Why is the screen stretched?
To understand whether you can cope with the problem of an elongated picture without outside help, open the “Menu” and select “Return to basic settings” in it. If after this the frame is still distorted, you will need the help of a professional technician. Do not try to fix the problem yourself.
The TV image is stretched horizontally or vertically - possible causes of the malfunction:
- LCD operates in preset mode according to the manufacturer's data;
- the backlight of the liquid crystal panel is partially out of order;
- During the software update process, the settings failed;
- matrix failure.
Any of the listed points can be eliminated by a competent master. Repairs and updates of programs are carried out only with licensed software. If you tamper with electronics or attempt repairs on your own, you may cause damage to your device.
What picture sizes can you choose?
The size of the picture depends on the source from which the image comes. The table shows a list of sources and available sizes.
If, when receiving over-the-air channels, you select the “Wide Zoom” image mode, then the picture is noticeably flattened vertically, and you cannot change the vertical size (you can only move the entire picture). If you select the “Enlarged” image mode, you can select the vertical size, but the picture turns out to be too enlarged and a lot is lost beyond the borders. If you select the “4:3” mode (with black bars on the left and right), then, on the contrary, the picture is slightly stretched vertically (!) That is, there is no way to get a picture that is not distorted in size! Approximately the same is observed for other signal sources (AV, Component). Is there any way to treat this? TV made in Russia.
Brightness, backlight settings, color palette
Despite the name, this setting actually adjusts the black level. We need to get maximum black depth without losing the detail of dark objects.
To adjust, raise the brightness level until the black bars above and below the frame turn gray, and then lower it until they turn black again.
There needs to be something dark on the screen to adjust the level on - for example, a jacket or shirt. Lower the brightness until the details begin to get lost in the shadows, then go back a little. Typically the brightness is set to around 50%.
This setting adjusts the overall brightness of the image, allowing you to adjust it for different conditions.
You can choose different values for day and night, lowering it slightly in a darkened room to avoid eye strain.
The value of the parameter depends on the situation and personal preferences; start from the middle of the scale and change according to taste.
You may not spend much time adjusting the color balance, as preset TV modes often automatically set it to about average.
Turn on a scene with a colorful color palette and make sure the colors look bright enough; if not, move the dial up to give them more energy. Conversely, if the colors seem oversaturated, turn it down a couple of points.
Then include a shot of people's faces to check if the skin tones are realistic. This is one of the most difficult settings to configure; take the time to achieve a natural shade.
Most TVs have a color temperature setting that ranges from cool (bluish tones) to warm (reddish); It's best to leave it as "neutral" or "normal" as possible.
Acceleration is necessary and rarely noticeable
Even with all its shortcomings, upscaling is good. It's a process that usually goes off without a hitch and allows you to watch multiple video formats on the same TV. It's perfect? Of course not. That's why some movie and video game fans choose to enjoy old art for its intended purpose: old-ass TVs. But, for now, upscaling isn't something to get too excited about. And it's not something to get too upset about.
It's worth noting that 8K, 10K and 16K video formats are already supported by some of the hardware we use every day. If upscaling technology can't keep up with these high-resolution formats, chances are it will result in a much greater loss of quality than we're used to.
With manufacturers and streaming services still dragging their feet towards 4K, perhaps we don't have to worry about 8K just yet.
Basic image parameters
Every manufacturer is interested in having a hardware store visitor buy its TV. For this purpose, the basic picture settings are set in such a way that it looks as rich as possible (especially in stores with good lighting). But, having bought a TV and installed it at home, it turns out that the image is not so colorful, so you have to adjust it further.
To set it up correctly, you need a little time and a remote control that has a “Menu” or “Settings” button. To adjust the basic parameters, go to the “Image” section.
Intensity
This term refers to color saturation. One of the common mistakes when setting up occurs when the user wants “as many colors as possible” and turns the intensity to maximum. Yes, the picture turns out juicy, but unnatural, which is why your eyes will quickly get tired.
