities (for example, on lifejournal.com);
— the Internet as a platform allows you to store an unlimited amount of information remotely, as well as use web applications that replace most paid programs (for example, docs.google.com);
— open web resources focus on collective wisdom rather than expert assessment (for example, Wikimedia.org);
— the development of the blogosphere allowed journalists to avoid self-censorship, and citizen journalism helped ordinary users quickly focus on current socio-political issues (for example, ohmynews.com).
COMPONENTS OF INTERNET TV
Corporate-based Internet channels
Despite the almost complete monopoly of terrestrial channels over television sets and the attention of millions, the management of federal channels also does not want to miss out on the dynamically developing Internet market and its socially active audience. By 2008, almost every federal broadcast channel was expanding into the Internet space.
At the end of 2007, it launched test broadcasting of five of its own various channels: Channel One broadcast, as well as four Internet channels: - the best of the seven seasons of the project, - the channel’s highest-rated programs, and .
Business news on the Internet has been provided by the RBC channel for several years. Streaming and video-on-demand of all currently aired programs are available on the site. In general, Internet information broadcasting is based on the traditions laid down by ntv.ru and then newsru.com. Since 2002, VGTRK has been mastering multimedia broadcasting, opening a multimedia project in almost every regional state-owned company and combining video materials on the company’s main multimedia website. The new version of the site, which was launched in 2007, offers the most current informational videos of the Vesti program of the Rossiya TV channel, the Vesti Regional News Agency, regional State Television and Radio Broadcasting Company, as well as the ability to watch live broadcasts of the Vesti information channel. In addition, it is possible for viewers to send their videos to the open section. The best reports end up on television.
The television channel, part of the VGTRK structure, also began Internet broadcasting at the end of 2007. Sportbox.ru has licensing rights and provides Internet broadcasting of leading sporting events. On the portal you can watch both archived video and live broadcasts.
Satellite TV channels duplicate broadcasts on the Internet. Thus, the socio-political channel RTVi broadcasts via satellite to viewers in America, Europe, the Middle East, North Africa and Australia. The channel's video broadcast is available on the Internet. The Rambler TV channel offers a special selection of programs on the Internet - the best documentary series and films from famous studios in the world. In addition, selected broadcasts of various programs are available on the website upon request.
The British television corporation BBC has created its own video service to organize Internet broadcasting of programs prepared by channels included in the holding. The iPlayer service https://www.bbc.co.uk/iplayer/ allows users to download popular programs seven days after they are broadcast on television. However, viewing programs is only available from computers connected in the UK.
The TNT television channel was the first of the publicly accessible Russian channels to enter into an agreement with the popular video portal YouTube. Previously, only the cable channel Russia Today promoted its video content in this way. For now, federal channels rely only on their own websites. The TNT channel now has an additional opportunity to “taste” its products and gain even more fans of the new humor. Here you can find promotional and advertising videos of the channel, selected fragments of the Comedy Club show, the sketch com “Our Russia”, the experimental humor show “Laughter without Rules”, “Slaughter League” and much more.
The air of TV channels that have not organized broadcasting on the Internet independently is broadcast by an Internet provider. Broadcasts from STS, Ren-TV, TV-Center, etc. are available in the stream.
Network Internet channels
Internet channels that exist only on the web can be considered separately from those duplicating broadcasts on the network simply because they combine professional television production standards with innovative approaches brought by the Web 2.0 era.
One of the most dynamically developing online channels is Joost.
testing of which began in early 2007, and on October 1, registration was already open to everyone. From a technological point of view, this is a rather complex peer-to-peer system; from the user side, Joost is a simple client program that allows you to select a TV channel from the list and watch it. Most of the video materials presented in the project were created by professionals. According to the developers, the service contains 1,500 shows in 250 channels. To watch the channel, you need to download the player program, then register on the server. This will allow you to personalize the space in the project, as well as vote for your favorite material. It should be noted that Joost displays advertisements. The player interface is intuitive. The video plays in full screen in higher quality than, for example, YouTube. The user can turn on any channel - Animation, Comedy, Documentary, Drama, Entertainment, Movies, Lifestyle, Music, Shows, News, Sports and Games - and then select a program upon request. The transmissions are pre-recorded, making the caching process easier.
