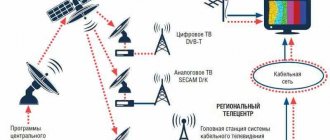
The development of wireless communications in recent decades has led to a significant change in the frequencies available to ordinary users. In radio stations used for civil communications, frequency division into subbands, which is not included in ITU (International Telecommunication Union) standards, is widely used. The most commonly used subbands are CB, LPD, PMR, dPMR, as well as VHF, UHF. According to ITU standards, VHF and UHF belong to the meter and decimeter ranges of radio waves. A small part of their radio frequency resource is used as dedicated subbands of the same name, and also has other names in areas intended for civilians.
What are the differences in radio frequency bands that do not require permission for use?
In each state, radio frequency channels are a strategic source that can only be used with permission. Radio waves: CB, VHF, LOW BAND, LPD, PMR and UHF allow “free” use and have distinctive standards. Each channel has a specific frequency resource, physical properties of waves and other features:
- CB “CB” – civil band.” May be used without any permission. Transmission frequency – 27 MHz is standard for Russian car owners;
- VHF range - high frequencies from 136 to 174 MHz. Waves propagate within visible boundaries;
- LPD – “Low Power Device Range”. It is 433-434.7 MHz. Used for short-range communications;
- LOW BAND – amplitude of radio signals – from 33 to 48, from 57 to 57.5 MHz. Used for overland travel;
- PMR – “Private Mobile Radio Band”. Limits 446-446.1 MHz. Popular in private household radios, the transmitter power of which does not exceed 0.5 W;
- UHF range - decimeter intervals from 400 to 430 MHz. Most often used on professional radio stations.
Legal entities and individuals may not receive permission to operate radio stations that have CB, LPD, PMR bands, subject to compliance with the established modulation and strength.
VHF and UHF also do not require a purchase permit, but they must be registered with the supervisory authorities for further use in the territorial radio frequency range. There are limited amateur areas - to use them, it is enough to obtain a license with power and signal that corresponds to the class of the recording radio station.
Sky Reviews
Microwave Sky 1.9 mm (WMAP)
The cosmic microwave background, also called the cosmic microwave background radiation, is the cooled glow of the hot Universe. It was first discovered by A. Penzias and R. Wilson in 1965 (Nobel Prize 1978). The first measurements showed that the radiation is completely uniform throughout the sky.
In 1992, the discovery of anisotropy (inhomogeneity) of the cosmic microwave background radiation was announced. This result was obtained by the Soviet satellite Relikt-1 and confirmed by the American COBE satellite (see Sky in the infrared). COBE also determined that the spectrum of the cosmic microwave background radiation is very close to that of the blackbody. The 2006 Nobel Prize was awarded for this result.
Variations in the brightness of the cosmic microwave background radiation across the sky do not exceed one hundredth of a percent, but their presence indicates subtle inhomogeneities in the distribution of matter that existed at an early stage of the evolution of the Universe and served as the embryos of galaxies and their clusters.
However, the accuracy of the COBE and Relict data was not enough to test cosmological models, and therefore in 2001 a new, more accurate WMAP (Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe) apparatus was launched, which by 2003 had built a detailed map of the intensity distribution of the cosmic microwave background radiation across the celestial sphere. Based on these data, cosmological models and ideas about the evolution of galaxies are now being refined.
CMB spectrum
CMB arose when the age of the Universe was about 400 thousand years and, due to expansion and cooling, it became transparent to its own thermal radiation. Initially, the radiation had a Planck (blackbody) spectrum with a temperature of about 3000 K
and accounted for the near-infrared and visible ranges of the spectrum.
As the Universe expanded, the cosmic microwave background radiation experienced a red shift, which led to a decrease in its temperature. Today the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation is 2.7 K
and it falls in the microwave and far-infrared (submillimeter) ranges of the spectrum. The graph shows an approximate view of the Planck spectrum for this temperature. The spectrum of the cosmic microwave background radiation was first measured by the COBE satellite (see Sky in the infrared), for which the Nobel Prize was awarded in 2006.
Radio sky at 21 cm, 1420 MHz (Dickey & Lockman)
Famous 21.1 cm
is another way to observe neutral atomic hydrogen in space. The line arises due to the so-called hyperfine splitting of the main energy level of the hydrogen atom.
