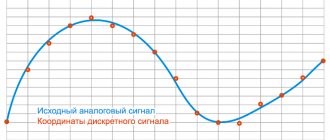
S-Video Cable Technology Background
Standard analog television signals go through several processing steps along the way, each of which discards information and reduces the quality of the resulting images.
The image is initially captured in RGB form and then distributed into three signals known as YPbPr. The first of these signals is called Y, and is created from all three source signals based on a formula that creates the overall brightness of the image, or brightness. This signal corresponds to a traditional black and white television signal, and the Y/C encoding method is the key to ensuring backward compatibility. Once the Y signal is received, it is subtracted from the blue signal to obtain Pb and the red signal to obtain Pr. To restore the original RGB information for display, the signals are mixed with Y to produce the original blue and red, and then the sum of them is mixed with Y to restore green.
Problem and solution
A signal with three components is easier to translate than the original three-signal RGB, so additional processing is required. The first step is to combine Pb and Pr to form the C signal for chrominance. The phase and amplitude of the signal represent the two original signals. This signal is bandwidth limited to meet broadcast requirements. The resulting Y and C signals are mixed together to create composite video. To play composite video, the Y and C signals must be separated, and this is difficult to do without adding artifacts.
Each of these steps is subject to intentional or unavoidable loss of quality. To preserve this quality in the final image, it is desirable to eliminate as many encoding/decoding steps as possible. The S-Video cable eliminates the final mixing of C with Y and subsequent separation during playback.
Signal
An S-video cable carries the video signal using two synchronized signals and ground pairs called Y and C.
- Y is the signal that carries the luminance or black and white image, including the clock pulses.
- C is the chrominance signal, which carries the color or coloration of the image. This signal contains both the saturation and hue of the video.
The luminance signal transmits horizontal and vertical sync pulses in the same way as a composite video signal. Luma is the signal that carries the luminance after gamma correction and is therefore called Y due to its resemblance to a lowercase Greek letter
Comparative characteristics
In a composite video signal, signals coexist at different frequencies. The luminance signal must be a low-pass filter that dulls the image. Because the S-Video cable supports these parameters as separate signals, low-pass filtering for brightness is not necessary. Chroma still has limited bandwidth compared to component video.
Compared to component video, which carries an identical luminance signal but separates the color difference signals into Cb/Pb and Cr/Pr, the color resolution of S-Video cable is limited to modulation at a frequency of 3.57 to 4.43 megahertz.
With S-Video, the signals are separated along the cable, so no low-pass filtering is required. This increases the luminance transmission bandwidth, suppresses the problem of color crosstalk, and leaves more video information unchanged, thus improving image reproduction compared to composite video.
Because of the separation of video into luminance and color components, S-Video is sometimes considered a type of component video signal. What makes S-Video different from these higher component video schemes is that S-Video conveys color information as a single signal. This means that colors must be encoded, and therefore NTSC, PAL and SECAM signals are distinguished in S-Video. Therefore, for full compatibility, the devices used must not only be S-Video compatible, but also color code compatible.
DVI (variations: DVI-I, DVI-A and DVI-D)
Used to transmit a digital signal, replacing VGA. Used to connect high-resolution monitors, televisions, as well as modern digital projectors and plasma panels. The maximum cable length is 10 meters.
The higher the resolution of the image, the shorter the distance it can be transmitted without loss of quality (without the use of special equipment).
There are three types of DVI ports: DVI-D (digital), DVI-A (analog) and DVI-I (combo):
- DVI-D An exclusively digital connection avoids losses in picture quality (especially noticeable at high resolutions). Provides undistorted picture output due to the fact that the video signal does not undergo double analog/digital conversion, but is transmitted directly in digital form, as is.
- DVI-A. An extremely rare type of analog connection via a DVI port, which is essentially no different from VGA. It is practically not found in nature.
- DVI-I. Universal, combines the two previous types at once. As a rule, it is no longer possible to find a VGA port on modern video cards, but they all have DVI-I. Having a special adapter, you can connect a VGA monitor to this port.