DNAStream
(https://dnastream.tv) is one of the Internet channels whose interface elements are very reminiscent of Joost.
However, users will not have to download an additional application; the interface is based on Flash technology. Another project Babelgum
(https://www.babelgum.com) is implemented according to the same principles as Joost, and also requires a client program. However, the viewing control panel is designed in the style of a classic remote control. Babelgum channels are categorized using tags.
In October 2007, Internet television (www.tvclick.ru) officially launched on the RuNet, which is positioned by the creators as the largest network of thematic niche TV channels, allowing the user to choose what and at what time to watch. The company was founded by top managers of Russian television and professionals in the field of new media and viral marketing. The format is five-minute programs, the frequency of release is from one to three times a week. Themes of the TV channels: office life (), relations between men and women (), cars (), music (author’s channel of Artemy Troitsky), sports and others. TV-Click plans to order 50 percent of the content from the professional community—students, graduate students of VGIK, young directors, screenwriters, for whom “it is more important than money to prove oneself and shine.” 10 percent of programs will be produced in-house, 30-40 percent of programs will be purchased, including in the regions.
Video hosting
YouTube video hosting has managed to accumulate an avalanche-like flow of original and professional videos, creative projects, commercials, clips, as well as various types of video garbage.
. Today it is the most cited video hosting site on the Internet with a monthly attendance of 68 million unique users. They can add, view and comment on videos, create their own channels, search for video materials using keywords, broadcast videos on external resources, and subscribe to video channels.
Since 2005, due to the rapid growth in the number of users, YouTube has managed to collect the largest video library. There are currently over 100 million video clips on YouTube. YouTube has many partnership agreements with content providers such as CBS, BBC, Universal Music Group, Sony Music Group, Warner Music Group, NBA, The Sundance Channel.
On November 13, 2007, YouTube announced the launch of the Russian version of YouTube (www.youtube.ru). The YouTube service is fully translated into Russian and has a localized home page and search system. With the launch of the new version of YouTube, Russian-speaking Internet users became part of the global YouTube community and gained access to Russian and global video content.
A huge contribution to the popularization of video hosting is made by bloggers and social network users who use videos in their diaries. Each video has HTML code for the user to use to embed the video on other web pages.
In March 2008, YouTube announced that it planned to begin streaming television on the Internet by the end of the year. With the help of the new service, millions of portal users will be able to broadcast their video live to the network 24 hours a day. In this way, it will be possible to organize a video broadcast from a party or wedding for those who were unable to attend. The latter will see everything that happens live on the Internet.
RuTube is trying to repeat the success of YouTube in RuNet.
is a Russian online service for sharing, displaying and broadcasting videos, created in 2006. Now the hosting delivers videos daily to 300 thousand Internet users and produces more than 35 million video impressions per month. It provides Internet broadcasting for several TV channels and radio stations, and also provides its users with the opportunity to create and maintain video blogs and their own virtual TV channels. Rutube.ru organized live video broadcasts from dozens of events from various interesting places, such as the State Duma, the Public Chamber, music festivals, openair, club parties, concerts, street processions, film premieres, conferences and conventions. According to the agreement with DTV, the best videos of the day are shown live on the channel.
With the advent of concepts, quite a lot of projects arose - both later and earlier than YouTube. Some projects literally copied the YouTube interface, but differed only in business models - paid and free services, and the use of advertising. Video hosting Viddler
forced to compete with YouTube by expanding functionality.
Viddler allows you to view videos in full screen mode and place your videos in such a way as to indicate exactly where the video should start when shown. This is very useful when the video is quite long, and the part you would like to draw viewers' attention to is somewhere towards the end. In addition, you can leave your comments not only on the clip, but also on any fragment of it. We especially emphasize that Viddler, unlike, for example, Veoh,
is the fastest video hosting, that is, it provides the fastest file downloading.
Residents of Russia, for whom the speed of downloading video materials is important, can use VideoRadar hosting,
which will give a head start to many foreign analogues.
If it is not the loading speed that is important, but a comprehensive popular service, then you can contact Video.Mail.Ru.
Another Russian player in the video hosting market is
Rambler Vision
(Video.Rambler.ru).
Video hosting sites are actively starting to master the high-definition format. Hosting Vimeo
so far the only service that supports downloading and displaying videos in HD.
