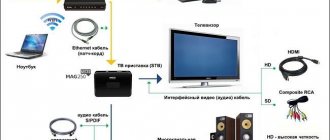
Interactive television or in other words IPTV is one of the latest developments in the field of telecommunications. This type of television can combine two different functions at the same time - providing users with access to the Internet and digital TV. If we compare interactive television with cable or analogue, then IPTV allows viewers to fully control not only the content offered, but also the viewing process itself and access to the Internet through the use of TV screens.
Meaning
The explanatory dictionary says that the object of study has the following meanings:
- Transmission over a distance and reception on the screen by means of radio electronics of images of moving and stationary objects and sound.
- A field of science and technology concerned with the technical feasibility and other problems of such transmission and reception.
- Institutions carrying out such broadcasts.
As you can see, everything is simple. Many probably guessed that something similar would be reflected in the meaning of the object of study.
Here, as in M.A. Bulgakov, it is impossible to mention one thing and not remember another - the film “Moscow Doesn’t Believe in Tears,” when Rodion/Rudolph enthusiastically prophesied that TV in 20 years would gain strength and absorb, like a huge monster, and cinema, theater, and other forms of entertainment. By the way, only because an even more global Network stood in the way of this monster, the scenario did not come true. But now the question of what the word “television” means suggests the answer: it means “last century,” and this is hardly a joke.
History of the term
Computer Engineering
If you look closely, it is not written anywhere where the definition came into the world - analog. In the West, the term has been used since the forties by computer professionals. It was during the Second World War that the first computer systems, called digital, appeared. And to differentiate, we had to come up with new epithets.
The concept of analog entered the world of household appliances only in the early 80s, when the first Intel processors came out, and the world was playing with toys on the ZX-Spectrum; today you can get an emulator for devices on the Internet. The gameplay required extraordinary perseverance, dexterity and excellent reaction. Along with children, adults also collected boxes and beat enemy aliens. Modern games are far inferior to the early birds that captured the minds of players for some time.
Sound recording and telephony
By the beginning of the 80s, pop music with electronic processing began to appear. The musical telegraph was presented to the public in 1876, but did not gain recognition. Popular music appeals to audiences in the broadest sense of the word. The telegraph was able to produce a single note and transmit it over a distance, where it was reproduced by a specially designed speaker. And although the Beatles used an electronic organ to create Sergeant Pepper, the synthesizer came into use in the late 70s. The instrument became truly popular and digital already in the mid-80s: remember Modern Talking. Previously, analog synthesizers had been used, starting with Novachord in 1939.
So, the average citizen did not have a need to distinguish between analog and digital technologies until the latter became firmly established in everyday life. The word analog has been in the public domain since the early 80s. As for the origin of the term, it is traditionally believed that the indicator was borrowed from telephony and later migrated to sound recording. Analog vibrations are directly fed to the speaker, and the voice is immediately heard. The signal is similar to human speech and becomes an electrical analogue.
If you apply a digital signal to the speaker, an indescribable cacophony of notes of different tones will be heard. This “speech” is familiar to anyone who has loaded programs and games from magnetic tape into computer memory. It doesn’t look like a human one, because it’s digital. As for the discrete signal, in the simplest systems it is fed directly to the speaker, which serves as an integrator. The success or failure of an enterprise depends entirely on correctly selected parameters.
At the same time, the term appeared in sound recording, where music and voice went directly from the microphone to tape. Magnetic recording has become an analogue of real artists. Vinyl records are like musicians and are still considered the best medium for any compositions. Although they show a limited service life. CDs now often contain digital audio that is decoded by a decoder. According to Wikipedia, the new era began in 1975 (en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_sound_recording).
Electrical measurements
In an analog signal, there is a proportionality between the voltage or current and the response on the playback device. The term will then be considered to come from the Greek analogos. What does proportional mean? However, the comparison is similar to the one above: the signal is similar to a voice reproduced by speakers.
In addition, in technology another term is used to refer to analog signals – continuous. Which corresponds to the definition given above.
Media is a synonym
Of course, one can argue about the title, because media is a broader concept. It refers to all sorts of ways of disseminating information, including TV as one of them. But the difficulty of determining a synonym for the word “television” is that, if you do not fall into vulgarity and slang, then there are not many options left. In order for the reader to see this for himself, we will provide possible replacements:
- blue screen;
- TV;
- box.
Moreover, we still fell into sin and used a slang word, but the temptation is great, let the reader not scold us too much, we do not offer more daring versions of the same thing. But to be honest, these synonyms are useless or outdated. Because now television is not a blue screen, because modern television receivers do not have a tube. Televisions can no longer be called boxes either, because they have become too thin, even for cats it’s uncomfortable to lie on them. TV is not a synonym, but an abbreviation for the word “television”. So it turns out that only a broader concept—the media—remains as a replacement. The latter, by the way, is also outdated and is used only here. In Europe, it has long been abandoned, because there it is considered inaccurate; instead, the abbreviation SMK is used, that is, “means of mass communication.”
