Digital television is gaining popularity today and is eventually replacing analogue broadcasting. Thanks to it, it became possible to transmit volumetric information and images in higher resolution. Today there are several broadcast formats of the DVB standard, but the most common is T2 broadcasting; it provides the user with free high-quality television. The article will discuss what the DVB-T2 standard is and what are its differences from other digital broadcast formats.
Possibilities
Digital technology is the compression of a multimedia file into binary code, which requires much less information space. Digital came to television from computer technology and was successfully introduced.
This approach opened up two possibilities for television:
- Broadcast video content in high definition (HD, Full-HD, 3D and 4K);
- Transmit less information for broadcast;
- Use less energy-intensive technical means with low throughput.
The received digital signal also needs to be decrypted, for which previously only receivers were produced, but now a TV tuner (decoder) built into the TV is used.
Broadcast standards and their differences
Digital TV has made it possible to reduce and simplify the required infrastructure for distributing television to users.
This made it possible to deploy modern television in several digital formats at once:
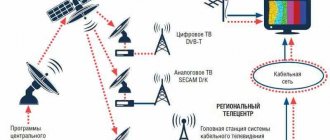
- Satellite TV (DVB-S). Initially, it was this that received great development of digital broadcasting. Satellite television had receivers, and analogue channels were broadcast in the decimeter range (1 - 3 GHz). Consequently, it is enough for a television company to launch a new broadcast format on the same frequency, and the user only needs to connect a cheap decoder to the receiver.
- Cable TV (DVB-C). It uses wired signal streaming technology. Wired data transmission has higher bandwidth and minimizes the risk of data loss, which allows you to broadcast a large volume of programs. Today, Russian operators offer a selection of paid viewing tariffs, which include from several dozen to more than 100 channels. Cable television can be considered the most advanced and reliable broadcast format in terms of providing content.
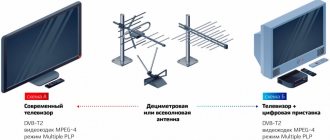
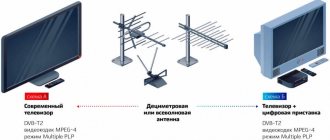
- Terrestrial TV (DVB-T). Works via analogue television technology. Signal transmission is carried out wirelessly using repeaters (terrestrial stationary towers). For reception you need a decimeter (UHF) or all-wave antenna. Terrestrial digital TV is the only broadcast format that is fully provided free of charge.
Each of the broadcast formats (DVB-S/C/T) provides an excellent option for compressing the image into a digital signal and requires a separate decoder to decode each of them.
Features of DVB-S2 and DVB-T2
The built-in digital satellite TV tuner has certain features. In order to watch freely available TV channels, it will not be enough for you to simply connect the satellite dish to the TV directly. You will also need to additionally purchase a CAM module.
The fact is that without it you will not be able to view encrypted channels, but only those that are fully open. This is due to the fact that the companies producing such TVs do not think much about this. In addition, it will be impossible to change the firmware or enter the code. External satellite tuners sold by us have firmware that already contains all the necessary codes.
That is why you will need to additionally purchase a CAM module, which must be inserted into the PCMCIA connector. After this, you will need to start searching for channels on the satellites specified by the provider and wait until the TV finds them. After this, you will be able to watch all closed and paid channels that the CAM module will open for you. This is very convenient, since you do not need to buy and connect an additional receiver, and you only need one remote control to change channels.
To connect over-the-air digital channels, you do not need to buy anything additional. Simply connect the antenna to the TV and configure DTV T2. Moreover, you can configure channels either manually or by selecting “Auto search” in the settings menu.
New TV broadcasting format
With the introduction of digital television, satellite TV experienced rapid development. Hundreds of channels began broadcasting. This led to the fact that it was more difficult for television companies to obtain a free frequency for broadcasting, and the user required more and more physical channels. As a result, the problem was solved by streaming, which opened up the possibility of delivering multiple channels on a single frequency and a single physical channel. This is how a new satellite broadcasting format appeared - DVB-S2.
Subsequently, streaming information transfer moved to broadcasting, and television began to be delivered in multiplexes - channel packages. This led to the opening of broadcasting in the DVB-T2 format. However, users do not have a great need for it, and today there are only dozens of on-air digital programs. For this reason, broadcasting in the DVB-T standard is actively maintained in many European and other countries.
In Russia, on the contrary, the spread of the T2 format began, and the development of DVB-T broadcasting was stopped.
In addition to streaming, the characteristics of the T2 standard have improved - this format has made it possible to speed up modulation, which is responsible for the speed of decoding. Overall, it accelerated 4 times from 64 to 256 QAM. The decoding process itself is almost instantaneous, and the delay does not affect the delivery of the finished image, which contributed to the inclusion of more than 4 programs on one physical channel.
For example, in Russia, one multiplex delivers 10 programs and 3 radio channels; in some countries, a digital package can include up to 13 channels.