The energy of an unexcited hydrogen atom depends on the relative orientation of the spins of the proton and electron. If they are parallel, the energy is slightly higher. Such atoms can spontaneously transform into a state with antiparallel spins, emitting a quantum of radio emission that carries away a tiny excess of energy. This happens to an individual atom on average once every 11 million years. But the huge distribution of hydrogen in the Universe makes it possible to observe gas clouds at this frequency.
Radio sky at 73.5 cm, 408 MHz (Bonn)
This is the longest wavelength of all sky surveys. It was performed at a wavelength at which a significant number of sources are observed in the Galaxy. In addition, the choice of wavelength was determined by technical reasons. To construct the survey, we used one of the world's largest fully rotating radio telescopes - the 100-meter Bonn radio telescope.
Main features of different ranges
With the development of wireless communication systems, ordinary users have the opportunity to choose civilian radio stations that have subbands that are not included in the standards of the International Telecommunication Union.
The most common are: CB, LOW BAND, LPD, PMR, UHF and VHF. Each of them has not only a distinctive frequency, but also many other characteristics that determine their use in a particular area.
VHF (VHF in Russian) is the amplitude of meter waves that propagate over a distance of 1-10 meters.
- Radio waves 30-300 MHz.
- Used in the field of radio and television broadcasting, in radars.
- Communications on such waves extend over several tens of meters.
- If solar activity is increased or artificial influence is applied, the short-wave part of the range reflects radio waves from the ionosphere and carries out long-distance communication up to 2 thousand km.
- The civil band has frequencies of 136-174 MHz. For different manufacturers, product boundaries are equipped with different grids from 6 to 25 kHz. Such systems are used for urban communications in open areas, subject to unobstructed visibility.
Sources
The Crab Nebula in radio wavelengths
The Crab Nebula is the best-studied supernova remnant. This image shows what it looks like in the radio range.
Radio emission is generated by fast electrons moving in a magnetic field. The field forces the electrons to turn, that is, to move at an accelerated rate, and with accelerated movement, the charges emit electromagnetic waves. From this image, which is based on observations from the US National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), one can judge the nature of the magnetic fields in the Crab Nebula.
Computer model of matter distribution in the Universe
Initially, the distribution of matter in the Universe was almost perfectly uniform. But still, small (possibly even quantum) density fluctuations over many millions and billions of years led to the fact that the substance fragmented.
The figure shows the result of a computer simulation of the evolution of the Universe. The movement of 10 billion particles under the influence of mutual gravity was calculated over 15 billion years. As a result, a porous structure was formed, vaguely reminiscent of a sponge. Clusters of galaxies are concentrated in its nodes and edges, and between them there are vast deserts where there are almost no objects - astronomers call them voids (from the English void
- emptiness).
Similar results are obtained from observational surveys of the distribution of galaxies in space. For hundreds of thousands of galaxies, coordinates in the sky and redshifts are determined, from which the distances to the galaxies are calculated.
True, it is possible to achieve good agreement between calculations and observations only if we assume that visible (luminous in the electromagnetic spectrum) matter makes up only about 5% of the total mass of the Universe. The rest is accounted for by the so-called dark matter and dark energy, which manifest themselves only by their gravity and the nature of which has not yet been established. Their study is one of the most pressing problems of modern astrophysics.
Quasar: active galactic nucleus
When too much matter accretes onto the supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy, a huge amount of energy is released.
This energy accelerates some of the matter to near-light speeds and ejects it with relativistic plasma jets in two opposite directions perpendicular to the axis of the accretion disk. When these jets collide with the intergalactic medium and are decelerated, the particles entering them emit radio waves.
The radio image of the quasar shows areas of high intensity radio emission in red: in the center is the active galactic nucleus, and on each side of it are two jets. The galaxy itself practically does not emit radio waves.
Radio galaxy: radio brightness contour map
To image space objects in radiation ranges other than visible, various techniques are used. Most often these are artificial colors and contour maps.
