When choosing a TV receiver, the user has to compare a huge number of characteristics. Information technologies are pushing modern technology to the forefront. The refresh rate of the TV screen is one of the main selection parameters. How image quality and its impact on human health depend on it, you will learn from our article.
What is TV refresh rate
Any marketing student will tell you that one of the secrets of marketing is this: “If you can't convince your audience, confuse them.”
Now this is what most TV manufacturers do when they advertise the refresh rate on their TVs.
The higher the TV's refresh rate, the better?
Technically this statement is true, right? 120Hz is better than 60Hz, 240Hz is better than 120Hz, and so on.
The refresh rate determines the number of times per second that the image is updated on the screen.
So if the refresh rate is 60Hz, the image is refreshed 60 times per second, etc.
So the logic is that the higher the refresh rate, the better.
Before we continue our discussion on refresh rate, let's understand the difference between refresh rate and video frame rate.
Other parameters for high-quality pictures
In addition to the refresh rate, there are other necessary parameters for a high-quality image that need to be taken into account when choosing a modern LCD TV.
Optimal resolution
The first thing you need to pay attention to is the resolution of the TV. The image on the display consists of small dots - pixels. Monitor resolution is the number of horizontal and vertical pixels. Modern television panels have resolutions of HD (1366x768), Full HD (1920x1080) and Ultra HD or 4K (3840x2160). When choosing a TV resolution, you need to consider the signal source and image quality. If a television receiver is purchased to watch digital terrestrial or cable television, then the picture will not be of the best quality.
HD resolution is sufficient for such content, but since it is considered outdated and is gradually fading into the background, it is better to overpay a small amount and purchase a Full HD TV receiver. In addition, you need to choose a diagonal of no more than 42 inches, otherwise the image will be very bad.
A television receiver with a resolution of 1920x1080 is suitable for satellite television or other high-quality signal, for example, for watching movies from USB drives or via the Internet. The screen diagonal can be any. Today a new standard is gaining popularity - Ultra HD. Even though there's not a lot of relevant content out there right now, it's worth buying a TV with a display that's capable of staying up-to-date even in a few years when 4K becomes widespread. Today, on such TVs you can watch Blu-Ray movies through an appropriate player connected to the TV receiver using an HDMI cable.
Matrix type
There are several types of TVs on the market today:
- LCD TV with CCFL backlight (fluorescent lamps) - budget models;
- LCD TVs with LED backlighting (light emitting diodes) are modern devices characterized by increased contrast and better images;
- OLED (Organic Light-emitting Diode) – TVs based on organic crystals. They do not require a separate backlight; these TVs provide high quality color reproduction and incredible depth of black.
Until recently, plasma TVs were popular on the market, but today this technology is not in demand due to its high cost and many disadvantages. In addition to the type of TV, image quality also depends on which of the three types of matrices is used in their manufacture - TN, IPS and VA.
TN matrices are installed on budget television receivers; they have low color rendering and a poor viewing angle. IPS matrices have a good color gamut, good contrast and a wide viewing angle.
At the same time, they are very expensive. VA is an intermediate link between TN and IPS. They have slightly worse color rendition and viewing angle than IPS matrices, but they have much better contrast and lower cost.
Flat screen or curved
Most modern television panels are equipped with a flat screen. Expensive TV models from manufacturers such as Samsung, Haier, LG, etc. have curved displays.
Watching movies on it is exciting because... the image turns out three-dimensional and realistic, but there is a drawback - the picture is distorted when viewed from the side. Therefore, you can only buy such a TV receiver if it is installed opposite the viewing location.
Smart TV or regular
When choosing a TV, you should decide for what purpose it is being purchased. A regular TV receiver is suitable for watching television channels. If you want to have a real entertainment center in your home, then you should choose Smart TV. It will allow you to watch movies and TV series via the Internet, watch the weather and news, communicate on social networks, etc.
Conclusion When choosing a television panel, first of all you need to take into account the TV refresh rate index, the type of TV receiver and the type of matrix, resolution.
A curved display is worth buying only if the chair or sofa will be located opposite the screen, and the presence of the Smart TV function is only relevant if the television receiver is purchased not only for watching TV programs, but also for actively using the Internet. The latter characteristic does not affect the image quality.