Promotes the distribution of video on the network and such a direction as video podcasting
— a method of publishing media streams (channels) on the network, in which they are announced through RSS feeds. This allows you to automate the download of new episodes to your playback device. To subscribe to a large number of channels, various players are used - iTunes, Miro, KatchTV, Open Media Network. The way to work with such players is as follows: the user downloads the player, selects a podcast, views the materials, subscribes to the podcast to stay up to date with new products. Players also allow you to track videos on video hosting sites or your local computer, download materials of interest, and create playlists. The player in this scheme acts as an Internet browser for video content.
Social networks and video
Social networks also accumulate video materials - Facebook,
which had 55 million active members registered on the site at the end of November 2007.
The Russian social network Vkontakte
opened a video section in June 2007. The service allows users to upload their videos to the site. The introduction of this function turned Contact into a video hosting service at the same time. Today, video hosting contains more than 20 million videos. The site has a video search with the ability to add it to your own videos. The service allows you to tag your friends in videos.
Author's streaming
In a world in which the effect of presence becomes, and communication and frequency of output is perceived only in real time, there is an urgent need for organizing direct personal broadcasting. On the JustinTV
The possibility of organizing original streaming has been implemented. The author of the service, Justin Kan, attracted public attention by starting a round-the-clock Internet broadcast from a camera that was attached to the cap that he constantly wore. On the JustinTV website, after registering, the user has the opportunity to open his own permanent channel. By connecting a webcam and microphone, you can broadcast online. Additional features - chat, comments, the ability to embed a broadcast into a blog or any external site. The broadcaster can record the live stream on the server and later access it on demand. The service also allows you to edit recorded video. The user can create a broadcast schedule and regularly go live.
Convergence (Internet TV and media)
Since the combination of text and photographs on the pages of the first newspapers, the Internet has provided an ideal medium for further convergence. Video broadcasts on the Internet have been mastered not only by television channels, but also by radio studios and even newspapers. Editor-in-Chief Alexey Venediktov maintains a video blog on current topics; programs by Alexander Plyushev and Argentum are streamed and available on demand. Also, a special section has been opened on the radio station’s website, which includes exclusive footage of editorial life (for example, the election of the editor-in-chief) and socio-political events (for example, the press conference of Kovtun and Lugovoy).
Newspaper editors are also moving towards information visualization. Thus, newspaper correspondents shoot video reports and illustrate texts with them, talk about the intricacies of mortgage lending and comment on the presidential elections in the United States.
Convergence has occurred not only within the media; projects such as Internet theater festivals, short Internet films and TV series for broadcasting on mobile phones appear on the Internet with regular frequency.
Selecting a tariff plan and additional options
Interactive TV tariffs may differ from each other not only in the number of TV channels included in a particular package, but also in their quality. The more channels a company offers, the higher the picture resolution and signal transmission speed, the higher the monthly fee for using the offered functionality will be.
It is worth noting that the highest possible picture resolution plays an important role only in the case of those TVs that have a large diagonal.
Users can also subscribe to thematic channel packages for a fee. For example, TV series, TV for adults, sports, etc. If we talk about additional operator services, they include the following.
- The most flexible packaging of interactive television, which provides easy-to-use subscription methods.
- Video rental. Users get access to movie libraries where they can purchase this or that movie at an affordable price.
- The user can independently control the viewing. Record programs, pause, rewind or return.
- There are parental controls that can be set both for TV viewing in general and only for certain channels.
- Karaoke.
- Users get access to a variety of information services. For example, they can look at the weather forecast, traffic jams, etc.
- The TV automatically integrates with today’s popular social networks.
- Multiscreen. The user can start watching a particular program on one screen, and then, if necessary, continue watching on another.
- Multiroom. You can connect several different TVs at the same time.
- Interactive television involves analyzing the preferences of a particular user and offers movies for viewing or a variety of TV shows.
Each provider can offer users different services, the list of which is advisable to familiarize yourself with in advance. It is worth noting that some services from one provider may be included in the offered package, while exactly the same services from another operator are purchased exclusively for an additional fee.
Payment for services
In most cases, the average cost of a set of equipment for interactive television is approximately 4,000 rubles.