Using artificial colors, you can show what an object would look like if the light-sensitive receptors of the human eye were sensitive not to certain colors in the visible range, but to other frequencies of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Contour maps are typically used to represent images taken at a single wavelength, especially in the radio wavelength range. According to the principle of construction, they are similar to contour lines on a topographic map, only instead of points with a fixed height above the horizon, they connect points with the same radio brightness of a source in the sky.
VHF Channel Frequency Table
| Frequency range (MHz) | Bandwidth (kHz) | Types of modulation and purpose (MHz) |
| 144,000-144,110 | 0.5 kHz | Only telegraphy. Mainly EME telegraphy. Telegraph calling frequency is 144.05 MHz. The frequency for MC communication without prior agreement is 144.100 MHz. Frequency band 144.0025 MHz - 144.025 MHz - primarily for space communications (space-to-Earth). |
| 144,110-144,150 | 0.5 kHz | Narrowband species. Predominantly digital narrowband EME modes. The center of activity of PSK31 is 144,138). |
| 144,150-144,165 | 2.7 kHz | Telegraphy, OBP, digital modes. Predominantly digital forms of EME. |
| 144,165-144,180 | 2.7 kHz | Telegraphy, OBP, digital modes. Mostly digital types. The calling frequency of digital modes is 144.170 MHz. |
| 144,180-144,360 | 2.7 kHz | Telegraphy and OBP. The calling frequency of the OBP is 144.300 MHz. frequency band for MC OBP communications without prior agreement is 144.195-144.205 MHz. |
| 144,360-144,399 | 2.7 kHz | Telegraphy, OBP, digital modes. The frequency for FSK441 communications without prior agreement is 144.370 MHz. |
| 144,400-144,491 | 0.5 kHz | Narrowband views are only lighthouses. |
| 144,500-144,794 | 20 kHz | All types. Calling frequencies: STV - 144.500 MHz; teletype - 144.600 MHz; fax - 144.700 MHz; ATV - 144.525 and 144.750 MHz). Recommended frequency bands for linear transpoders: 144.630-144.600 MHz - transmission, 144.660-144.690 MHz - reception). |
| 144,794-144,990 | 12 kHz | Telegraphy, digital modes, digital voice communications, digital automatic stations. The center of activity for APRS is 144.800 MHz. Recommended frequencies of digital automatic stations for digital voice communication: 144.8125, 144.8250, 144.8375, 144.8500, 144.8625 MHz. |
| 144,990-145,194 | 12 kHz | FM, digital voice communication - only for repeaters, reception. Frequency ratings 145,000-145,175 MHz, step 12.5 kHz. |
| 145,194-145,206 | 12 kHz | Telegraphy, FM, digital voice communications. Mainly for space communications. |
| 145,206-145,594 | 12 kHz | Telegraphy, FM, digital voice communications, digital automatic FM stations (“Echolink”). Calling frequencies: FM - 145.500 MHz, digital voice communication - 145.375 MHz. The center of activity for amateur radio emergency service stations is 145.450 MHz. |
| 145,594-145,7935 | 12 kHz | FM, digital voice communication - only for repeaters, transmission. Frequency ratings 145.600-145.775 MHz, step 12.5 kHz. |
| 145,794-145,806 | 12 kHz | Telegraphy, FM, digital voice communications. Mainly for space communications. |
| 145,806-146,000 | 12 kHz | All types are for space communications only. |
UHF (UHF in Russian) are decimeter waves that expand to one meter.
- Scope of application: for TV, Wi-Fi, tropospheric and mobile communications, radar.
- The civil subband is characterized by a frequency interval from 403 to 520 MHz, the grid step is adjustable from 6 to 25 kHz. Excellent for communication in urban areas over short distances.
- Under normal circumstances and with direct visibility, the communication signal can diverge several kilometers.
Loop antenna
A homemade device will consist of the following elements:
- aluminum strips measuring 320 mm;
- mast;
- reflector;
- amplification device;
- cable.
First, a frame of four strips is assembled. Fastening to each other is carried out using screws. A cross is installed in the middle of the frame. From the center, each part of the cross is shortened by 5 mm. The parts of the cut plates closest to each other are connected by a conductor, forming two internal, separated squares. The cable is soldered to these plates, the central core to one, the braid to the other. Next, the antenna is installed on the mast, and the amplifier is attached.