What affects the refresh rate of a TV screen?
Let's go back a little and understand how a video is made. Videos capture live action by taking multiple still images, or what we call frames.
As these shots come closer together, we see continuity in movement. Typically, analog video frame rates are based on the frequency of the local electrical supply.
Therefore, the frame rate should be different in the US compared to Europe.
Have you ever noticed the words PAL/NTSC on earlier VCRs and VCPs?
- PAL regions included the UK and large parts of Europe, where the frame rate was 25 fps.
- NTSC regions include the US, where the frame rate is 30 frames per second.
- Film content is recorded at 24 frames per second.
Analog video interweaving is usually done to save bandwidth during transmission. Which involves splitting one frame into two fields containing an even number of lines and an odd number of lines. When displaying content, the TV screen will do so in the correct order.
Thus, the interlaced video frequency in PAL regions was 50 Hz, and in NTSC regions it was 60 Hz.
TVs in the PAL and NTSC regions had refresh rates of 50Hz and 60Hz, respectively.
Although these frame rates were developed for analogue televisions, they are well suited for digital broadcast systems, DVB in Europe and in the USA.
Modern video broadcasts support several additional frame rates, such as:
- 24p-24 progressive frames per second
- 25p-25 progressive frames per second
- 30p-30 progressive frames per second
- 50i-25 interlaced fps
- 60i-30 interlaced fps
- 50p-50 progressive frames per second
- 60p-60 progressive frames per second
The higher the frame rate of the video, the smoother the movement will be.
So we conclude that fps determines how smooth images appear on a TV, not the TV's refresh rate.
Read: What is Dolby Vision technology on TV?
Thus, it is established that the TV displays what was originally captured on video.
We believe this clears up the concept that the standard refresh rate for a TV is either 50Hz or 60Hz.
If this is true, then why do we see TV manufacturers advertising refresh rates of up to 120Hz, 240Hz, 480Hz and so on?
Let's now clarify one aspect. The maximum refresh rate for flat screen TVs today is 120 Hz.
So every TV you buy will have a refresh rate of 120Hz, 60Hz, or 50Hz if you go with the older standard.
According to European standards, it should be 100Hz or 50Hz. These TVs can support 120Hz/60Hz respectively.
Therefore, we can say that the 240Hz and 480Hz that TV manufacturers mention is a marketing gimmick.
The higher the number, the better it looks, but in reality, it doesn't really matter at this time.
There's not a lot of 120Hz content these days anyway. Remember that television cannot in any way improve the quality of the source material.
Let's now compare the different refresh rates, starting with 60Hz and 120Hz.
Let's sum it up
Concluding the analysis of the parameter, we can highlight several key points:
- The pixel change rates of modern TV models range from 50 (60) to 200 (240) Hz. Large values are practically invisible to the eye. In certain cases, they render images worse than 200 Hz screens.
- The level of clarity and realism of the picture largely depends on the input signal. TVs with high screen refresh rates are not able to improve an image that was originally captured in poor quality.
- TVs with the maximum pixel refresh rate are necessary for viewing content in Ultra HD 4K, 3D, and for playing games on the big screen. A high indicator is needed for TVs with a diagonal larger than 24 inches.
- Screen refresh rates above 50Hz are not harmful to the eyes. The higher this value, the less strain your eyes experience when using the TV.
The refresh rate of the TV screen is an indicator on which the comfort of viewing the picture depends. However, you can’t limit yourself to just that. Screen size and resolution, brightness and contrast have a greater impact on the quality of the output image.
Which TV screen refresh rate is better: 60Hz or 120Hz?
We have seen that broadcast content is usually a maximum of 60 frames per second. Therefore, this content looks great on a TV with a 60Hz refresh rate.
If this image was to be displayed on a TV at 120Hz, each frame would need to be repeated twice (60fps x 2 = 120fps).
If you have 30p video content, the TV must repeat the content four times (30 fps x 4 = 120 fps).
Modern TVs can switch from a 120Hz refresh rate to 60Hz if the input video signal is 60fps. So it's more or less equal to a 60Hz TV.
Does this now mean that you shouldn't buy a TV with a 120Hz refresh rate? No, this is not the case because video content is now available at higher frame rates. Especially gaming.