To ensure the screen produces optimal colors, this parameter is set to medium values. For ease of adjustment, it is recommended to select a test image with relatively desaturated colors, for example, a natural landscape.
Brightness
This term is the balance of black in relation to the entire palette. To put it simply, the parameter determines the quality of display of dark areas. On many TVs, including LG, the brightness is set to extremely high, so most users are accustomed to thinking that brighter is better. In fact, this is not the case. If you adjust the brightness too high, blacks become gray, reducing picture clarity.
If you set the brightness to low, dark pixels become more visible, but it is more difficult to distinguish similar shades of black. This parameter must be configured in the room where the TV will be installed. The level of illumination is also taken into account. As a rule, people watch TV early in the morning or in the evening, after work, that is, in the dark. Therefore, adjustments are carried out in low light conditions.
You can find the optimal brightness by eye. To do this, they turn on the film and, when there is a picture with textured black and shadows on the screen, they pause it. As you decrease the brightness, the blacks will become more intense and the shadows will appear darker.
The optimal setting is when black is perceived as truly black and not gray (high value). At low brightness, dark areas appear less detailed.
Contrast
This setting is the opposite of brightness. It determines the white level, how intense the light parts of the image will be. The goal of the adjustment is to achieve a bright picture in which individual details are clearly visible.
The easiest way to check contrast is in scenes with clouds - set it to maximum and gradually lower it until details are visible instead of white spots.
On many LCD monitors, the contrast level is set to 80 - 90%. It’s better to reduce it to 65% and dance from this mark. In the case of plasma TV, it is recommended to set lower values to avoid panel burnout.
Adjusting the contrast on your TV.
TV cuts off laptop desktop when connected via HDMI
What is described in the other answers apparently also happens, but in my case it turned out to be different, because the video card was just producing the correct signal. There is a switch somewhere in the TV settings related to image size, I don’t remember now. Kick the TV!
Try installing the latest drivers for your video card. I think you will find them on the manufacturer's official website. Helped me...
well, yes, in the card driver you need to find the dimensions and position of the screen (something like this), you can also try setting the resolution to 1680*1050 - it helps me personally, although I have a computer
Right-click on the screen, graphics parameters, there is a panel device and already there - zoom to full screen.
HDMI cables have their own versions - 1.0 1.1, etc. You need to try a cable with a newer version.
In the TV settings, you need to set the “scale” in the screen format
Right-click on the desktop -> Picture/Graphics Settings -> Display -> Display 2.1 -> Move the slider all the way to the right.
Who has intel hd graphics do the following: right mouse button on the desktop>graphics characteristics>display>where it says select display (upper left corner) select your TV>then in the bottom center button select aspect ratio and on the right is the image. there you play with the sliders vertically and horizontally until there is a normal image on the TV
On TV, turn on PC Mode and you will be happy)
in Panasonic this is “additional settings” “overscan mode”
Upscaling tries to achieve optical resolution, too
So, nearest neighbor interpolation is incorrect. This is a brute force method for increasing image resolution and does not take into account optical resolution. This is why TVs use two other forms of interpolation along with nearest neighbor interpolation. They are called bicubic (smoothing) interpolation and bilinear (sharp) interpolation.
Left: example of bilinear interpolation. Right: An example of bicubic interpolation. Dean Drobot/Shutterstock
With bicubic (smoothing) interpolation, each pixel added to an image refers to its 16 neighboring pixels to produce a color. This results in an image that is distinctly “soft.” On the other hand, bilinear (sharpening) interpolation looks at only the two nearest neighbors and produces a "sharp" image. By combining these techniques and applying some filters for contrast and color, your TV can produce images without any noticeable loss in optical quality.
Of course, interpolation is still a guessing game. Even with proper interpolation, some videos may increase ghosting after upscaling, especially if your cheap TV sucks at upscaling. These artifacts also become more noticeable when ultra-low quality images (720p and below) are upscaled to 4K resolution, or when images are upscaled on insanely large, low-pixel-density TVs.