UHF channel frequency table
| Frequency range (MHz) | Bandwidth (kHz) | Types of modulation and purpose (MHz) |
| 430,000-432,000 | 20 | All types |
| 432,000-432,025 | 0.5 | Only telegraphy and PSK31. Mainly EME. (When conducting EME communications for the first category, the permitted power is 500 W) |
| 432,025-432,100 | 0.5 | Narrowband species. Activity centers: telegraphy - 432.050 MHz, PSK31 - 432.088 MHz. (When conducting EME communications for category 1, the permitted power is up to 500 W |
| 432,100-432,400 | 2.7 | Telegraphy, OBP, digital modes. The center of activity of the OBP is 432.200 MHz. The frequency for FSK41 communications without prior agreement is 432.370 MHz. The frequency for planning communications in the microwave and EHF ranges is 432.350 MHz. (When conducting EME communications for category 1, the permitted power is up to 500 W) |
| 432,400-432,500 | 0.5 | Telegraphy and digital modes are only beacons. |
| 432,500-433,000 | 12 | All types. Activity centers: APRS - 432.500 MHz, teletype - 432.600 MHz, fax - 432.700 MHz. |
| 433,000-433,400 | 12 | FM, digital voice communication - only for repeaters, reception. Frequency ratings 433.025-433.375 MHz, step 25 kHz. |
| 433,400-433,575 | 12 | FM, digital voice communication. The center of activity of STV is 433.400 MHz. Calling frequencies: digital voice communication - 433.450 MHz, FM - 433.500 MHz. Amateur Radio Emergency Service Activity Center - 433.450 MHz. Recommended channels for simplex communication 433.400-433.575 MHz, 12 kHz step |
| 433,600-434,000 | 20 | All types, digital automatic stations. Activity centers: teletype - 433.600 MHz, fax - 433.700 MHz. Recommended channels for digital voice communications 433.625-433.775 MHz, 25 kHz step |
| 434,000-434,025 | 0.5 | Only telegraphy and PSK31. Mainly EME. (When conducting EME communications for category 1, the permitted power is 500 W |
| 434,025-434,100 | 0.5 | Narrowband species. Activity centers: telegraphy - 434.050 MHz, PSK31 - 434.088 MHz. |
| 434,100-434,600 | 12 | All types, ATV. |
| 434,600-435,000 | 12 | FM, digital voice communication only repeaters, transmission. Frequency ratings 434.625-434.975 MHz, step 25 kHz. |
| 435,000-438,000 | 20 | All types, ATV. Mainly space communications. |
| 438,000-440,000 | 20 | All types, ATV, digital automatic stations. Recommended channels for digital automatic stations are 439.800-439.975 MHz, 25 kHz step. Recommended channels for digital voice communications are 438.025-438.175 MHz, 25 kHz step. Recommended frequency bands for experiments with new types of communications are 438.550-438.625 MHz. |
CB is the short wave band used for commercial and personal purposes.
- Communication is allowed at a distance of 30 to 40 km at the intersection of the city or inside it.
- Has some interference in urban communication conditions.
Balancing antennas
Balancing devices prevent currents from entering the outer area of the outer conductor (braid) of the coaxial wire. It is impossible to connect without such a device, as this leads to curvature of the antenna radiation pattern and a decrease in reception noise immunity. When the input impedance of the antenna differs from the characteristic impedance of the wire, then such a device is also used as a matching device.
a matching device for an antenna yourself. Usually a quarter-wave bridge or a wave U-elbow is used. The bridge is a two-wire short-circuited line with a length of Lcp/4, connected to the vibrator terminals. The bridge consists of two tubes, an insulator and a short-circuited shunt. A cable is passed through one of the tubes (for example, the left one). The outer conductor (braid) is connected to the left tube of the vibrator and the left tube of the bridge, the central contact is connected to the right tube of the vibrator .
The wave bend is made of cable and consists of two sections with a characteristic impedance of 75 Ohms, respectively, lengths Lc/4 and Lc/3, where Lc is the average wavelength in the cable. to maintain a certain distance between cables. The operating frequency band is 12–15 percent.
a wire-wire transformer can also be used .