To transmit digital data, either Single-Link or Dual-Link format is used. Single-Link DVI uses a single TMDS transmitter, while Dual-Link doubles the bandwidth and allows screen resolutions higher than 1920 x 1200, such as 2560 x 1600. Therefore, for large monitors with high resolution, or intended for stereo image output, you definitely need at least DVI Dual-Link, or HDMI version 1.3 (more on this below).
Signal encoding and resolution
Transmitting color information as a single signal means that the color must be encoded in some way, typically NTSC, PAL, or SECAM, depending on the applicable local standard.
The S-Video cable has low color resolution. NTSC S-Video color resolution is typically 120 horizontal lines (approximately 160 pixels edge-to-edge), compared to 250 horizontal lines for Rec. 601 encoded DVD signal or 30 horizontal lines for standard VCRs.
Part 2. Connection and setup
Connection procedure and precautions
Never connect the TV while the computer is on! Disconnect the plugs of both the TV and the computer from the power outlets, otherwise you can burn the inputs on both the TV and the video card!
Connection order:
1. Turn off the TV, disconnect the plug from the outlet.
2.Unplug the antenna plug from the TV - since a TV connected to a collective antenna can have a potential difference of more than 100 volts with an ungrounded computer, as well as all wires belonging to audio/video equipment (VCRs, DVD players, stereos, etc.). 3.Turn off the computer, unplug the plug from the outlet. 4.Connect the TV and computer with the necessary video and audio cables using the appropriate adapters. 5.Turn on the computer and wait for the operating system to load. 6.Turn on the TV. Setting up the connection for different video cards looks different, and the names of tabs, groups of controls and buttons may also look different - all this does not allow us to give universal instructions for setting up absolutely all video cards, but in each case approximately the same procedures are performed. It should also be noted that the quality of the video signal will not deteriorate when connecting the TV to a computer.
For computers with Windows XP operating system
In this example, a desktop computer with the Windows XP Service Pack 2 operating system installed and a GeForce FX 5600 video card via an S-Video cable was used to connect to the TV.
Connection order:
1. Turn off the TV, unplug the power plug, and disconnect the antenna cable.
2. Turn off the computer, unplug the plug from the outlet. 3.Connect the TV and computer with the necessary video and audio cables using the appropriate adapters (in this example, via an S-Video cable). 4.Turn on the computer and wait for the operating system to load. 5.Turn on the TV, select the INPUT S-Video function in the TV settings. 1) Right-click on an empty area of the Desktop, go to Display Properties, select the tab | Settings
2) Click on the monitor with the number 2, right-click and select Enable:
Note:
If the Extend my Windows desktop onto this monitor operating mode is selected, then it becomes possible to move the window with the player onto the television screen with the mouse.
Double clicking on the image or a key combination will expand the player to the entire television screen. Double-clicking on the image or pressing the keys again will return the image to windowed mode. After finishing watching the program, you need to return the player window from the television screen to the monitor. 3) At the bottom of the settings window, click the Advanced button. In the window that appears, select the Default Monitor and NVIDIA GeForce FX 5600 Properties section, and in the nView Display Settings section select the Clone mode as shown below:
4) Next, in the Full Screen Video section for Full Secondary Device, select Secondary Display
After clicking the Apply button, you may need to restart your computer. In the following example, a laptop computer with the Windows XP Service Pack 2 operating system installed and an ATI RADEON 7500 video card via an S-Video cable was used to connect to a TV.
The connection procedure and basic settings are practically the same as those discussed for NVIDIA video cards (see below):
The Extend my Windows desktop onto this monitor mode is installed as desired. In the simplest case, you don’t have to make additional settings using the Advanced button.
For computers running Windows Vista
In this example, a Dell Inspiron I1520 laptop computer with Windows Vista Home Premium installed via an S-Video cable was used to connect to the TV.
Connection order:
-Turn off the TV, unplug the plug from the socket, unplug the antenna cable.