Picture without jerks and artifacts
According to Panasonic Russia TV and audio product manager Alexander Kosyak, the company’s TVs use Intelligent Frame Creation technology - an intelligent system for creating additional frames. Its main task is to provide dynamic scenes with smooth, but clear transmission without jerks or artifacts. In older models of Panasonic TVs, the frequency reaches 1600 Hz. “For us, this is a technology that, in combination with other company know-how, allows us to obtain high-quality images. Anything above 100Hz can be considered high frame rate,” he says.
Comparison of still frames of video content having different frequencies
According to Dmitry Kurapov, head of product marketing for TV-Audio at Samsung Electronics in Russia, high frame rates are very important in games. The manufacturer's 2018 TVs with screens running at 120 fps, and all 2021 QLED TVs, can run games at resolutions up to 1440p at 120 fps. In 2018, Samsung TVs did not allow playback of 4K content at 120 fps, but in 2019 this became possible in the Q80, Q90 and Q900 series models.
Samsung has also provided support for FreeSync/VRR technologies in 2021 QLED TVs. The variable screen refresh rate (Variable Refresh Rate, VRR, - Tele-Sputnik's note) made it possible to achieve a minimum output latency of 6.8 ms. “Typically, the display shows an image at a constant refresh rate, such as 60 frames per second. But the graphics core in the PC running the game updates data at a different frame rate. This frequency is determined by how complex the game's graphics are, what scenes are drawn in the game, and the nature of the game's interactions. As a result, there may be some discrepancy between these refresh rates. Up to a situation where the display will reproduce a frame consisting of two halves of different frames from the GPU (graphics processor - Tele-Sputnik's note). At the same time, the effect of a torn image will appear on the screen,” explains Dmitry Kurapov. With the FreeSync/VRR technology used in Samsung's 2019 QLED TVs, such problems do not arise, since the TV's refresh rate matches the refresh rate of the GPU. According to him, FreeSync VRR technology is automatically enabled by default and allows you to work with extremely fast response times. Thanks to this, new TVs are almost as powerful as premium gaming monitors, but at the same time have a larger diagonal.
Benefits of TVs with a 120Hz refresh rate
Today, video content and games are available at 120 frames per second. This content should be exclusive to a 120Hz TV.
However, users should note an essential point here. HDMI input signals are usually fixed at 60Hz, as is the current limit of the HDMI 2.0 specification.
If your TV has an HDMI 2.1 connection, it should support 4K and 8K video at 120Hz.
We already covered earlier that films are shot at 24 frames per second. So this shouldn't be a problem for watching movies on a 120Hz TV. Repeating each frame five times should be enough.
Videos look smoother on a TV with a 120Hz refresh rate compared to 60Hz.
A 60Hz TV uses a 3:2 capture method to display movies. It is not possible to show the content of a movie shot at 24 frames per second directly on a TV with a 60Hz refresh rate.
There should be repetition of frames, but not in an even order. Therefore, a slow panning scene may appear jumpy.
Some of the latest TVs automatically adjust the refresh rate to 24Hz to overcome this problem.
Another advantage of 120Hz TVs is that they can add motion interpolation to a 60Hz video source.
Because the TV has a higher refresh rate, it can display additional interpolated frames.
A 60Hz TV cannot interpolate a 60Hz video source because the TV cannot display more than 60 frames per second.
Yes, such a TV can interpolate a video source with a lower frame rate. It is also known as the soap opera effect. We'll look at motion interpolation and the soap opera effect later in this article.
A 120Hz TV turns out to be handy when dealing with motion blur. Motion blur can occur when you encounter fast-moving scenes such as action movies and intense sports action.
Read: How and which TV is better to choose and buy: Everything you need to know
A higher refresh rate helps in handling this issue better. However, motion blur can occur due to various reasons, and the refresh rate cannot solve all of these problems. We'll discuss motion blur at a later stage.
A TV with a faster refresh rate can help combat other problems such as flickering.
Modern 4K TVs typically come with a 120Hz refresh rate. Some TV manufacturers are touting higher refresh rates. However, this is not always the case. Low-cost models come with a 60Hz refresh rate.
Reaming Process Technical Description
To understand what a refresh rate is and how frames are completed, you need to understand the types of LCD TVs and monitors that are on the market today.