It transforms the antenna's input impedance to an impedance of 73 ohms. Two pairs of transformer coils are wound alternately on two frames with a diameter of 5–7 mm. The winding is continuous, in two wires. The gap between the frames is 15-20 mm. Installation is carried out on a metal board, to the ends of which the feeder braid and the ends of the windings are soldered.
CB Channel Frequency Table
| Channel | FREQUENCY GRID (EUROPE), kHz | |||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | |
| 1 | 26065 | 26515 | 26965 | 27415 | 27865 | 28315 | 28765 | 29215 | 25165 | 25615 |
| 2 | 26075 | 26525 | 26975 | 27425 | 27875 | 28325 | 28775 | 29225 | 25175 | 25625 |
| 3 | 26085 | 26535 | 26985 | 27435 | 27885 | 28335 | 28785 | 29235 | 25185 | 25635 |
| 4 | 26105 | 26555 | 27005 | 27455 | 27905 | 28355 | 28805 | 29255 | 25205 | 25655 |
| 5 | 26115 | 26565 | 27015 | 27465 | 27915 | 28365 | 28815 | 29265 | 25215 | 25665 |
| 6 | 26125 | 26575 | 27025 | 27475 | 27925 | 28375 | 28825 | 29275 | 25225 | 25675 |
| 7 | 26135 | 26585 | 27035 | 27485 | 27935 | 28385 | 28835 | 29285 | 25235 | 25685 |
| 8 | 26155 | 26605 | 27055 | 27505 | 27955 | 28405 | 28855 | 29305 | 25255 | 25705 |
| 9 | 26165 | 26615 | 27065 | 27515 | 27965 | 28415 | 28865 | 29315 | 25265 | 25715 |
| 10 | 26175 | 26625 | 27075 | 27525 | 27975 | 28425 | 28875 | 29325 | 25275 | 25725 |
| 11 | 26185 | 26635 | 27085 | 27535 | 27985 | 28435 | 28885 | 29335 | 25285 | 25735 |
| 12 | 26205 | 26655 | 27105 | 27555 | 28005 | 28455 | 28905 | 29355 | 25305 | 25755 |
| 13 | 26215 | 26665 | 27115 | 27565 | 28015 | 28465 | 28915 | 29365 | 25315 | 25765 |
| 14 | 26225 | 26675 | 27125 | 27575 | 28025 | 28475 | 28925 | 29375 | 25325 | 25775 |
| 15 | 26235 | 26685 | 27135 | 27585 | 28035 | 28485 | 28935 | 29385 | 25335 | 25785 |
| 16 | 26255 | 26705 | 27155 | 27605 | 28055 | 28505 | 28955 | 29405 | 25355 | 25805 |
| 17 | 26265 | 26715 | 27165 | 27615 | 28065 | 28515 | 28965 | 29415 | 25365 | 25815 |
| 18 | 26275 | 26725 | 27175 | 27625 | 28075 | 28525 | 28975 | 29425 | 25375 | 25825 |
| 19 | 26285 | 26735 | 27185 | 27635 | 28085 | 28535 | 28985 | 29435 | 25385 | 25835 |
| 20 | 26305 | 26755 | 27205 | 27655 | 28105 | 28555 | 29005 | 29455 | 25405 | 25855 |
| 21 | 26315 | 26765 | 27215 | 27665 | 28115 | 28565 | 29015 | 29465 | 25415 | 25865 |
| 22 | 26325 | 26775 | 27225 | 27675 | 28125 | 28575 | 29025 | 29475 | 25425 | 25875 |
| 23 | 26355 | 26805 | 27255 | 27705 | 28155 | 28605 | 29055 | 29505 | 25455 | 25905 |
| 24 | 26335 | 26785 | 27235 | 27685 | 28135 | 28585 | 29035 | 29485 | 25435 | 25885 |
| 25 | 26345 | 26795 | 27245 | 27695 | 28145 | 28595 | 29045 | 29495 | 25445 | 25895 |
| 26 | 26365 | 26815 | 27265 | 27715 | 28165 | 28615 | 29065 | 29515 | 25465 | 25915 |
| 27 | 26375 | 26825 | 27275 | 27725 | 28175 | 28625 | 29075 | 29525 | 25475 | 25925 |
| 28 | 26385 | 26835 | 27285 | 27735 | 28185 | 28635 | 29085 | 29535 | 25485 | 25935 |
| 29 | 26395 | 26845 | 27295 | 27745 | 28195 | 28645 | 29095 | 29545 | 25495 | 25945 |
| 30 | 26405 | 26855 | 27305 | 27755 | 28205 | 28655 | 29105 | 29555 | 25505 | 25955 |