Let us remember that the media are mass media. The whole difference between the terms lies in the presence/absence of feedback. The latter, as is easy to understand, exists objectively, because now almost all programs include viewers in their broadcast in one way or another (calls to the studio, surveys, etc.), who ultimately decide whether the program lives or dies, and one more factor is sponsorship. Since this topic is almost endless, we’ll stop, cut off this particular thread of the conversation here and move on.
What are multiplexes
Analogue broadcasting is carried out by each channel at a different frequency. With the development of digital television in Russia, streaming has become possible - broadcasting several channels on the same frequency.
All TV channels sent by different television centers on the same frequency are combined into a multiplex on a repeater, which already carries out packet distribution to receivers.
This broadcast technology allows you to solve a number of problems:
- All programs are on the same TV channel, which are easy to find by auto-tuning. To change the broadcast program, the user does not need to physically switch the TVC.
- Bureaucracy. For analogue broadcasting, each TV channel was required to obtain a license allowing it to occupy specific frequencies of digital channels in each region. With the advent of signal streaming, this need has disappeared, hence digital channels are expanding their presence much faster.
- Organization. Repeaters operating on a single frequency are simpler in design, in contrast to multi-frequency analog towers. They are unfolding faster, which means television is spreading faster.
Today there are two active and one test multiplexes. Each of them is at a specific stage of work and with different geographic coverage.
This is due to the fact that a particular multiplex requires a separate tower to broadcast, and each of the digital channel packages appeared at a different time. While the first multiplex has been active for more than five years, the second has recently appeared, and the third has not yet been officially launched.
First multiplex (RTRS-1)
What is multiplex in television? This is a broadcast from several television centers in a single wireless signal. It includes the first 10 channels that began broadcasting in digital format. Their composition and broadcasting period are regulated by Roskomnadzor, i.e. they cannot change.
The list of the 1st multiplex (RTRS-1) includes 10 channels, most of which are federal level programs, known from analogue broadcasting:
- First,
- Russia 1,
- Match TV,
- NTV,
- Channel Five (St. Petersburg),
- Russia-K,
- Russia 24,
- Carousel,
- OTR,
- TVC (TV Center).
Also, three radio channels can be received from RTRS-1 repeaters: Vesti FM, Mayak, Radio Russia. Now the channels of the first digital television multiplex operate anywhere in Russia, regardless of the population of the area and the distance from the tower.
Second multiplex (RTRS-2)
Includes 2nd digital channel streaming package. Like the first, the second multiplex includes 10 programs of federal and regional significance.
It included:
- REN TV,
- SAVED,
- STS,
- Home,
- TV3,
- Friday!,
- Star,
- WORLD,
- TNT,
- Muz TV.
The second digital TV multiplex opened recently and is not distributed throughout the country. To broadcast it, you need independent repeaters, the deployment and equipment of which takes time.
When the 2nd multiplex in the area will be turned on, you can find out on the map - towers under construction or planned for deployment are marked with a gray icon. There is no radio broadcasting in the second package.
Third multiplex (RTRS-3)
At the moment it is in test mode. The start of broadcasting is scheduled for 2020. Unlike the first two, the third multiplex includes more than 40 federal and regional channels that broadcast at different times. In terms of the volume of digital broadcasting, the entire television package is comparable to the daily operation of 10 channels.
The third multiplex is currently available only to residents of the Moscow region. Broadcasting is already underway from the Ostankino Tower. There are no RTRS-3 repeaters, and the digital signal with the third package can only be received directly from the television center.
Important! The package of channels currently broadcast is not final. It may change over time.
Broadcast frequencies
Each region has its own broadcast frequency for each digital multiplex. This is due to the parallel development of regional channels, which, before the installation of the repeater, had already managed to occupy part of the frequency range.
Below is a table with broadcast frequency and digital television channel (TVC) for Moscow and a number of large cities.
| Moscow | Saint Petersburg | Ekaterinburg | N. Novgorod | Rostov-on-Don | |
| 1st multiplex | 546 MHz (30 TVK) | 586 MHz (35 TVK) | 674 MHz (46 TVK) | 530 MHz (28 TVK) | 602 MHz (37 TVK) |
| 2nd multiplex | 498 MHz (24 TVK) | 666 MHz (45 TVK) | 786 MHz (60 TVK) | 730 MHz (53 TVK) | 610 MHz (38 TVK) |
| 3rd multiplex | 578 MHz (34 TVK) | – | – | – | – |
You can find out the broadcast frequency and television channel for your city and region on the website rtrs.rf. It is currently unknown when the third multiplex will be launched in the regions.