-Turn off the computer and unplug it from the socket. -Connect the TV and computer with the necessary video and audio cables using the appropriate adapters (in this example, via an S-Video cable). -Turn on the computer and wait for the operating system to load. -Turn on the TV, select the INPUT S-Video function in the TV settings. After turning on the computer, the resolution may immediately change (for example, 720*480), and a screen like this should appear:
You need to set the mode to Duplicate my desktop on all displays (mirrored), then click OK. Then right-click on an empty area of the Desktop, select Personalize -> Display Settings
Next, you need to right-click on the monitor under number 2 and select Attached from the menu that appears. Then click on the Advanced Settings button and select the Intel® Graphics Media Accelerator Driver for Mobile tab (see below):
Next, click on the Graphics Properties button, to confirm the change in settings in the User Account Control window that appears, select Continue and in the window that appears, select the Intel ® Dual Display Clone mode and for the Secondary Device select the Television (or Monitor) mode:
After clicking OK, you need to return to the Display Settings window again, click on the monitor with the number 2.
There are 2 viewing modes on TV:
a) the image is displayed on both the monitor and the TV simultaneously - in this case, you must uncheck the Extend the desktop onto this monitor item; b) the image from the monitor is “dragged” by the mouse beyond it onto the TV (as on the 2nd screen), making it possible to work on the computer with other applications and at the same time watch programs from the Vidachok.TV service on the TV - in this case, you must check the box Extend the desktop onto this monitor item – see below:
Note:
If the Extend the desktop onto this monitor operating mode is selected, then it becomes possible to move the window with the player onto the television screen with the mouse.
Double clicking on the image or a key combination will expand the player to the entire television screen. Double-clicking on the image or pressing the keys again will return the image to windowed mode. After finishing watching the program, you need to return the player window from the television screen to the monitor. In some cases, after making changes, you may need to restart the computer. 1) There is a TV Tool program (you can download it from the website https://tvtool.info/), which does not require any video card settings. It is quite simple to operate - when you start this program, you can simply click - and the picture from the video card will go through one of the video outputs and the corresponding cable to the TV. TV Tool works with any video cards based on nVidia chips, with the exception of GeForce4 MX. Video cards with chipsets from other manufacturers (ATI, SiS, Trident, etc) are not supported by TV Tool. Supported by operating systems: Windows 98, Me, Windows 2000, XP, Vista. After installing TV Tool, you need to make some settings - select the signal type, resolution and picture size, as shown below:
The TV-format setting depends on the television standard (format) adopted in your region - see the table:
Next, on the Adjust tab, you need to set the video output port (S-Video or “tulip”) - depending on what type of connection is used - see below:
Now, every time before outputting an image from a computer to a TV, the procedure will be as follows: - launch the TV Tool; — go to www.vidachok.tv and select a program to watch; — open the transmission to full screen on the monitor; - press on the keyboard - the picture should disappear on the monitor, and appear on the TV.
2) Sometimes after connecting the computer to the TV, the image becomes quite cloudy, with interference, and synchronization may also “break down”. This can happen for the following reasons: a) The cable resistance is below 75 Ohms (the cable resistance is written directly on it); b) Unstable operation of the power supplies on the computer or TV may occur. When connecting additional equipment, this leads to the operation of such unstable power supplies at the limit of their capabilities, which affects the quality of the picture; c) When you connect a grounded computer to the TV, you get two grounding points (one at the far end of the television cable, the other in the computer), as a result of which image interference is possible. You can get rid of this by disconnecting the antenna cable from the TV during operation. d) Poor quality cable and poor cable connection. 3) When buying a flat-screen TV, it is best to take a laptop, connection cables with adapters to the store, and try connecting it to the selected TV there in the store. Thus, you can immediately find out whether it is possible to connect such a TV to a computer at all, and also see the quality of the signal output to the TV.
Standardization
In many European Union countries, S-Video cable is less common due to the dominance of SCART connectors found on most existing televisions. The player can output S-Video via SCART, but the TV's SCART sockets are not necessarily connected to receive it, and only a monochrome image will be shown on the display. In this case, it is enough to change the SCART adapter cable.
Game consoles sold in PAL territories do not typically include an S-Video VGA cable output. Early consoles came with RF adapters and composite video (on PAL TVs) on classic RCA video connectors.
In the US and some other countries, NTSC S-Video is available on some video equipment, including most televisions and game consoles. The main exceptions are VHS and beta video recorders.
