Varieties in the type of television channels and the style of television programs are in particular determined by the interests of the audience . It is not possible to list all the TV channels in the world due to their excessive number and the lack of such statistics. But in order to imagine the volume and essence of television, we can divide all channels into types and formats : There are not so many federal channels, but at one time there were countless regional channels. So, in each regional center of Russia there are 2-3 regional channels + in each more or less large city in this region, there is its own cable operator, which also broadcasts on its own cable resources, completely free of charge. If regional and regional TV channels can be classified into one format , then federal TV channels each broadcast in their own style , which determines the types of TV programs broadcast . Public, public and state channels are trying to combine as many formats as possible in order to be popular among the largest number of viewers and attract the maximum audience.
Analog and digital TV
Initially, television was distributed using analog data transmission, which led to a significant deterioration in image quality. Among other things, the possibilities for receiving such television were significantly limited. However, already in the nineties of the last century, digital TV appeared, which significantly expanded the capabilities for transmitting video and audio signals. Among the advantages of such digital TV, we note the excellent image quality, which will be appreciated by owners of large TVs.
Packages and tariff plans
Having decided which operator is best suited for the region of installation, you need to select a favorable tariff package.
The largest satellite television operator, which is today preferred by more than 12 million Russian families, the Tricolor company, offers basic and additional tariffs. Basic:
- “Unified”, providing reception of 224 TV channels for 1500 rubles/year.
- “Unified Multi” - 215 television channels for 2000 rubles/year.
- “Unified UHD” transmits 231 TV channels for 2,500 rubles/year.
- “Extra” - 225 channels for 2000 rubles/year.
Important: The Ultra HD tariff plan can only be used if you purchase a UHD receiver, as well as if you have an ultra-high definition image transmission function on your TV.
Additional packages include:
- Ultra HD - 7 channels;
- "Children's", broadcasting 22 TV channels;
- “Nochnoy”, broadcasting 7 TV channels for adult audiences;
- "MATCH! Premier" with two sports channels;
- "MATCH! Football" - 6 TV channels.
Another popular satellite television provider among Russian residents,
Telekarta company has the following tariffs in its line of offers:
- "Master". For a payment of 149 rubles. 140 channels are available to the user per month.
- “Leader” - 220 TV channels for a monthly fee of 249 rubles. per month.
- "Premier" for 399 rub. per month the user gets access to 240 TV channels.
- "Pioneer". The most economical tariff, including 95 channels for 67 rubles. per month.
What is cable television
Cable television operators appeared at the end of the last century and gained great popularity in the market. As the name suggests, such television is transmitted via cable, and the providers themselves include various thematic channels, including entertainment, sports, films and information. Cable television can be offered on a paid or free basis.
If we talk about the advantages of such cable television, we can note the maximum possible selection of channels, as well as the ability to select a package of TV channels that will fully satisfy your needs. All cable television is broadcast in digital format, which ensures image quality and maximum picture realism.
What is it and how does it work
Cable television is a type of television in which the signal is sent through a wire route using coaxial or optical cable.
There is nothing complicated about installing cable TV. A terrestrial broadcast system is being deployed in a populated area, which includes different types of infrastructure and information transmission. For users, broadcasting is represented by a cable that is routed into the living room and connected to the TV. At the heart of the functioning of this type of television is a center in which data is processed and channel packages are created for subsequent broadcast.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of cable broadcasting:
- good picture and sound quality;
- high immunity to interference;
- a large number of channels;
- a wide range of additional services.
In addition to the above, it is worth noting that the cable is laid underground, which means it is protected from intruders.
You can connect more than one TV to such a wire with independent channel viewing. Compared to satellite TV, cable TV has a lower cost and therefore almost everyone can afford it.
The disadvantage of such broadcasting is the possibility of damage to the antenna under adverse weather conditions. In addition, low-quality consoles often break, and this creates additional inconvenience and financial costs.
What is satellite television
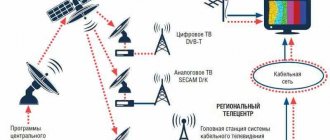
Satellite television first appeared in the eighties of the last century, but this technology received its greatest distribution already in the 20th century. The technology of such satellite television is extremely simple. There are numerous telecommunications satellites in low-Earth orbit, broadcasting a signal over the airwaves, which is received by subscribers using special antennas, and the data is subsequently decoded and displayed on the TV screen.