Spelling
Many people are probably interested in the question of how the word “television” is spelled. There is only one difficulty in it - the word is a dictionary word, so it is best to remember its spelling. Naturally, we used it without error, so feel free to use the spelling that is presented here - “television”. To better remember the spelling of a noun, you can resort to a forbidden technique and remember the following: the word “tel” is written with two “e”, which means the prefix tele- too. Otherwise, it seems that the definition should not cause difficulties.
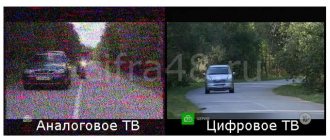
What do the spectra of an analog and discrete signal look like?
The image of signals can be represented as two functions. The figure clearly shows how a continuous signal differs from a discrete signal. The source voltage changes smoothly, while the processed voltage changes intermittently. The discrete spectrum periodically coincides stepwise with the continuous spectrum.
Discrete changes occur abruptly, after a certain period of time. The level in a digital system is encrypted and any voltage value is described in binary code. The smoothness of the transformation and the originality of the transmitted data depend on the frequency of measurements. The more accurately the signal level is described and the more often the measurement is carried out and processed, the more accurately the spectrum of the initial and transmitted signals matches.
Information function of television
Be that as it may, the content of TV programs, compared to Soviet times, has changed a lot and has become more diverse. In those days, programs had to, first of all, correctly orient the audience. Nowadays television is primarily entertainment. Moreover, some have fun by following the ups and downs of the relationship between Alla Borisovna and Maxim Galkin, others watch scientific and educational programs, and still others empathize with Shakespeare’s heroes - all this is modern television. Thus, the information function is fulfilled to a sufficient extent.
Basic principles
number of televisions per 1000 people
| 1000+ 500-1000 300-500 | 200-300 100-200 50-100 | 0-50 No data |
Television is based on the principle of sequential transmission of image elements using a radio signal or wires.
The image is decomposed into elements using a Nipkow disk, cathode ray tube or semiconductor matrix. The number of image elements is selected in accordance with the radio channel bandwidth and physiological criteria. To narrow the bandwidth of transmitted frequencies and reduce the noticeability of flickering on the TV screen, interlaced scanning is used. It also allows you to increase the smoothness of motion transmission. The analog television path in general includes the following devices:
- Television transmission camera. Serves to convert the image obtained using a lens on the target of the transmitting tube or semiconductor matrix into a television video signal.
- Telecine projector. Converts the image and sound on film into a television signal, and allows you to show movies on television.
- Video recorder. Records and at the right time plays back the video signal generated by the transmitting camera or telecine projector.
- Video mixer. Allows you to switch between multiple image sources: cameras, VCRs and others.
- Transmitter. The high frequency carrier signal is modulated by a television signal and transmitted by radio or wire.
- The receiver is a TV. Using the synchronization pulses contained in the video signal, the television image is reproduced on the receiver screen (kinescope, LCD display, plasma panel).
In addition, to create a television broadcast, an audio path similar to the radio transmission path is used. Sound is transmitted at a separate frequency, usually by frequency modulation. In digital television, audio, often multi-channel, is transmitted in a common data stream with the image.
Does television educate people?
The answer to the question is ambiguous, because now the person himself is responsible for what material he prefers to be formed from. Television diversity has been discussed above. Gone are the days when the press, radio and television broadcasts were tightly controlled. True, censorship, one way or another, exists, but it has changed its form somewhat. But in any case, neither television nor the Internet profess a clearly defined ideology, which gives a certain freedom of choice. Another thing is that TV continues to influence minds and hearts, especially for programs where people demonstrate their talents in one form or another. Thanks to such programs, many boys and girls, men and women find and find themselves in life. Therefore, we cannot say that television is completely evil.
Types of signals
There are several types of classification of available signals. Let's look at what types there are.
- Based on the physical medium of the data carrier, they are divided into electrical, optical, acoustic and electromagnetic signals. There are several other species, but they are little known.
- According to the method of setting, signals are divided into regular and irregular. The first are deterministic methods of data transmission, which are specified by an analytical function. Random ones are formulated using the theory of probability, and they also take on any values at different periods of time.
- Depending on the functions that describe all signal parameters, data transmission methods can be analog, discrete, digital (a method that is quantized in level). They are used to power many electrical appliances.
Now the reader knows all types of signal transmission. It won’t be difficult for anyone to understand them; the main thing is to think a little and remember the school physics course.
Should we talk about the death of television?
No, because in one form or another it still exists.