Nerd's Passion
The above image is not an example of scaling from a TV. Instead, this is an example of an upscaling done for the HD DVD release of Buffy The Vampire Slayer (taken from the Passion of The Nerd video essay). This is a good (albeit extreme) example of how bad interpolation can ruin an image. No, Nicholas Brendon doesn't wear vampire wax, that's exactly what happened to his face during the scaling process.
While all TVs offer upscaling, some may have better upscaling algorithms than others, resulting in a better picture.
Where to place the TV?
Installing the TV in a suitable place, and not at the first available point near an outlet, is the simplest thing that will help you achieve the best quality.
First of all, try to provide as many spectator seats as possible directly in front of the screen. When viewed at an angle, colored and black objects become faded - this is especially true for LCD TVs. For OLED models, the problem is less acute, since the image does not noticeably lose quality when viewed at an angle - but we still prefer to sit directly in front of the screen so that the entire picture is in the palm of our hand. If the dimensions or shape of the room do not allow this, a TV with a swivel stand will help.
Viewing angle and distance
The screen should be located at eye level of the seated viewers, so take care of a high-quality stand of the required height, on which you can place other necessary devices - a set-top box, Blu-ray player or sound bar.
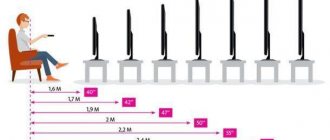
There is no specific recommendation regarding viewing distance - it depends on both the screen size and the resolution of the TV.
On average, for Full-HD models it is worth choosing a place at a distance of 1.5 to 2.5 screen diagonals, and for 4K TVs - from 1 to 1.5 diagonals.
The distance recommendations are based on the fact that the larger the screen size, the larger each pixel is - and if you sit too close, you're more likely to see them separately (as well as any image artifacts).
However, in the case of 4K screens, the increased resolution results in smaller pixel sizes, so you can sit closer to the screen (almost one and a half times the distance from a Full HD TV) and not notice them.
Ultimately, the choice of distance is determined by your personal preferences and room parameters.
Adjusting Contrast
Contrast, in other words, white level, determines how white the brightest parts of the image will be. The goal is a bright picture with individual details clearly visible.
A good way to test contrast is with scenes with clouds; set it to maximum and lower the level until you start to see details instead of just white spots.
Many LCD screens have a fairly high contrast ratio - up to 80-90%. Start with 65% and change it to your liking; but if you have a plasma TV, choose lower settings to avoid panel burn-in.
The same rule applies to OLED models, despite the fact that they are inferior in absolute brightness to LCD TVs. You need to make the bright areas of the image energetic enough that they contrast sharply with the pitch blacks without losing any fine detail.
Changing the picture format on a TV set-top box
If the TV is powered by a set-top box, it is possible to change the picture parameters using its functions. Usually you need to open the menu, go to the “Settings” section, where select the “Display” tab. In this menu you can change the following parameters:
- image resolution (screen resolution);
- picture position (screen position);
- screen rotation;
- switching HDR mode.
The list of options may also vary depending on the model and manufacturer of the set-top box. Some series of set-top boxes do not allow you to customize frame parameters at all, using only the parameters specified in the TV itself.
TV
The image is stretched - what to do
When the TV stretches the image, watching your favorite programs is not only difficult, but also dangerous. When the frame is completely distorted, it is more difficult for the brain to process information, and the eyes can be damaged due to color and light aberrations. Therefore, you cannot delay repairs.
You can try to repair a stretched screen and improve the picture using the following settings:
- To check the incoming signals from your devices, try switching from one broadcast source to another. From television to player, flash drive and back.
- If the hidden services Closed Caption - CC or Extended Data Services - XDS are enabled in the settings, they can cause specific distortion of the picture. To level it, you need to turn off one or the other option.
- On some channels (sports, music), programs are broadcast with a news ticker or advertising banners on any part of the display. This may distort the picture; in such cases, adjustment is useless.
- Widescreen modern panels have a 16:9 aspect ratio. The fractional number shows the ratio between the sides of the monitor. If black bars appear at the top and bottom, and the screen is not 100% filled with the picture, it means that the movie or program was recorded in 21:9 format. If on the sides - 4:3.