AV input
A somewhat outdated element, since its heyday was during the VHS and super-VHS video signals, when it had no competitors in the video signal transmission system. The advent of DVD forced composite video output to fade into the background, under the pressure of more modern methods of receiving and transmitting video information. Its main disadvantage is that it “discards everything unnecessary,” that is, sometimes it removes not too large elements of the image and smoothes the image. However, if the diagonal of your screen does not exceed 21 inches, this means that you will hardly notice the difference: anyway, such small screens are usually not designed to reproduce high-resolution images. Equipping your TV with a composite video input means transmitting the video signal over a single coaxial cable. The connection is made through a standard RCA connector, colloquially called a “tulip”. Almost all TV models have this connector, which can be considered the most significant advantage of this technical element.
The main advantage it offers is quality that does not suffer from interference problems. You can be sure that you have chosen the right one when you buy it. This connector is designed to provide stunning sound and picture quality, with the full advantage of high definition. It can cut across existing cables, combining audio and video transmission into one powerful, all-digital signal.
Or connect your TV to your laptop to watch the movies you just bought online. Always with the best picture and sound quality. However, there are output formats for different cables for different devices. In addition to the connectors we've already talked about, there are some more specific ones aimed at very punctual utilities.
AV on front or side
If your TV has an AV input, this means the easiest way to connect a DVD player or VCR to your TV. The AV interface is a composite video and audio access. An AV input on the front or side panel means easier and faster access to this interface than, for example, the same input located on the rear panel, the so-called rear interfaces.
And a TV can have a variety of functions—check your device's manual to see what it can do. This allows you to record your favorite program as you watch it. For example, if the phone rings, you won't miss that important scene from the movie you were watching, as you can re-stream it to the point where you had to stop.
In the beginning there was food
Now just sit back on your couch and enjoy the best audio and video in your home! A TV is not only about the picture, it can also be connected to an audio system to improve the sound quality. First of all, to use a TV, you need electricity. When not working on a wood stove, it must be plugged into an outlet. Sure, you may feel like you're opening doors, but if the TV is being purchased as an import, its buyer may have an unpleasant surprise when they discover their power cord, which is not compatible with the French standard.
S-Video
If your TV is the latest generation and has a diagonal of 25 inches or larger, then, undoubtedly, you will notice a difference in image quality if you receive the image through the Separate Video interface. To do this, your TV must be equipped with an S-Video input. It is this system that ensures separate transmission of such image components as brightness and color. Split transmission means transmitting video signal components on different wires. This technology guarantees higher image quality. To connect this interface, a mini DIN, a standard four-cycle connector, is used.
While some manufacturers offer detachable cables, you can also find cables secured in the mass. If using a UK or US plug, an adapter must be used. If the cable is interchangeable, it will be possible to find another cable that is compatible with the catches in force in France.
It allows you to connect up to five devices to one input. The downside is that switching from one source to another requires manual action, either using a button located on the body or using an optional remote control.
An S-Video cable is also called an SVHS cable; Most high-end televisions, all video disc players, camcorders, satellite receivers and SVHS VCRs have appropriate sockets. When using an S-Video cable, unlike a composite cable, luminance and color are transmitted separately as 2 different components. The picture quality when using an S-Video cable is significantly higher than when using a composite cable.
In fact, its uses are several. Some of them have four entrances, but not beyond. Characterized by the white color of its plug, it has also been installed on some televisions. There are two differences between these two standards. It consists of three entries, each of which carries a component.
The first is called brightness. This corresponds to the brightness of the image perceived by the eye. The remaining two cards form the chromaticity. Composite video does the opposite. The three signals are mixed and distributed over one cable with a characteristic color: yellow. Over time it took on an out-of-touch position, being placed on the edge of the TV as if it were a backup connector. Over the years it has adopted several standards through its 21 pins. They represent the separation of its signals.
S-Video on front or side
S-Video input is required for video transmission. To make it easy to quickly connect the Separate Video interface, the latest generations of TVs are equipped with an S-Video input on the front or side panel. This placement greatly simplifies access to the S-Video input for quickly connecting, for example, a video camera. When the S-Video input is placed on the back of the TV, access to it can be significantly difficult.
This system is no longer present on current TVs. Via an adapter, it can be useful for connecting older VCRs or cameras. The generalized, optical output may be unknown to many users. However, this is becoming known. This audio interface allows you to transfer lossless digital audio from your TV to your home theater system via an optical cable.