If such a moment ever comes and YouTube channels celebrate a complete and final victory, then it will be possible to say that television has come to an end, but it’s too early to talk about it. Why? Even if we watch a television channel via the Internet, we are influenced by it. The programs would not have taken place without presenters, editors, directors, directors and other wonderful people. Television will disappear when something fundamentally new arises. Of course, our topic is voluminous and inexhaustible, but the main thing is to give a general idea of the meaning of the word “television” and the phenomenon that is hidden behind it. It seems that we have lost our way with the task, and where to direct our steps next is up to the reader to decide.
Which communication systems use a digital signal and which analog?
Despite its archaic nature, analogue technology is still used for telephone and radio communications. Many wired networks are still analog. These are mainly traditional telephone lines of local operators. But digital channels are already widely used for backbone data transmission. Analogue technology is also used in simple and cheap portable radio stations.
All newly created systems use digital signal processing technology. These are fiber optic and wire lines, signaling and telemetry, military and civil industrial communications. And of course, television is switching to digital broadcasting. The analogue method of data transmission has exhausted itself. It has been replaced by a new high-quality and secure connection.
Historical reference
In total, before the Second World War, 19,000 electronic televisions were produced in the UK, 1,600 in Germany and 7,000 in the USA. In 1942, in the countries of the Anti-Hitler Coalition, the production of televisions was suspended until August 1945.
After the war, unlike devastated Europe, in the United States the population did not lose purchasing power, and the radio-electronic industry, which had increased its enormous capacity due to defense orders, found a field of activity in the form of teleconnection in the country. If in 1947 there were about 180,000 televisions here, then by 1951 their number exceeded 10 million! Thanks to mass production, prices for goods fell sharply, making it possible for everyone to buy a TV. While in 1946 only 0.5% of American households could boast of their own television set, by 1962 90% of households had acquired black-and-white televisions. Combination devices—teleradios—containing a television, an electrophone, and a high-quality radio in a common housing have become popular.
In the USSR, despite the post-war devastation, the development of television was declared one of the priorities. Already in 1947, serial production of the Moskvich T1 and Leningrad T1 televisions was mastered, and in 1949 the first mass Soviet television, KVN-49, was put into production.
In 1956, the American (English Zenith Radio Corporation) introduced the world's first wireless remote control, developed by Robert Adler. Volume control and channel switching were carried out using ultrasonic signals modulated by appropriate commands.
The modern infrared remote control was released in 1974 by Grundig and Magnavox. The event coincided with the introduction of teletext, which required more precise control not found in televisions themselves. The appearance of digital buttons on remote controls is connected precisely with the need to find the necessary pages on the TV screen. In the 1980s, televisions acquired another function: they began to be used as a monitor for the first household computers and game consoles. To make it easier to connect these devices, as well as video recorders that have become widespread, televisions began to be equipped, in addition to the antenna input, with an additional component input, which allows them to send signals bypassing the high-frequency channel selector.
The next revolution in the TV market occurred in the mid-2000s, when low-cost plasma panels and LCD TVs appeared. By the beginning of the 2010s, CRT televisions were almost completely replaced by flat LCD and LED devices, a significant part of which can be directly connected to the Internet and provide viewing of 3D content. Today (2018), almost all manufactured TVs support high-definition standards, and the most expensive models support ultra-high definition. Modern flat-panel TVs often serve as a key element of home theaters, while maintaining the ability to watch over-the-air and cable television.
First experimental television broadcast
Experimental television broadcasting with a mechanical scanning system of 30 lines started in 1929-1931. in leading countries of the world almost simultaneously. The 30 line format, created in Germany, has become the de facto international standard.
The newspaper “Pravda” on April 30, 1931 published the following message: “Tomorrow, for the first time in the USSR, an experimental transmission of television (far vision) by radio will be carried out. From the short-wave transmitter RVEI-1 of the All-Union Electrotechnical Institute (Moscow), an image of a living person and a photograph will be transmitted at a wave of 56.6 meters” (Pravda. 1931. April 30). This first public television broadcast showed laboratory employees (moving images!) and photographic portraits - without sound, “silent”.
After a number of experimental television communication sessions, it was decided to conduct test television broadcasts. For this purpose, equipment was transferred from the laboratory of the All-Union Electrotechnical Institute to the building of the Moscow radio broadcasting center on Nikolskaya, 7, from where it was possible to supply a signal to broadcast radio transmitters and where a small studio was equipped. The first test transmission took place on the night of October 1, 1931 through the radio station of the Moscow Council of Trade Unions. It is not known how many televisions received it at that moment, but contemporaries claimed that there were at least ten of them. The broadcasts became regular. The content of these programs was not specially prepared; it was an amateur performance. And they had to perform in a dark studio, which was illuminated by a “running beam” created by the light of a powerful film lamp, covered with a rotating Nipkow disk.