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) was one of the first developments of LCD televisions. These days they are relatively cheap as many improved models and new technologies have emerged. Thus, LCD panels are inferior to LED in terms of comparative characteristics. Image formation is carried out using CCFL fluorescent illumination. Such devices do not have good picture clarity, but when scanning over 100Hz you can count on a complete absence of flicker.
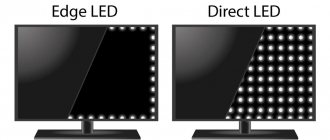
- LED (Light-emitting Diode) are improved LCD monitors, complemented by a new image illumination system using LED diodes. These monitors have higher contrast. Please note: the placement of diodes over the screen area may be different, which affects the quality of picture transmission. Models marked “Full LED”, “True LED”, “Direct LED” are of higher quality; in them, the diode backlight is distributed over the entire area of the screen, but the “Edge LED” marking means that the backlight is concentrated in the end parts. You can read more about these nuances in the article about LED technology. Such a TV will be much cheaper, but the image will be slightly worse.
- The Plasma Display Panel does not require additional illumination: plasma cells are illuminated due to the effect of ultraviolet rays on phosphors. Plasma provides higher contrast compared to the two types described above and deeper dark shades. The affordable cost of the panel is compensated by its fragility: after 3–4 years the panel fades somewhat and the image quality noticeably decreases. The list of shortcomings is complemented by significant energy consumption and frequent failures when detecting removable modules. Such a TV may not see a hard drive or flash drive, headset or similar connected devices.
- OLED (Organic Light-emitting Diode) in the modern world is the pinnacle of technical television progress. These were the first curved TVs in 2015, but the extravagant design was not in great demand, and after that the usual flat OLED devices appeared. Manufacturers have achieved high picture quality without any additional backlighting. The advantages of this technology compared to LED are obvious.
Now about the display refresh rate technology itself. The television series provided via non-switched communication channels produces 50 frames per second. Digital video processing made it possible to copy each frame and show it twice, and the 100Hz scan was born. The technology made it possible to eliminate the most uncomfortable image defect – flicker.
Further developments borrowed technologies from computer animation, when the technique takes two frames as a basis and creates everything in between intelligently, creating smooth and clear movement. Unlike a computer, a TV does not have the concept of a “future frame,” but this turned out to be enough. Additional frames are drawn based on the analysis of previous ones, which ensures high accuracy and smoothness of images. Objects moving at high speed are clear and not blurred.
Advantages of TVs with maximum screen refresh rates of 240 Hz and 480 Hz
A TV with a 240Hz or 480Hz refresh rate sounds very impressive, but the actual refresh rates available today are 60Hz and 120Hz.
These are the native refresh rates. TVs available today cannot upgrade more than these units.
Thus, we can conclude that the higher figures advertised by TV manufacturers are inflated.
TV manufacturers have their own individual names for the processing technology they use to increase the refresh rate.
Screen resolution
The refresh rate index on a TV is an important, but the only parameter for obtaining a high-quality image. In addition to the scan, you should also pay attention to the screen resolution, which is measured in pixels.
High resolution technology started at 720 pixels. Today, this parameter has increased significantly. 4K technology supports 120 Hz scanning and transmits significantly more colors than its predecessor, FHD. In 2021, most films are shot in FHD or 1080 pixels. The industry has not yet developed for 4K, although it is the future.
Advice! If you plan to use the TV to watch TV shows, then you should focus only on the incoming cable signal. Replacing a TV with a model that supports 4K will entail updating all the peripherals: cables, adapters, high-speed router, etc.
TCL TV refresh rate
Almost all TCL TVs have a 60Hz refresh rate, except for their most expensive model, which comes with a 120Hz refresh rate.
TV manufacturers use these names to confuse people, especially those who don't understand the concept of refresh rate.
They claim that the update rate is higher than the actual figure.
For example, Samsung advertises a motion speed of 120 for a 4K TV. However, these TVs have a native refresh rate of 60Hz. Likewise, a TV with a motion speed of 240 is actually a TV with a refresh rate of 120 Hz.
TV manufacturers are using innovative techniques to make footage look smoother than it already is.