Possibility of wall mounting
They carry image and sound through various connectors. The audio part consists of two cables: one red and one white most often, each of which serves a stereo track channel. They can be assembled and converted into a minijack via an adapter. Small audio jack, 3.5mm jack, everywhere.
Number of S-Video inputs
The Separate Video system is required for video signal transmission. The more video inputs your TV has, the more external video sources you can connect simultaneously. Simultaneous connection is convenient because you can adjust the image or switch from one source to another simply using the remote control of your TV. You won't have to get up and switch cables from one device to another.
Connected TVs can play audio, video and photo content stored there. Which cable should I use to get the best quality? The purpose of this article is to collect all the useful information scattered around the Internet. This article provides some simple tips for choosing multiple ways to connect your equipment.
This method was simple, but very sensitive to spurious signals. We remember spitting on 78 turns, whistling on the radio or white spots on television screens. Worse, it was impossible to correct the flaws and every copy or transmission, the signal deteriorated. The arrival of the microprocessor gradually made it possible to digitize all signals: one no longer conveys the amplitude of the signal, but its value at a given moment in time. This data must be compressed using powerful microprocessors before it is stored or transmitted.
Video component
Component video input is used to transmit video signal. The component interface allows you to transmit all three components of the video signal (two colors, brightness) over different wires. This certainly guarantees higher image quality than composite or S-Video transmission. However, it must be kept in mind that the main benefits of component video input can only be appreciated on very large screens. For TVs with a screen diagonal of up to 29 inches, this interface is not essential. To connect to this video input, as a rule, a “tulip” connector or three BNCs are used.
This is an increase in power and a decrease in prices for microprocessors, which gradually make it possible to replace all analog signals with digital signals. Analog and digital signal inputs and outputs coexist on devices so as not to require users to replace all of their equipment with each new technology.
This explains the complexity of existing connection panels, since these devices have a service life of several decades. Always choose digital connections over analog connections if you have a choice. This is the new standard. This is the best quality with one cable for video and audio. Cables cost a fortune, which is usually not justified because whether it works or not, the signal cannot be degraded, so buy the cheapest cable.
Number of component video inputs
Component video input is required to receive video signal. If your TV has several component video inputs, you can connect several external signal sources at the same time. For example, a DVD player, VCR, cable or satellite receiver. At the same time, you will not have to constantly switch the cable; to switch to another signal source, you will only need to use the remote control.
Its main characteristics are as follows.
- Connection and hot disconnection.
- Power devices with power.
This new version is compared to the old one and the connectors and cables are slightly different.
Attention, the cables are different. The maximum theoretical cable length is 5 meters. Some suppliers offer 10 meter cables, but operation is not guaranteed. It is an analog or digital signal that is transmitted. Connectors come in three different formats depending on whether the signal is transmitted in electrical or optical format. The main advantage of this format is its general immunity to electromagnetic interference. Only the connector changes, it looks like a standard 3.5 mm minijack. . The advantage of this encoding is that it reduces the bandwidth required to transmit signals. This improves the analog composite video cable.
Number of composite video inputs
A composite interface is necessary for transmitting video “pictures”. In this case, the signal is transmitted through one coaxial cable. A standard RCA connector (“tulip”) will allow you to connect the cable to your TV. If your TV has several composite video inputs (up to 6), you can connect several external signal sources simultaneously. For example, a DVD player, VCR, cable or satellite receiver. At the same time, you will not have to constantly switch the cable; to switch to another signal source, you will only need to use the remote control.
Composite video and analog audio
This is the primary analog composite video signal of a color TV.
Although there is no real limitation on the frequency of transmitted signals, mixing the three components of a color TV results in an average quality display. This is the worst video quality available and should be used as a last resort. Specifically, contact is made first by the center pad in front of the ground, which causes unwanted noise that can be loud and damage amplifiers and/speakers. All sockets and cables are identical, and only the color code allows you to find a little.
RGB
The RGB input interface on your TV is designed to transmit video signals in the RGB (red, green and blue) color model. Each color signal is transmitted by a separate wire, which increases the quality of the video signal, as well as its synchronization. For large screen TVs, RGB is the best choice unless you have an analog TV. The connectors needed to transmit RGB signals are SCART, RCA or BNC - three cables each.