Today, satellite television is offered on a paid and free basis. Its advantage is the largest possible selection of TV channels, as well as excellent image quality. Regardless of your preferences, you can choose an offer package that will fully meet your needs. Moreover, if previously the cost of such equipment for receiving satellite television was extremely high, today you can easily select inexpensive options for receivers and antennas that will be available to every buyer.
Signal processing. Television standards and formats
WHAT ARE TV STANDARDS AND FORMATS AND WHY ARE THERE SO MANY?
Initially, TV standards were developed based on a television receiver with a masked kinescope and phosphor phosphor triads, so they reflected the technological limitations inherent in this type of display.
Color television is based on the known properties of human vision, primarily its inertia, as well as the physical capabilities of the means display. From here follow the basic standards of television: the minimum frame rate at which the eye does not notice flickering and fragmentation of movements, and the additive principle of adding three colors - red, green and blue. Initially, TV standards were developed based on a television receiver with a masked kinescope and phosphor phosphor triads, so they reflected the technological limitations inherent in this type of display.
Basic conditions for obtaining a high-quality image:
- update at least 50 times per second,
- white color is obtained when the ratio of the glow intensities of red ER, green EG and blue EB phosphors is EY = 0.3ER + b.59EG + 0.11EB.
The general rule is that the electron beam traces the lines from left to right and from top to bottom. Finally, when developing color television standards, the condition was set for backward compatibility with black and white TV. Therefore, instead of three color components - R, G and B - in television, unlike computer graphics, brightness (luminance intensity) and color difference components were used, obtained by subtracting each color component from the brightness signal. The full television signal had to be included in the standard BW channel range (6 MHz), so the number of components was reduced to three due to color difference green, the share of which is quite large in the luminance component. The remaining Y (luminance), Pr (chroma red) and Pb (chroma blue), carried on separate lines, represent the analog component signal. But such a signal is not suitable for transmission over the air, so the main type of signal is composite, in which brightness and color are encoded in different ways. At the receiving end, the demodulated signals are fed to a matrix in which the original components of the three primary colors are restored (color TV) or everything except the luminance signal is simply discarded (B&W TV).
Despite the general principles of image transmission using electrical signals, there are many TV standards (systems) in the world. A standard is a set of specifications that define the number of lines and frames, the structure of the signal and the timing relationships of its components, the levels of white, black and blacker than black (synchronization), the order of changing fields (half-frames) in a frame, and color coding methods. Here are the main specifications listed above.
Levels.
30% of the signal swing from below (blacker than black) falls on the synchro part, the remaining 70% is on the brightness signal, on which the subcarriers modulated by chrominance signals “sit”. The white level is 100%. The damping level is the same 30%, the black level is slightly higher.
Temporary parameters.
In order to reduce the frequency band occupied by the full television signal, the frame is divided into two half-frames, or fields: in one, odd construction sites are transmitted, in the other, even ones. The resulting interlaced scanning method makes it possible to fulfill the initial condition of the screen refresh rate with a smaller frequency band occupied by the signal. Within 1 second, 50 half-frames (fields) are transmitted in PAL and SECAM systems and 60 in NTSC. Accordingly, the vertical scanning frequencies are 25 and 30 Hz. Each frame contains 625 (PAL, SECAM) or 525 (NTSC) lines, of which 576 and 480 are active (visible). In accordance with these parameters, the durations of the lines, as well as line sync pulses, field blanking, equalizing and synchronizing pulses are strictly defined , which define the structure of the complete video signal.
Individual standards form systems, of which, if we talk about traditional analog television, there are only three in the world: NTSC, PAL and SECAM (each of them has several varieties). Television format is a broader concept that, in addition to the standard, also includes an interface: the physical medium of signal propagation with its standardized parameters (say, the characteristic impedance of the cable) and regulated voltages and powers. In addition, the TV format determines specific types of cables and connectors that are suitable for a specific signal and ensure transmission line matching. For example, an terrestrial TV format, which is a carrier emitted into the air from one of the TV channels, modulated by a composite signal. Or the same composite in its “pure” form, transmitted over a 75-ohm coaxial cable. Next: S-Video, which differs from composite in separate lines for transmitting brightness and color signals, component (not two, but three separate lines: brightness and two color difference signals). Or digital component - SDI, etc.