Can't adjust the screen? Most likely, it is impossible to combine the format of the received signal coming from an external digital or satellite TV receiver with the parameters of a specific model.
Important: by adjusting, you can straighten a stretched image on a TV if the screen has the appropriate dimensions and the equipment responds to the control input.
What is the optimal and best screen resolution for watching LCD TV?
Save the article for yourself or share it on your favorite social networks:
What is the optimal and best screen resolution for watching LCD TV?
How to choose the right screen resolution and which is better? Some people believe that buying a large TV in a store means turning their apartment into a real cinema, with all its advantages. But by paying a huge price for a 50-inch one, such as the Panasonic TX-P 50 G 10, we do not take into account the fact that the dimensions must be commensurate with the size of the room in which they are installed.
Agree, a giant one will look ridiculous if it props up the walls of a room whose area does not exceed 10 square meters. The opposite statement is also true. If you buy a 32-inch Sony KDL-32 V 5500 and place it in an area of 30 square meters, you can lose not only the remote control, but also the TV itself! Yes, in modern stores there really is a lot to choose from. But when buying a TV, you need to be guided by certain selection rules, which we are going to tell you about.
Size
Modern LCD TVs are usually produced in 16:9 format, and their diagonal dimensions are indicated not in centimeters, but in inches (an inch is equal to approximately 2.5 centimeters). If it is to be installed in a standard living room, then its dimensions should be at least 32 inches. More is possible! You can choose from plasma TVs from 32 to 52 inches or more. You get used to the big screen quickly. However, 32 inches is perhaps the most optimal figure for watching programs. If you want to enjoy watching high-quality Blu-ray video, then choose something with a diagonal of 42 inches or more.
Viewing distance
Large TVs for small rooms are not recommended, not only because they will look ridiculous, but also because they are simply uncomfortable to watch. Although here everything will depend on the image quality. Remember the basic rule. The viewing distance should be twice the width of the screen. And that's the minimum! That is, if you bought a 50-inch TV, then you should sit at a distance of 2.5 meters from it. This is about watching high quality videos. This distance will be optimal in order not to see frame defects when viewing. If we are talking about watching regular movies or programs, you will have to sit even further.
What does expansion mean on TV?
It's no secret that the price of an LCD TV depends not only on the diagonal, but also on the resolution of the TV screen. The high and maximum resolution of the TV allows you to create a clearer image. The “HD Ready” standard, which appeared back in 2005, allows you to obtain a resolution of 720 lines with a 16:9 ratio. On many modern LCD TVs you can see the corresponding logo. They are designed for viewing HD images. Interestingly, the HD Ready format was announced ahead of the 2006 FIFA World Cup.
However, HD Ready 720p is a thing of the past. Modern screens are increasingly equipped with “Full HD” logos, which means “HD Ready 1080p”. Such models are capable of generating an image with a resolution of 1920*1080 pixels in 1080 lines. Only on them you can enjoy HDTV video. Blu-ray, documentaries, modern blockbusters, and many DVDs - all of this looks much better if the TV is labeled Full HD. The most popular resolutions at this time are 1366x768, 3840x2160, 1920x1080, 1366x768, 2560x1600.
Full HD or HD Ready?
As you can imagine, Full HD has many advantages over HD Ready. The only drawback is their high price. However, the quality of watching videos and TV programs negates all regrets about spending money.
Useful information about modern TV:
Advantages of LED TVs
What is it like, a good LCD screen?
- Do-it-yourself repair of a household mixer, features of engine operation.
- Washing and drying machine for clothes, instructions for use.
- What types of air purifier filters exist and their purpose.
- Air purifiers from A to Z, what to choose for your home?
- Review of baby monitor models from Philips Avent (Philips Avent), reviews from manufacturers.
- Self-repair of juicer, spare parts and attachments for meat grinder.
- The best air purifiers for those with allergies to hair, pollen and dust.