| 31 | 26415 | 26865 | 27315 | 27765 | 28215 | 28665 | 29115 | 29565 | 25515 | 25965 |
| 32 | 26425 | 26875 | 27325 | 27775 | 28225 | 28675 | 29125 | 29575 | 25525 | 25975 |
| 33 | 26435 | 26885 | 27335 | 27785 | 28235 | 28685 | 29135 | 29585 | 25535 | 25985 |
| 34 | 26445 | 26895 | 27345 | 27795 | 28245 | 28695 | 29145 | 29595 | 25545 | 25995 |
| 35 | 26455 | 26905 | 27355 | 27805 | 28255 | 28705 | 29155 | 29605 | 25555 | 26005 |
| 36 | 26465 | 26915 | 27365 | 27815 | 28265 | 28715 | 29165 | 29615 | 25565 | 26015 |
| 37 | 26475 | 26925 | 27375 | 27825 | 28275 | 28725 | 29175 | 29625 | 25575 | 26025 |
| 38 | 26485 | 26935 | 27385 | 27835 | 28285 | 28735 | 29185 | 29635 | 25585 | 26035 |
| 39 | 26495 | 26945 | 27395 | 27845 | 28295 | 28745 | 29195 | 29645 | 25595 | 26045 |
| 40 | 26505 | 26955 | 27405 | 27855 | 28305 | 28755 | 29205 | 29655 | 25605 | 26055 |
| 41 | 26095 | 26545 | 26995 | 27445 | 27895 | 28345 | 28795 | 29245 | 25195 | 25645 |
| 42 | 26145 | 26595 | 27045 | 27495 | 27945 | 28395 | 28845 | 29295 | 25245 | 25695 |
| 43 | 26195 | 26645 | 27095 | 27545 | 27995 | 28445 | 28895 | 29345 | 25295 | 25745 |
| 44 | 26245 | 26695 | 27145 | 27595 | 28045 | 28495 | 28945 | 29395 | 25345 | 25795 |
| 45 | 26295 | 26745 | 27195 | 27645 | 28095 | 28545 | 28995 | 29445 | 25395 | 25845 |
LPD is the best method of voice radio communication that does not require a license.
- The transmitter power is 0.01 W and has a built-in whip antenna.
- Frequencies in the range 433.075-434.75 MHz are divided into 69 channels.
- It is used in security services that work at hotels, shops, etc.
- Also used for radio remote control and vehicle alarms.
LPD channel frequency table
| Channel number | Frequency (MHz) | Channel number | Frequency (MHz) |
| 1 | 433.075 | 35 | 433.925 |
| 2 | 433.100 | 36 | 433.950 |
| 3 | 433.125 | 37 | 433.975 |
| 4 | 433.150 | 38 | 434.000 |
| 5 | 433.175 | 39 | 434.025 |
| 6 | 433.200 | 40 | 434.050 |
| 7 | 433.225 | 41 | 434.075 |
| 8 | 433.250 | 42 | 434.100 |
| 9 | 433.275 | 43 | 434.125 |
| 10 | 433.300 | 44 | 434.150 |
| 11 | 433.325 | 45 | 434.175 |
| 12 | 433.350 | 46 | 434.200 |
| 13 | 433.375 | 47 | 434.225 |
| 14 | 433.400 | 48 | 434.250 |
| 15 | 433.425 | 49 | 434.275 |
| 16 | 433.450 | 50 | 434.300 |
| 17 | 433.475 | 51 | 434.325 |
| 18 | 433.500 | 52 | 434.350 |
| 19 | 433.525 | 53 | 434.375 |
| 20 | 433.550 | 54 | 434.400 |
| 21 | 433.575 | 55 | 434.425 |
| 22 | 433.600 | 56 | 434.450 |
| 23 | 433.625 | 57 | 434.475 |
| 24 | 433.650 | 58 | 434.500 |
| 25 | 433.675 | 59 | 434.525 |
| 26 | 433.700 | 60 | 434.550 |
| 27 | 433.725 | 61 | 434.575 |
| 28 | 433.750 | 62 | 434.600 |
| 29 | 433.775 | 63 | 434.625 |
| 30 | 433.800 | 64 | 434.650 |
| 31 | 433.825 | 65 | 434.675 |
| 32 | 433.850 | 66 | 434.700 |
| 33 | 433.875 | 67 | 434.725 |
| 34 | 433.900 | 68 | 434.750 |
| 69 | 434.775 | ||
In addition to 69 channel radio stations, there are also 8 channel radio stations in the LPD band. The analogue from the 68 channel range is indicated in brackets.