In the field of TV formats and standards, there is a certain terminological confusion: the same signal can be transmitted over different interfaces, the term “format” itself is often used to refer to screen proportions, and a large number of standards adopted in different countries makes clear systematization difficult.
In the field of TV formats and standards, there is a certain terminological confusion: the same signal can be transmitted over different interfaces, the term “format” itself is often used to refer to screen proportions, and a large number of standards adopted in different countries makes it difficult to clearly systematize
The diversity of TV standards and formats is explained by many factors, including economic and political. The emergence of color television occurred during the Cold War, and the on-air disunity between countries of different camps fully corresponded to the specifics of the era. Moreover, due to the relatively high frequencies, the on-air distribution of TV programs had a limited range. Actually, the authors of color television are three countries: the USA, Germany and France. The rest of the countries simply adopted one or another modification of one of the three world standards.
A serious contribution to the global disunity in color television was made by the initial difference in power system standards, essentially dividing the world into two TV camps. In America, the frequency of the alternating current power supply network, as is known, is 60 Hz, and in European countries - 50 Hz. The frame rate was strictly tied to these values, since in early “mechanical” television systems, which used a Nipkow disk with holes arranged in a spiral, the latter was spun using a synchronous motor. Subsequently, when mechanics completely gave way to electronics, a sufficiently high stability of the frequency of the power supply network was a ready-made solution that lay on the surface. This contradiction has survived to this day and continues to create difficult and expensive problems to solve.
TRADITIONAL TV STANDARDS
NTSC (National Television System Committee)
The advantage of NTSC is full color coding in each line. The disadvantage is the high sensitivity to cross-phase distortions that occur in the transmission channel and lead to noticeable color distortions
Adopted in 1953 in America, it also became widespread in Japan, Canada, and Mexico. Each line contains, in addition to the luminance component Y, information of two color difference signals ER-Y and EB-Y, with which the 3.58 MHz subcarrier is modulated. Quadrature modulation provides synchronous encoding of two independent signals. To do this, the subcarrier is divided into two components with a phase shift of 90°, one of which is amplitude modulated by the ER-Y signal, and the other by EB-Y. These components are then added together. The result is a signal modulated in both amplitude and phase, which can be represented as a vector. The vector module uniquely determines the color saturation, and the phase angle determines the color hue.
The advantage of NTSC is full color coding in each line. The disadvantage is the high sensitivity to cross-phase distortions that occur in the transmission channel and lead to noticeable color distortions. That is why NTSC TVs provide a tint adjustment (Tint), designed to compensate for color distortion already at the level of the restored component signal. In addition, due to the relatively small number of lines, the NTSC system is limited in vertical resolution.
PAL (Phase Alternation Line, or lines with variable phase)
The PAL standard has a number of important advantages: since the subcarrier itself is suppressed and only the sideband of the spectrum is transmitted, there is no characteristic noise in uncolored areas of the image. Twice the signal-to-noise ratio. No phase distortion
Developed in Germany by Telefunken in 1963 in order to correct the inherent shortcomings of NTSC. Quadrature modulation is also used here, but the 4.43 MHz subcarrier, which is modulated by the ER-Y signal, changes its phase by 180° from line to line. A color synchronization signal is introduced into the blanking horizontal pulse in the form of a “flash” in several subcarrier periods with the corresponding phase. On the receiving side, decoding occurs by adding and subtracting the corresponding color-difference signals of each pair of lines (which requires a delay line for the duration of one line). Balanced demodulation allows you to completely get rid of crosstalk - the main disadvantage of NTSC. The dependence of image quality on distortions and interference in the transmission line is significantly reduced, and the requirements for the stability and accuracy of electronic components and components are reduced. The only exception is the precision delay line. It was precisely because of the labor intensity of its production that the USSR at one time refused to adopt the PAL standard, which became widespread in many countries of Western Europe, Asia and Africa.