Connection from most providers is completely free, but this does not mean that the user does not have to pay a subscription fee every month. The minimum payment for monthly use is 220 rubles. If you order additional services, the cost may increase up to 1,700 rubles. If desired, you can order various additional options that are not included in the package offered by the provider. Among the wide range of options, each user will be able to find the most suitable option for themselves.
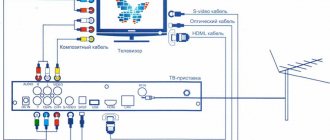
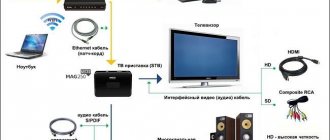
Connecting and setting up network equipment
In most cases, providers offer users a full package of services, which includes setting up a variety of equipment. But if you wish, you can configure it yourself without any problems.
First of all, you should make sure that the router has a special function for broadcasting multicast or IGMP traffic.
It can be activated directly in the router settings. Additionally, you need to switch one of the router ports to bridge mode. The next stage is connecting a special set-top box to the router and TV. Once the connection is complete, a login window will appear on the TV screen. In its fields you need to enter a password and login, which will be specified in the agreement concluded with the operator. It is worth noting that some operators can provide the opportunity to use interactive television not only on televisions, but also on computers or a variety of mobile devices. Access will be via a browser. To do this, just install a special web interface and you can start using all the capabilities of modern interactive television.
PROBLEMS OF INTERNET TV
Internet television is developing along with the development of Internet infrastructure. With the spread of ADSL connection technology, the quality is also improving. Internet television is becoming accessible not only using computers, but also using mobile devices - PDAs, mobile phones. However, Internet television has a number of problems. One of the main problems is the quality of video and sound. Broadcasters themselves must adapt the video for broadcast on the network and compress it, which negatively affects the quality. The main factors that affect the quality of video on the Internet are the speed of user connection to the network and the price for traffic. The impetus for the development of Internet TV is the gradual liberalization of prices for unlimited Internet connection. This changes user content preferences in the same way as switching from dial-up to ADSL connections.
In addition, there are a number of problems with copyright and related rights to video materials. Most traditional television channels, including the BBC, limit the broadcast of their programs on the Internet to the territory of the country, since they do not have rights to cross-border broadcasting. In turn, YouTube rules prohibit uploading videos to the site whose content is prohibited by US copyright law. Company employees often remove pirated content. However, despite this, a huge amount of copyrighted video continues to be uploaded to the service. Company employees can pay attention to it only after a complaint from copyright holders or users of the service. However, sometimes user complaints result in legitimate videos being flagged as pirated.
Internet speed and how it is measured
Surely you know that the speed of movement of a car, person, train or any other vehicle is measured in different units. If we are talking about a car, then its speed can be 100 km per hour, the speed of movement of an ant or a turtle would probably be more logical to measure in meters per hour and the speed of space objects in thousands of kilometers per hour. In the same way, there is a scale for measuring Internet speed.
If the speed of a car is calculated by the number of kilometers the car travels per unit of time, then the speed of the Internet connection is calculated by the amount of information transmitted per unit of time. The unit of information is considered to be a bit or byte. One byte contains 8 bits. And by analogy with many other units of measurement, the prefix kilo (1000), mega (1000000), giga (1000000000), etc. can be attached to these same bits and bytes.
Recently, megabits per second (Mb/s) are most often used to indicate the speed of an Internet connection. For example, a speed of 20 Mbps means that in 1 second you can download (or upload) a file of 20 megabits in size.
Many people often get confused and lost in units of measurement. As we said above, 1 byte is equal to 8 bits. Thus, 20 megabits is 2.5 megabytes (20 : 8 = 2.5). And by analogy, a speed of 20 megabits per second is the same as 2.5 megabytes per second.
It is customary to abbreviate bits with a small letter b and bytes with a capital letter B. This is mainly why confusion arises. 20 Mb/s is 20 megabits per second and 20 MB/s is already 20 megabytes per second. Be careful with this, because the same letter typed in a different case means a value 8 times smaller or larger. So, for example, 20 MB/s is 8 times faster or faster than 20 MB/s.
When talking about Internet connection speed, we usually talk about the maximum possible speed. But not always and not under all circumstances this speed can be achieved.