- Which juicer is better to buy for home and garden, consumer reviews.
- The principle of operation of the juicer, instructions for use, how to use.
- What's new in Samsung TVs, technologies, prices for models.
domisad.org
Why do streaks appear or the image become distorted?
If the image size is smaller than the TV screen, black bars may appear on the screen.
If the image size is wider than the TV screen, the aspect ratio on the screen may change and the image may be distorted.
To adjust the image size on the TV there is a “Picture Size” function.
Differences in settings on TVs from different manufacturers
The names of menu items may differ on TVs of different brands. There may also be differences in different TV series from the same manufacturer. Sometimes certain options may be missing. Therefore, it is recommended that you first refer to the instructions from the manufacturer. For example, Sony models often have significantly more settings compared to TVs from Samsung and Philips.
Image perception depends on ambient light
One of the features of LCD screens is that the image quality depends on the lighting in the room. Because LCD displays are backlit and act like a flashlight in a dark room. For example, black clothing visible on the screen in normal lighting may appear gray in a dark environment. Manufacturers are aware of this and are trying in every possible way to eliminate this defect using filters and backlighting. Plasma and OLED displays are based on self-emitting diodes and do not have such distortion. Their image even improves in dark environments, which is why they are appreciated by fans of the cinema atmosphere. But still, LED and LCD displays should not be completely discounted. To achieve high-quality viewing, place a lighting fixture behind the TV. Some manufacturers even meet customers halfway in this matter. For example, Philips, with its Ambilight feature, has built backlighting into the TV to mitigate the negative effect.
Connecting your TV to the Internet
Online video streaming services are becoming increasingly popular with a huge catalog of TV shows and movies in different formats, including 4K, available on Netflix and Amazon Prime Video. To access all these treasures, you need to connect your TV to your home network. Time-lapse services such as BBC iPlayer and many other smart applications found on modern TVs also require an Internet connection.
Most often, this can be done in the “Network” section of the settings menu. Despite the convenience of connecting using Wi-Fi (especially if the TV is located far from the router), we traditionally recommend a more stable and reliable Ethernet connection.
This will be especially true for those who frequently watch streaming or broadcast content in 4K format - they will not have to deal with interruptions or stops in the signal.
How to resize a picture
First method (for any remote control)
Enter the TV menu.
How to enter the menu
On the keypad, press the “MENU” button.
On an R, M, N, Q, LS, K-series TV, press the “HOME” button, scroll left and select “Settings” on the TV screen.
On the J-series smart remote control, press the “MENU/123” button and select “Menu” on the TV screen.
On the H-series smart TV remote control, press the “KEYPAD” button and select “Menu” on the TV screen.
On the F-Series TV smart remote, press the “MORE” button and select “Menu” on the TV screen.
Select "Image".
Select "Picture Size".
Select “Picture Size” again.
Select the appropriate size from the list.
Second method (for a push-button remote control)
Press the "P.Size" button until you find the appropriate picture size.
Upscaling reduces optical resolution
There are several ways to interpolate an image. The most basic is called “nearest neighbor” interpolation. To perform this process, the algorithm adds a grid of "blank" pixels to the image and then guesses what color value each blank pixel should have by looking at its four neighboring pixels.
For example, a blank pixel surrounded by white pixels will become white; whereas a blank pixel surrounded by white and blue pixels may turn out light blue. It's a simple process, but it leaves a lot of digital artifacts, blur, and sharp edges in the image. In other words, interpolated images have poor optical resolution.
Left: Unedited image. Right: After nearest neighbor interpolation. Dean Drobot/Shutterstock
Compare these two images. The one on the left is not editable, and the other on the right is a victim of the nearest neighbor interpolation process. The image on the right looks terrible, even though it has the same physical resolution as the one on the left. This happens on a small scale whenever your 4K TV uses nearest neighbor interpolation to upscale the image.
“Wait a minute,” you say. "My new 4K TV doesn't look like this!" Well, that's because it doesn't rely entirely on nearest neighbor interpolation—it uses a combination of techniques to scale images.