The PAL standard has a number of important advantages: since the subcarrier itself is suppressed and only the sideband of the spectrum is transmitted, there is no characteristic noise in uncolored areas of the image. Double the signal-to-noise ratio by doubling the chrominance signals during decoding. There are no phase distortions that interfere with color reproduction, as well as cross-distortion between color difference signals. The only drawback is that the vertical color resolution is lower than that of NTSC: color information is averaged for each pair of lines. This is not so noticeable, since the sensitivity of vision to the brightness of small details is significantly higher than to their color gradations. In addition, PAL is superior to NTSC in the number of NTSC lines (although it is inferior in frame refresh rate, although only slightly).
SECAM (Sequentiel Couleur Avec Memoire, or sequential color transmission with memory)
The SECAM standard does not allow any interference with the signal, therefore TV programs are produced in the PAL system, and in SECAM the signal is transcoded immediately before being broadcast on air
The standard was developed by engineer Henri De France in 1954, adopted by France and Russia simultaneously in 1967. The fundamental difference between this standard and the other two (quite similar to each other) is that there are two subcarriers: 4.25 MHz (for ER-Y ) and 4.406 MHz (for EB-Y), and the modulation is not amplitude, but frequency, which provides much higher noise immunity. Color signals are transmitted one by one, through a line, and each line has color synchronization flashes of the corresponding frequency as part of the blanking horizontal pulses. Using a delay line (the duration of one line), the chrominance signals are delayed for the duration of one line. Thus, as in the PAL standard, the vertical color resolution is half the brightness resolution, but the number of lines is greater than in NTSC. Low sensitivity to interference and path errors make SECAM signals ideal for transmission. However, the SECAM standard does not allow any interference with the signal, so television programs are produced in the PAL system, and in SECAM the signal is transcoded immediately before being broadcast.
All video standards use signal spectrum multiplexing. Regions in which the energy of the luminance signal, the spectrum of which has a pronounced unevenness, is practically absent, are allocated to the chrominance subcarriers with their sidebands. This makes it possible to fit a full color signal into the standard 6 MHz range, which was also adopted for black-and-white television. Sound is transmitted using frequency modulation of a separate subcarrier, shifted upward along the frequency axis so as to exclude mutual interference with video information. A signal that includes all the luminance and chrominance components with their subcarriers, plus the audio part, is called a complete television signal, and without an audio subcarrier - a complete color signal. The basic type of full color signal is a composite signal transmitted over a single cable or over-the-air channel.
Composite signal (CV)
| BNC connector | RCA type connector |
Rice. 1. Composite signal diagram (one line), connectors
The disadvantages of a composite signal are the ability to transmit only standard definition video. Noise due to luminance and chrominance beating, limiting image quality
Band up to 6 MHz. The most universal signal, which is usually transmitted over a 75 Ohm coaxial cable over a distance of up to 50-100 m or longer in the presence of active repeaters with correction of high-frequency losses. The composite interface uses RCA connectors (in consumer equipment) or BNC connectors (in professional equipment). The second type is preferable because it allows you to maintain the normalized impedance of 75 Ohms. Due to the relatively narrow frequency band, the composite signal is quite unpretentious. It can also be transmitted over other interfaces, for example, over twisted pairs, fiber optic lines, etc., if appropriate converters are available. At the same time, the transmission distance increases significantly.
The disadvantages of a composite signal are the ability to transmit only standard definition video, inapplicability in the HDTV area, only interlaced scanning, as well as interference due to beating of the luminance and color signals, limiting image quality.
S-Video signal (Super, Separate Video)
Rice. 2. S-Video signal diagram, 4-pin DIN connector for it
Allows you to achieve much higher image quality due to the absence of beats in the brightness and color signals and the moire that arises from them
It differs from composite in that the luminance and synchronization signals are transmitted along one line, and the chrominance signals on the other. This difference makes it possible to achieve much higher image quality due to the absence of beats in the luminance and color signals and the moire that arises from them. The result is almost three times higher clarity. The S-Video interface is available only for NTSC and PAL standards, but not for SECAM. For transmission, 75 Ohm coaxial cables are used (but no longer broadcast). Connectors are four-pin, DIN standard.
Neither composite nor S-Video are suitable for high-definition formats (HDTV, or HDTV). The latter are implemented in component signals, analog and digital.