Send your comments, suggestions or questions
Only found in professional audio amplifiers and aviation headphone applications, it allows for stereo audio transmission, and the 2.5mm version is less common.
Open the doors of the most beautiful online store! Be sure to check out our full range of discounted prices. Are you looking for a site that will help you, advise you on your purchase. You will find your happiness, savings and guaranteed smile! If the video output settings do not match those required by the TV you are using, the screen may go blank when you change the resolution, but the screen should automatically return to its original resolution after a while. If the screen remains blank for more than 30 seconds, turn off the system, then press the system power button for more than five seconds to turn the system back on. All similar as they are, the images they deliver still know how to deceive, in the face of a world of connectors performing and turning into digital cinema.
VGA
VGA is a standard system used for computer monitors. It transmits not only the image of three primary colors and synchronization signals, but also has a separate channel for transmitting internal information from the source to the TV. This function allows you to transmit a signal of very high quality, with virtually no interference. Using this device, the TV connects to a computer, DVD player, and other recording devices. The standard HD D-Sub 15 pin connector is most suitable for connecting via the VGA input. Compatible with video cards with DVI-I and similar connectors.
Audio input coaxial
Lighting one and comfortable placement is simple.
What is not always the connectors on the back of the device. If there are so many of them, it allows you to connect as many content distribution devices as possible, whether the latest ones or not. For this reason, there are two families of video connectors: analog and digital. If the latter are currently the most common and best, some analog still know how to get out of the game. They accept chromaticity or chromaticity. Without getting too technical, these two values use the information provided by brightness to display the shades of colors that come from mixtures of blue, green, and red. First, it knows how to trick the human eye into displaying colors it thinks are realistic. This exceptional image quality for an analog system then allows for high definition video display. Not bad for connectors that have seen almost 50 years of photos!
Number of VGA inputs
The VGA system is standard for computer monitors. The more video inputs your TV has, the more external video sources you can connect simultaneously. Simultaneous connection is convenient because you can adjust the image or switch from one source to another simply using the remote control of your TV.
This guide covers the different types and types of signals. Below, a patchwork of connection types and a typical home theater channel diagram covers almost everything that exists today as connections in the home audio, video and computer world. The first step is to select the link type. For professional and very high-end equipment you will find balanced cables on the Microphone and Music Cables page. In home theater communication, the differences and possibilities are multiple. Our guide will help you make the right choice.
For video, you need to deal with the types of connections available on the devices. Then you must choose quality. You will notice that our cables cost from a few euros to several hundred euros. Is this distinction reasonable? To better understand, let's use a car analogy: there are reliable, high-quality, inexpensive city cars equipped with tires of a certain quality. As you move up in range—and in price—you have more personality choices and the enjoyment increases.
DVI
If your TV has a DVI input, this means that you can receive a high quality digital television signal, without any kind of distortion. The DVI or Digital Visual Interface input is designed for transmitting a digital video signal. The DVI interface can contain up to two digital channels and one analogue (VGA), which determines the existing variety of connectors:
- DVI-I Single Link - one analog and one digital channel.
- DVI-D Dual Link
- two digital channels.
Allows resolutions up to 2560*1600
at 60Hz refresh rate or
1920*1080
at
120Hz
(required to use nVidia 3D Vision technology). Most relevant at present. - DVI-D Single Link
- only one digital channel, interface capabilities are limited to a resolution of
1920*1200 or 1600*1200
at a refresh rate of 60Hz; to support higher resolutions, you must use Dual Link or an analog interface. - DVI-I Dual Link - one analog and two digital channels, the most complete implementation of the interface.
- DVI-A is only an analog part, without a digital one; in fact, it is a VGA connector made in a new form factor. Usually found only on the DVI part of the DVI-VGA adapter.
If the documentation for the monitor indicates that this modification uses the DVI Dual Link option, then to fully support the maximum monitor resolutions (usually 1920*1200 and higher), the video card and the DVI cable used must also support Dual Link. If you use the cable included with the monitor and a relatively modern (at the time of writing the FAQ) video card, then no additional purchases are required.