Apart from using these fancy names, they also use techniques like motion interpolation, black frame insertion, etc. to enhance the image quality. You should be aware of these factors before purchasing a TV.
The most current offers today
The most powerful TV models today can support a scan frequency of 600-800 Hz. The Sub-Field Driving feature helps achieve this frame update rate.
However, many users are very skeptical about the described capabilities of modern brands. And this is not due to technical problems at all, but to marketing. When the first televisions with LCD screens entered the market, marketers, in order to achieve high sales, began to massively attribute non-existent characteristics to such televisions. With each new generation, expectations increased, but quality improved at a slower pace. This problem has now been resolved. All manufacturers assure that the parameters of their equipment fully comply with the characteristics described in the attached passport. And so that the quality does not deteriorate over time, it is necessary to purchase only that additional equipment that is permitted in the instructions.
What affects the picture quality on TVs?
Motion interpolation
Interpolation, the name suggests that you are adding frames to the video source before displaying the images.
So it concludes that you are adding frames that don't exist at the time of the original recording.
The technique involves creating additional frames by guessing the movement between two frames. It's like taking two frames and creating an in-between frame to enhance the effect of movement.
Read: OLED vs QLED, compare technologies and choose the best TV
When this is done effectively, it can make the movement look smoother. Motion interpolation works great for fast-moving sports and action scenes.
However, it can sometimes create an unnatural image, primarily if you use this technique with films. This effect is also known as the soap opera effect.
Motion interpolation can be useful for watching TV, but it can make gaming difficult because it introduces lag. Images may stutter and look awkward at times.
Black frame insert
TV manufacturers use other techniques to improve motion, such as inserting a black frame and scanning the backlight.
The trick is to turn the screen black between each video frame, thereby tricking the eye into seeing smoother motion.
Read: What is NanoCell technology? And which is better OLED and QLED
This method works because of a phenomenon called motion blur. TV pixels, especially LCD displays, don't switch colors quickly enough.
Thus, the color remains for a fraction of a second longer than it should, thereby causing blurred images, especially in fast-moving action scenes.
One way to solve this problem is to insert a black border between two consecutive frames to make the color transition sharper and cleaner.
Other factors affecting the image
The parameters described above are responsible for color rendering capabilities and blur when the picture moves on the screen. But there are indicators that have no less impact on the quality of playback. It’s better to say that all these parameters taken together give an overall picture of the visual perception of the image .
- Contrast. This indicator may be indicated in technical documentation as 1000:1. It indicates the ratio in which dark tones differ from light ones.
- Brightness. Adjusting this parameter affects the color saturation. The recommended value is 300 cd/kV.
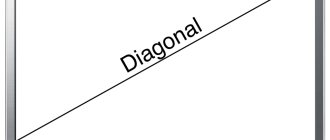
- Diagonal. This indicator refers to the screen (and not to the TV) and depends on the area of the room in which the TV will be placed. This is due to certain standards for the distance of video equipment from the viewer.
- Viewing angle. It should be noted that only plasma panel manufacturers correctly indicate this parameter. Its value corresponds to 170-180°.
- Connectors. The best option would be at least two HDMI and definitely USB. But it is better that television equipment has all possible types of inputs.
- 3D. The three-dimensional option allows you to see a three-dimensional image, but with special 3D glasses. It has not yet become widespread, and only some models have the technical ability to reproduce in this resolution.
Important! According to experts, the pmi indicator is nothing more than a marketing ploy and can only be taken into account when purchasing an LG TV. The manufacturer claims that the higher this parameter, the brighter the display of dynamic scenes.
What is motion blur on TV?
TV motion blur is a significant aspect that can affect your TV viewing experience.
Many people are confused between refresh rate and motion blur because they assume that a higher refresh rate eliminates motion blur.
In fact, motion blur has nothing to do with refresh rate.
Motion blur occurs whenever there is fast movement on the screen, especially in sports content. Images may appear blurry.
What are the advantages of 100Hz, 200Hz and 60fps
Frame rate , frame frequency (eng. Frames per Second (FPS), Frame rate , Frame frequency ) - the number of frames changed per unit of time in computer games, television and cinema. The concept was first used by photographer Eadweard Muybridge , who carried out experiments on chronophotographic photography of moving objects with several cameras in succession. The generally accepted unit of measurement is frames per second .