Component signal (YPbPr, YCbCr, YUV)
Rice. 4. Component signal diagram
| Composite video | Component video |
Rice. 5. Component signal quality compared to composite signal
Component signal is the most advanced of all analog video signals, allowing the implementation of HDTV formats
There are no longer two, but three independent transmission channels, usually implemented using 75-ohm coaxial cables with RCA or (which is better) BNC connectors. Thus, the sync-mixed luminance signals and both chrominance signals are completely separated. There is no need for subcarriers and modulation, crosstalk and phase distortions, beats and other artifacts completely disappear. The component signal is the most advanced of all analog video signals, allowing the implementation of HDTV formats. A digital component signal is also known - SDI, which differs from analog in that the information of the same channels has a digital representation. Moreover, when switching to the SDI digital interface, there is no need for three cable channels; one is enough, as is the case with composite video. Therefore, to implement SDI paths, you can use the existing composite path infrastructure. Information (4:2:2, depth 8/10 bits per component) can be transmitted at a bit rate of 270/360 Mbit/s and accumulated in buffers on the receiving side. In addition to video, it becomes possible to transmit up to 16 channels of digital audio and time code. The SDTI (Serial Digital Transport Interface) option, unlike SDI itself, allows the transmission of both uncompressed and compressed streams without intermediate decompression. The transmission range via coaxial cable can reach up to 300 m (with repeaters or more), via optical fiber – up to 50 km.
HDTV STANDARDS
The advantage of HDTV standards is significantly higher image quality
With the widespread introduction of pixel displays (plasma and LCD panels, CLD and DLP projectors), as well as digital video signal processing and the development of digital television, a large number of new TV standards have appeared, which have become customary to denote the number of vertical pixels and indicate the scan type. HDTV formats start at 480p (progressive, or progressive, scanning), or 720 x 480p at a frame refresh rate of 60 Hz. Next come 576p, 1080i, 1080p. Standards with lower resolutions than 720p (for example, 480i) are classified as SDTV (standard definition TV). At different times, other HDTV standards of Japanese and European origin arose, but they were not widely used and were forgotten.
Rice. 6. HD-SDI BNC connector
The advantage of HDTV standards is significantly higher image quality. Moreover, thanks to powerful digital processors, both built-in and external, even signals from standard definition sources (for example, a DVD) can be brought closer in quality to the actual HDTV programs. An increase in picture quality has become especially relevant recently, when the size of displays has increased significantly: if on TVs with a screen diagonal of 21-25" image artifacts are almost invisible even when playing a regular broadcast program, on large screens, especially when it comes to projection systems , everything is visible: the lines move apart, leaving dark gaps, the inclined lines become jagged, and the movements become intermittent. Therefore, the role of high-quality conversions of TV formats using advanced interpolation algorithms (synthesis of new lines and fields), compensation for the consequences of converting scanning to line-by-line and smoothing discrete movements on the screen is increasing.
TRANSFORMATION OF STANDARDS
It is extremely difficult to convert NTSC to PAL or SECAM due to different frame rates
A similar problem has to be solved very often: in studios - to show a foreign program on TV, and in household appliances - to bring the original signal to the display’s own resolution. In different cases, this problem can be solved easily or practically impossible when it comes to maintaining the original quality. For example, converting NTSC to PAL or SECAM is extremely difficult due to different frame rates. After the advent of digital signal processing technologies, the task has been significantly simplified, but the cost of the equipment is very high: the signal has to be completely reconstructed with digitization and inverse conversion, buffering, interpolation synthesis of intermediate scales and fields, and transfer to a new line-frame basis. The situation is much simpler with PAL/SECAM conversions, since both the frame rate and the number of lines in these standards are identical. We are talking only about recoding color signals. Therefore, there are a lot of inexpensive integrated circuit transcoders.
Rice. 7. General circuit of a composite video signal converter to RGB
During the conversion process, the luminance and color difference components, as well as the sync mixture, are restored from the original composite signal. In S-Video, the sync pulses and the luminance signal are separated, as well as the color difference components Cb and Cr. The component signal provides all this in finished form; all that remains is to separate the sync mixture. Then the conversion is carried out to RGB, a standard in which the weighting coefficients of the main color components are equal to 1.
| Signal YPrPb | RGB signal |
Rice. 8. Levels of primary colors YPrPb and RGB
After this, the signal is digitized and placed in a buffer, from where it is read in accordance with the new synchronization frequency grid.