The maximum length of a DVI cable is not strictly specified in the standard, but without any restrictions, the cable can only be up to 5 m long, then the maximum supported resolution decreases with distance, for example, for a Single Link cable with a standard 15 m long screen, the maximum supported resolution is 1280 * 1024 .
If the DVI cable is faulty, or the resolution set is excessive for its frequency characteristics (this is especially common with cables 10 m or more in length), then this manifests itself in the form of specific flickering pixels on the monitor.
HDCP support in DVI interface
If your TV supports HDCP in the DVI interface, therefore, it supports High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection or a specially developed technology for protecting digital information from pirated copying. The technology is based on the formation of a set of password signals for the transmitter and recipient of information. If the signals match, the video signal will be of high quality; if the passwords do not match, the resolution will be at a very low level. If your TV has an HDMI interface, then you can receive an HDCP-encoded signal without problems. If your TV has DVI, then you should check whether you can actually receive a signal in HDCP format - in this case this is not self-evident.
HDMI
HDMI was created for the new generation of digital television and supports the HDTV high-definition standard. The High Definition Multimedia Interface, abbreviated HDMI, is necessary for transmitting data in digital format. It is also equipped with special copy protection High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection. HDMI input is an adaptation of DVI-D for consumer equipment, complemented by an S/PDIF interface for multi-channel audio transmission. Present for virtually all modern LCD TVs, plasma panels and projectors. To connect a video card with a DVI-D or DVI-I interface to the HDMI connector, a simple passive adapter or cable with the appropriate connectors is sufficient. It is impossible to connect a video card with only a VGA (D-Sub) connector to HDMI!
But if you choose between DVI and HDMI, it should be noted that HDMI allows you to get the highest quality image and sound.
HDMI on front or side
The HDMI input (High Definition Multimedia Interface) is used to transmit video signals and multi-channel audio in digital form (see “HDMI input”). The location of the input interfaces on the front panel makes them much easier to access. This arrangement can be convenient in cases where you need to quickly connect an external video source to the TV (for example, a video camera to view a filmed video).
Number of HDMI inputs
The High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) input is used to receive video and multi-channel audio in digital form. If your TV is equipped with several of these interfaces, this will allow you to connect several types of external equipment to the TV at once, and then easily connect to each of them. This could be a DVD player, a VCR, or a cable or satellite receiver. In this case, each device can be connected using a simple remote control.
Number of audio inputs
The TV's audio inputs are used to transmit audio from an external source. If your TV has multiple interfaces, this will allow you to connect several types of audio and video signals from external equipment to the TV at once, and then connect to each of them with ease. This could be a DVD player, a VCR, or a cable or satellite receiver. In this case, each device can be turned on using a simple remote control.
Audio optical
If your TV has a digital optical audio input, this can significantly improve the sound quality of your equipment. The main difference between the optical input is that in this case, not an electrical cable, but a fiber optic cable is used to transmit the signal. It is this difference that makes it possible to avoid almost any electromagnetic interference during optical signal transmission by transmitting multi-channel audio over a single cable. The remaining functions are similar for the user: the audio signal (both stereo and multichannel) is transmitted from the media in digital form.
Audio coaxial
The digital coaxial input is used to transmit audio signals from any external source in digital format, both in stereo and multi-channel mode. Any recording or transmitting device with an appropriate interface can be used as an external source. The advantages of transmitting a signal in digital format are obvious: it is playback with virtually no interference and noise and the transmission of a multi-channel signal over a single cable. A standard shielded RCA cable will allow you to connect to the digital coaxial input.
D.V.
If your TV has a DV or IEEE 1394 input, this means that you can easily connect a digital video recorder or camcorder that supports the miniDV standard to your TV. Basically, DV is designed for the TV to receive digital audio and video signals.
The IEEE 1394 standard dates back to the early 1990s, when Apple developed the FireWire bus specification for connecting a computer to peripheral devices. In 1995, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) adopted the FireWire standard and named it IEEE 1394. IEEE 1394 is a high-speed serial data technology for connecting computers to peripherals. Unlike USB, which is optimal for low speeds and, accordingly, connecting keyboards, mice, joysticks, IEEE 1394 is aimed at high-speed multimedia peripherals, for example, digital video cameras, external drives (CD drives, hard drives, backup devices), music synthesizers. IEEE 1394 data transfer speeds reach 400 Mbit/s. In March 2002, an agreement was reached to use a common logo for FireWire and IEEE 1394 to promote the standard.