Frame scan is the vertical component of television scan, used to decompose the image into elements and its subsequent reproduction. Reaming can be mechanical or electronic. In a narrower sense, frame scanning is a part of the electronic circuit of a transmitting camera, television receiver or computer monitor that decomposes the image or reproduces it in the vertical direction. Most often, this concept is used in relation to devices that use a cathode ray tube to generate a sequence of frames of a television image at a given frequency. However, the concept of frame scanning also applies to devices with semiconductor matrices and screens. Expressed in Hertz (Hz, Hz).
Never confuse these two concepts because... these are slightly different things. So that you can understand the difference even more clearly, here is a simplification: You will be able to watch a video file with a frame rate of 60fps and on a screen with a scan rate of 50Hz.
To better understand the differences between Frame Frequency and Frame Scan, let’s dive into history. Once upon a time, when television was analog and TV screens were small, the image signal was transmitted through air or wires. And an effective and simple way was invented to reduce the cost of its transmission.
Interlace scanning is a television scanning method in which each frame is divided into two half-frames (or fields), made up of lines selected one after another. In the first field, odd lines are expanded and reproduced, in the second - even lines located in the spaces between the lines of the first field.
Therefore, Frame Scan (or, more accurately, reflects the essence of “screen flicker frequency”) is how many such frames or half-frames your screen can display per second. But this was a long time ago and is relevant only for outdated types of CRT screens and, with some tension, for plasma screens.
In the modern world, liquid crystal screens dominate, so they come closest to the frame rate: the refresh rate of an LCD screen is the frequency at which signals about changes in pixel color are sent to the monitor matrix. To simplify again: a video file with a frame rate of 60fps on a 50Hz screen will be shown with losses. Or the opposite example: modern video cards are capable of producing images up to 400 Hz. Imagine: you bought a PC with such a card. And your monitor outputs a maximum of 75Hz. It turns out that your monitor does not transmit to you everything that the video card transmits to it.
Even if 15 frames per second is enough to create the illusion of movement, more frames are needed to create an immersive effect. Visual studies have shown that even if individual images cannot be distinguished, frame rates around 60-80 make video more realistic, enhancing clarity and increasing the smoothness of movement. Higher frame rates reduce visual motion artifacts—especially noticeable in movies. Moving objects can have, for example, a stroboscopic effect.
Filming and projection frequencies
- 16 - standard frequency of shooting and projection of silent cinema;
- 18 - standard frequency of shooting and projection of the amateur format “8 Super”;
- 23.976 - telecine projection frequency in the American 525/60 resolution standard, used for lossless interpolation;
- 24 is the global standard for filming and projection frequency;
- 25 - filming frequency used in the production of television films and television reports for conversion to the European resolution standard 625/50;
- 29.97 - exact frame rate of the NTSC color television standard;
- 30 — filming frequency of an early version of the Todd-AO wide-format film system;
- 48 — frequency of shooting and projection using the IMAX HD system;
- 50 is the half-frame frequency of the European decomposition standard. Used in electronic cameras for HDTV;
- 59.94 - exact half-frame frequency of the NTSC color television standard;
- 60 - filming frequency in the American HDTV standard and the Showscan system.
Even Apple introduced mobile devices with 120Hz displays - then you probably shouldn’t take a TV set at 50-60Hz when there is a 100Hz one nearby.
- Scanning provides a smooth image and a clear storyboard of moving objects.
- The resolution ensures realistic rendering of each frame, when you can see all the details; color, movement of water or people are accurately conveyed.
- When choosing which screen model is better, it is worth analyzing all the key characteristics together so that both the screen resolution and frame refresh rate are at the same level.
The effect of frequency on vision.
In LCD monitors, light originates from the backlight lamps, which in any case have a frequency above 150 Hz. For LCD monitors, although the refresh rate is indicated, it means the speed at which the TFT matrix itself changes the image. LCD monitors with LED backlighting, in particular cheap ones, are used to regulate brightness by changing the flickering frequency of diodes using PWM, which sometimes leads to visible blinking. This causes additional eye fatigue. There are 2 options - either increase the brightness more, loading the eyes, or decrease it, also loading the eyes with blinking. It is better to choose the golden mean - the maximum, comfortable brightness value.