Specifications
What is the difference between DVB-T2 and DVB-T digital television formats? Let's look at the emerging advantages of the second version:
- Why did DVB- T2 appear? If we do not take into account the support for a number of additional functions, which largely depend on the capabilities of a particular provider or channel, the new standard was required due to increased requirements for content compression. Even the first generation of DVB took up too much “space” in the stream and forced television producers to use additional frequencies to transmit the signal. With the DVB-T2 standard, the situation has changed: more content can be accommodated, signal quality is better, and costs are noticeably lower.
- Difference between DVB- T2 and DVB- T . Before comparing, it is important to determine compatibility - despite the similar basis from the release, they are not interchangeable and cannot be combined in any way. The rest of the difference is expressed in the modified encoding of audio and video data (MPEG-4 is used instead of MPEG-2) and the ability to transmit several types of data in a digital stream at once: subtitles, radio and video signals.
- Additional potential . The DVB-T2 standard supports teletext (some channels broadcast news or weather forecasts using pop-up messages, and at the same time run subtitles over video content). At the same time, it authorizes the television program schedule. “Electronic” is much more detailed than its “newspaper” counterpart - many providers talk about the plot, list the actors and even display in real time how much time is left before the start.
- Dry residue . To summarize, DVB-T2 support opens up only advantages for viewers: lightning-fast data transfer speed, the ability to “mix” third-party information into the signal, such as teletext and subtitles, changing priorities, codecs and quality (480p is no longer the limit). Additionally, there is protection against annoying interference and constantly missing access to some channels. Football broadcasts, TV series and films will no longer be interrupted in the wrong place.
Necessary equipment
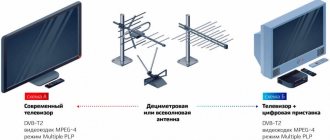
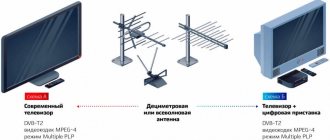
To organize and use terrestrial digital television, the user requires the following equipment:
- Receiving device. Terrestrial antenna of the decimeter wave range (UHF) for receiving a signal from a repeater.
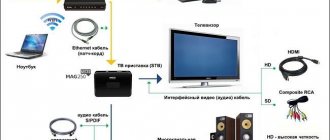
- Decoder. A device for decoding a digital signal into a familiar form. Modern TVs have a built-in decoder (TV tuner). If it is not available, connect a digital set-top box with the function of decoding the DVB-T2 TV signal.
- TV. The finished image is displayed on it. If you use a Smart receiver with a monitor, you can watch digital TV on it.
The best digital TV set-top boxes DVB-T2
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the rating of the five best digital set-top boxes (receivers), which are recommended to be chosen for viewing DVB-T2:
- Oriel 963 DVB T2. The receiver is designed to operate 20 digital channels. This model is perfect for those who are accustomed to comfort and do not like to understand the settings. Although it belongs to ordinary digital set-top boxes, it has a channel search principle comparable to that of Smart receivers. Supports digital decoding in DVB-T/T format. Features a highly durable aluminum housing. The cost of the receiver starts from 1,150 rubles.
- Selenga T40. Simple and compact decoder. It cannot be called a full-fledged receiver, however, it is the cheapest option for decoding DVB-T2. It does not have a dashboard or USB inputs, and the device is controlled only using the remote control. This set-top box can be purchased for 650 rubles.
- BBK SMP240HDT2. A standard receiver that includes 20 physical channels for receiving digital and analog TV. It does not stand out with a unique feature or additional capabilities. This model is recommended by users for its favorable price/quality ratio. The receiver is offered on the domestic market from 850 rubles.
- Harper HDT2 1005. Another inexpensive and simple receiver. Unlike the previous model, it has a USB input. However, a limited number of video codecs are supported and you can connect an external drive to the receiver only for watching movies. There is also inconvenience of control due to the small buttons on the remote control. You can buy this model for 950 rubles.
- Iconbit movie T2. Combo receiver with support for DVB-T2 and interactive television. Includes built-in services and devices for searching working IP addresses and synchronizing the device with a remote server. There is a USB input for connecting an external drive. There is no downloading of codecs, but the receiver already accepts a large number of multimedia files. The developer supports frequent software updates. The cost starts from 1550 rubles.
How to connect and configure a digital receiver
To begin with, before setting up, you should connect the DVB-T2 set-top box to the TV. The diagram is presented below.
Setting up the receiver requires minimal effort. The main thing you need to do is set up the channels. Go to the channel search menu and select auto search. Don't forget to set the country correctly. After a few minutes, the set-top box will find a certain number of channels. In the next menu item “Video” we set the necessary settings (mostly those that are set by default are suitable). In the “Time” item we set the region and time zone. Next, set the language for the menu, subtitles and audio. In the “System” tab you can set parental controls and a password. You can also choose to return to factory settings, update the software, or read information about the set-top box. In the “USB” item you can select the playable format (music, photo, video) and configure PVR.
It is worth noting that each digital media receiver has its own configuration features; above is a general overview.