Conversion of standards should be accompanied by as little color shifts as possible. If at the same time the scan is transformed at the same time, the characteristic artifacts of this transformation should not be noticeable (“comb effect”, etc.). Also, discrete movements should not occur due to incorrect transition to a new frame rate, if such occurs. Finally, a significant factor is the cost of the equipment, which can vary greatly depending on the specifics of the conversion task.
With the advent of HDTV standards, conversions have become more relevant - not a single medium- or large-screen display can do without them.
With the advent of HDTV standards, conversions have become more relevant - not a single medium- or large-screen display can do without them. First of all, interlaced scanning is converted into progressive scanning, and various tricks have to be used to minimize such characteristic distortions as the “comb effect” (due to a time shift between the fields of one frame), jagged oblique lines, and flickering of adjacent lines. Along the way, interpolation is performed, movements are smoothed, and screen proportions are changed if necessary.
Conversion without and with anti-aliasing
“Comb” effect when an object moves on the screen
Digital compression artifacts (on the right side of the example)
Motion Blur
Rice. 9. Conversion Artifacts
CHANGING FORMAT
Often there is a need to switch to another format or interface without going beyond the TV standard. This task usually does not cause problems and is solved using inexpensive devices, often analog. There are a large number of different converters that make it possible to receive the same signal in several formats at once, such as composite, S-Video and component, and even not only formats, but also standards.
Rice. 10. Universal converter of formats and standards
SPECIAL CASES OF TRANSFORMATION
The main one is the mutual conversion of computer and television formats. In order to convert a computer signal into video, scan converters, or scan converters, are used. For the reverse conversion, use scalers. These are universal devices, many of which are built on the principle of “any signal at the input - any signal at the output,” meaning all the attributes of this signal: resolution, types of scans, analog or digital representation.
With the advent of digital TV formats and effective compression algorithms (MPEG2, MPEG4, etc.), the need for transformations associated with changing the degree of compression or its method has sharply increased. In addition, network television is successfully developing, delivering programs over the IP protocol. There are many successful solutions using the Wi-Fi wireless interface. Typically, the latter is combined with a local Ethernet network infrastructure running on twisted pairs and longer external fiber optic backbones. All this requires many transformations at the input and output of each interface. However, today transformations have almost completely left the analogue domain and are concentrated in the digital domain, so their number no longer has a negative impact on the signal. Moreover, during many transformations, the signal is reconstructed while eliminating jitter.
What is IP television
IP television has also become widespread today, which allows you to view various TV channels on the screen of a mobile phone, computer or TV. This opportunity has arisen thanks to the development of high-speed Internet access. Such IP television is offered today at affordable prices, and there is a choice of free channels, including thematic packages.
If we talk about the advantages of such IP television, we can note the excellent image quality and the ability to select TV channels that will be of interest to every homeowner. However, it must be taken into account that in order to comfortably watch such programs, you must have high-speed Internet access, and television itself is offered in most cases on a paid basis.
How to connect
To connect cable television, the presence of specialists is required; the subscriber will not be able to cope on his own. Unauthorized tapping into the system entails criminal or administrative liability. Therefore, if you want to enjoy cable broadcasting, the user should contact the provider. Our specialists will independently carry out all connection work quickly and efficiently.
After connecting cable TV, the user has the opportunity to view hundreds of channels, as well as videos, weather forecasts and much more.
For a relatively small subscription fee, the subscriber will receive high-quality broadcasting and pleasant emotions.
What is broadcast television
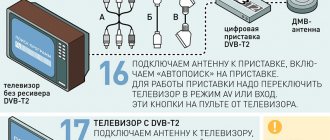
Terrestrial television is distributed using appropriate repeater stations located on the ground. Today, this type of television is most widespread in Russia. To receive such terrestrial television, you must have an appropriate active or passive antenna, digital decoder and TV.
Currently, terrestrial television is completely switching to digital broadcasting, which allows for the highest possible image quality. The supply of TV channels has also expanded significantly, which for many domestic operators exceeds several hundred different all-Russian, foreign and regional channels. Everyone will be able to choose the best option for them to offer such terrestrial television, which can be distributed both free of charge and for a small additional fee.