| Channel number | Frequency (MHz) | Channel number | Frequency (MHz) |
| 1 (1) | 433.075 | 5 (12) | 433.350 |
| 2 (2) | 433.100 | 6 (17) | 433.475 |
| 3 (6) | 433.200 | 7 (23) | 433.625 |
| 4 (10) | 433.300 | 8 (30) | 433.800 |
PMR is a system for organizing communication via voice transmission with unobstructed visibility.
- This range does not require a license or permit.
- The frequencies are divided into 8 channels, the step of which is 12.5 KHz.
PMR channel frequency table
| Channel number | Frequency (MHz) | Channel number | Frequency (MHz) |
| 1 | 446.00625 | 5 | 446.05625 |
| 2 | 446.01875 | 6 | 446.06875 |
| 3 | 446.03125 | 7 | 446.08125 |
| 4 | 446.04375 | 8 | 446.09375 |
LOW BAND - the signals of this system are most susceptible to industrial interference, and emanating from household and electrical appliances.
- The devices should be used outside the populated area, since radio interference is lower in sparsely populated areas.
- The low frequency portion of LOW BAND may extend beyond direct vision.
- This amplitude shows excellent results for long-distance communications between car and stationary radio stations.
- Walkie-talkies have a shorter signal range because the wavelength is longer than the helical antenna.
The presented ranges have pros and cons that relate to their radio wave propagation systems:
- LPD, PMR - are the best for short distances within urban areas. They have less interference. It is important to take into account the short communication range and the fact that radio waves are unable to pass through obstacles.
- The PMR sub-band is least susceptible to interference, and therefore creates high-quality signal transmission. Increased power makes it possible to transmit signals over increased distances.
- They are universal, have optimal dimensions, but they require documentation and payment for permits for use.
- CB is used for long-distance communication outside the city. Because outside a residential area, the impact of radio interference is reduced.
Technological differences in the equipment used for work
Due to the differences in frequencies used by civilian radio stations, the sizes of their antenna devices vary significantly. For the CB band, where the wavelength is 11 meters, it is necessary to use a standard quarter-wave antenna 2.7 meters long. In the LPD band, the wavelength is 0.69 meters, so a full-size antenna would be 17 cm long. In practice, these antennas are smaller due to the use of various technical tricks, but the size difference remains the same. Differences in the power of the transmitters used cause differences in the power supplies used.
The 10 milliwatt LPD transmitter does not require bulky batteries, so these walkie-talkies are much smaller. CB radios have high power (10 watts), so they require the use of powerful and bulky batteries. In addition, they have large remote antennas, so they are most often available in portable or stationary versions.
Which range is better?
Many people who need to choose a range are often confused about their preferences. It is important to understand that each radio wave amplitude has a specific task, so it is impossible to determine the “best” one. The selection of a device should be based solely on the purpose and location of its use.
For long-distance connections you need to choose CB. It is often used by logisticians and security agencies that need to coordinate the actions of employees at a distance. Also, this type of communication is excellent as an amateur connection.
If there is a need for better communication over short distances, you can choose high-frequency systems. Many modern walkie-talkie models allow you to support both frequency ranges. The presence of digital voice broadcast allows you to achieve high-quality communication. If distance does not matter, and the main role is played by signal transmission, then you should choose models with this range.
Experts have divided the amplitudes of radio waves so that different categories of users have the opportunity to choose the desired frequencies without mutual interference.