For active shutter 3D glasses and some passive ones, LCD matrices are used with a refresh rate of ~120Hz, 60Hz for each eye. These monitors/TVs can be used at a frequency of 120 Hz and without glasses, which is ideal for gaming enthusiasts, since the number of real frames per second will be twice as high as the standard 60 fps. They also use special lamps or diodes with an increased operating frequency, which puts much less strain on the eyes. It is almost impossible to encounter flickering on these monitors, but they also have a significant reserve of brightness of the backlights.
Popular video hosting sites, including YouTube, are introducing support for streaming high-quality video at 60fps. Therefore, you can see the benefits of this type of video right now:
To summarize the above
When compact discs first appeared, many criticized them for making the music too clean and lacking the characteristic sound of vinyl. This is very similar to the situation with high frame rates (hereinafter: HFR). Simply put, there is always a use for low frame rates, but using HFR is preferable because... You can always go back to a lower frequency. However, as mentioned above, HFR is not necessary everywhere, so over time, the technology may simply become a tool in the same way that shutter angle is used today. A huge step has been made in terms of resolution - with the development of 4K cinema - which also deserves detailed consideration and research. But ultimately, our eyes receive an image of the environment in infinite frames, infinite resolution, in 3D; our brain processes the information it receives and turns it into either video or individual frames. Higher frequencies and 4k+ resolution bring us closer and closer to reflecting reality in cinema.
Peter Jackson's The Hobbit was recently released and was shot at 48 frames per second (twice the film standard of 24). Peter said at the time: “Many film critics will give a cold shoulder to the lack of motion blur and strobe artifacts, but our entire crew - many of whom are film experts - have been supportive since the film's release. You quickly get used to the new frame rate and begin to perceive it more naturally. This is similar to the time when CDs replaced vinyl records. I believe the same will happen in cinema and we are very quickly approaching the point where high frame rate films will be released en masse."
But there is another way to look at this situation. For example, Naim Sutherland refers to high frame rates: “The purpose of cinema is not to mirror our reality or show it in detail. For example, I want to create a small physical connection between you and my films. I want to immerse the viewer in the world of the story itself, so that he believes in it and forgets about himself, his life and is only alone with the film. By not showing enough information visually, we force the brain to work and fill in the gaps of information itself... which immerses the viewer even more in the film. And that's part of what makes the viewer laugh, cry, or get scared."
What causes motion blur on TV?
The TV panel can sometimes be responsible for motion blur. Some TVs can switch between panels at incredibly fast rates.
OLED technology is outstanding in such conditions. Motion blur is commonly seen in LCD TVs and LED TVs.
- Read: OLED and QLED TVs
Another cause of motion blur is the sample-and-hold technique used in some TVs.
This method involves the TV screen to hold the pixels for a moment. As images move quickly, the viewer experiences motion blur.
Motion blur can also occur when shooting video using slow shutter speeds. This can even happen if you compress videos, especially during online streaming services.
Motion blur can be annoying. Techniques such as motion interpolation and black screen insertion can eliminate motion blur. Having a higher refresh rate can also help, but to a certain extent.
Best deals 2021
The unprofessional actions of marketers of past years, who inflated the numbers in the passport data of televisions, led to a persistent distrust of consumers in equipment manufacturers. But today the situation has changed: numerous checks have established that the data specified in the instructions for LCD TVs corresponds to the actual parameters. According to them, the modern market represents three categories of displays.
- TVs with a scanning frequency of 50-90 Hz. They belong to the lowest price category. There is no longer screen flickering, but the image of some dynamic scenes still leaves much to be desired.
- TV with a scan rate of 100-200 Hz. This technique is the best option both in cost and technical terms.
- Samples whose update is beyond 400 Hz. They are characterized by very high cost. But the image quality matches the price. However, the paradox is that many experts claim that the human eye is not able to see this difference.
Sometimes in the technical data sheet of some models you can see a screen refresh rate of 1200 Hz. If this is indicated in the characteristics of products from a renowned manufacturer, then most likely this is the case. But even with the reality of these data, it is impossible to see the difference by eye, which means it is impossible to verify the truth of the information.