Types and types of TV programs and TV channels
To choose a TV channel, you need to look deep and determine what is interesting to you. To do this, let’s sort programs and all television content by type and find out what there are :
- Most popular look programs for regional channels, and for state television companies - this is news. The main task of information programs is warning. This is also a good way of PR, disguising an unimportant event as important news. The best news-type TV channels that you can watch for free - in Russia - Russia 24 (24/7 news), world famous BBC.
TV news channel logo - Highly specialized, news and information programs notify about events narrow character, for example: sports or crime news, medical or election races. The principle of ordinary news, but in details about every event certain direction. An important feature of news channels and television programs is that to a large extent they work live. Narrow specialization of the best TV channel in this field RBC - is a business.
Fragment of the live broadcast of the RBC TV channel - Analytical and informative -
programs that group and summarize, as well as summarize and summarize data, news and rumors on important cases and facts,
certain topics, for a specified period of time (week, month, year). A good example of this type of TV show there will be a TV program known since Soviet times - Person and law.
Screensaver Man and the Law - Intellectually distracting - for example: morning programs (without crime and politics). More like a conversational style show with funny stories. Main don't outweigh to one side, and not turn in entertainment type or purely informational.
RUssia morning - Cultural - educational the program supports the goal of familiarizing the viewer with moral values. The subject of such programs is historical events, the mood of art, the situation in music and theater. This could be a conversation in a studio setting, a live broadcast from a theatrical production, or an authentic movie based on real events. There are even certain types and styles of video shooting used for this purpose. The best TV channel of this genre in Russia is Culture.
TV channel Culture - Children's programs and children's television in general, as well as cartoons and animation, carry important educational, upbringing and socialization tasks for the younger generation. Every parent knows what TV programs there are for children and what to turn on for their child. Judging by the ratings of television channels, the best TV channel in this category is Cartoon.
Screensaver of the Mult TV channel - Particularly relevant during the World Cup - sports programs, sometimes including live and full coverage of the match and awards ceremony. Best sports in digital television - channel Match.
TV channel match - Feature (actor) films - an integral part of the entertainment and recreational component of each channel. But there are also channels completely based on films, mostly they are included in separate paid packages of satellite and cable TV - Amedia Premium HD And TV channel Dom Kino.
TV channel logo – House of Cinema - TV serials - You can watch online on the Internet and in good quality, but initially all series are filmed for television. The genres of series can determine the genre of an entire TV channel. The best TV channel with TV series, founded by the best company filming TV series - Netflix.
Film company producing TV series - Entertainment programs are needed for relaxation and are divided into 4 types: humorous, talk shows, TV quizzes, and reality shows. The best TV channel that includes only entertainment types of television programs in Russia is TNT Comedy. Entertainment TV channel logo
- The last type of television content can become the main component of an interesting TV channel, but still only the BBC can cope and develop without it - this is advertising (other interesting facts about TV). And the best TV channel whose main and only video is advertising is Shop on the Sofa , and it’s immediately clear what kind of TV shows there are.
TV channel - “Shop on the couch”
If you have chosen a TV channel and are thinking about which TV is best to connect , you should think about it and test your choice on the Internet, since many of the best TV channels can be watched online , free of charge and in good quality. Because for most television representatives, the essence of their work lies in the number of viewers, on which their advertising .
Which one is better to choose?
Most often, an offset-type parabolic antenna is installed in ordinary apartments and private houses. The first thing you should pay attention to when choosing a device is its diameter. The standard dish size is 55–65 cm; in remote regions with poor signal levels the figure is 80 cm or more.
Experts call Supral 0.9 one of the most current TV antennas aimed at enhanced reception. Satellite operators call this device one of the most reliable. Due to its diameter, the antenna is quite heavy. This simultaneously makes it more difficult to install, but also makes it more reliable and weather-resistant. Such a plate can withstand any gust of wind.
Lans 65 is a perforated satellite dish with a diameter of 65 cm. This is a budget option, but according to expert comments, one of the most functional. It provides high signal quality, does not require additional cleaning - due to the holes in the surface, snow and debris do not collect on it, and has an interesting design and ease of installation.