After the notes on choosing a TV, I decided to arrange a small educational program on inputs and outputs.
Everyone is familiar with the TV antenna socket.
Any TV has a simple composite video input and analog audio inputs (tulips).
The picture quality through this input is the lowest; only low-resolution video can be transmitted.
The S-Video connector also transmits low-resolution video.
The picture quality is a little better, but almost insignificantly.
The 21-pin SCART connector can contain inputs and outputs of composite video, analog audio, S-Video and RGB inputs, providing maximum quality of low-resolution analog signal.
On different TVs, only some of the signals listed above can be output to the SCART connector.
Component connectors also provide the best analog signal quality, and also support high-definition video up to 720p.
The sound is transmitted through two separate tulips. There are 5 connectors in total.
VGA connector (aka D-SUB). 15-pin connector for connecting a computer.
The TV works like a standard monitor. Sound is also transmitted through two separate tulips. Unfortunately, new TV models often do not have a VGA connector, and while a desktop computer (possibly after modification and installation of a video card) can be connected to the TV via HDMI, then most laptops, alas, cannot.
HDMI connector. A digital input, which, unlike all previous ones, transmits not only video, up to the maximum FullHD resolution, but also digital sound.
HDMI is the most modern and standard connection method.
When connecting a TV to a computer via HDMI or VGA, it is desirable that the TV displays “point to point”, that is, if the image is FullHD, the 1920 pixels in width produced by the computer must exactly match the 1920 pixels displayed by the TV. Often, TVs have the Overscan mode turned on by default, which slightly enlarges the picture and does not allow point-to-point display. It needs to be found and disabled. You can check the correctness of the display by carefully looking at the computer desktop displayed on the TV. All letters should be very clear without smeared edges. Sometimes there are LCD TVs with a screen resolution that does not allow you to display a picture point to point at all. HD Ready plasmas usually have a resolution of 1024x768 with a 16:9 screen format, and each point is not square, but rectangular. At the same time, if you set the resolution on your computer to 1024x768, a big problem arises - the image is stretched, because the computer thinks that the dots are square. To correctly watch movies in this mode, you can use GOM Player and KM Player, which have options for displaying images on a wide TV. The display of photographs is getting worse - I have never been able to find a program that would correctly display photographs on a monitor with rectangular pixels.
Headphone jack. Surprisingly, not all TVs have it.
Sound outputs.
An output that can be connected to an external amplifier to watch TV programs with better sound quality. There are linear (unregulated) and adjustable outputs. The signal level at the adjustable output will depend on the volume level setting on the TV.
Digital audio output (usually optical). Allows you to connect your TV to an AV receiver with a digital audio decoder.
USB connector - allows you to connect USB devices (flash drives, hard drives, keyboards, Wi-Fi adapters) to the TV.
The functionality of the USB connector on each TV is different. Some TVs have a built-in player that plays almost all video formats.
SD memory card slot.
Depending on the model, it allows you to watch photos and videos on TV. Videos, as a rule, are only in certain formats.
Local network (LAN) connector.
Allows you to connect your TV to your home network and the Internet. The functionality is also different for all models that have such a connector. Some can show videos from YouTube, surf the Internet and even allow you to make video calls via Skype; some can play video over the network from a computer or home DLNA server.
In addition, TVs also have quite exotic connectors. For example, my LG 42PC1RR plasma has an RS-232 connector, which allows you to control the plasma from a computer instead of a remote control, but this functionality is unlikely to ever be needed in everyday life.
Physical connectors
The four-pin mini-DIN connector is the most common of several types of S-Video cinch cable connectors. The same mini-DIN connector is used on Apple Desktop Bus for Macintosh computers, and the two cable types can be interchanged. Other connector options include the seven-pin locking "redundant" connectors used on many professional S-VHS machines, and the two Y and C BNC connectors often used for S-Video patch panels (HDMI cables). Early Y/C video monitors often used RCA connectors that switched between Y/C and composite video input. Although the connectors are different, the Y/C signals for all types are compatible.
Mini-DIN cables are prone to damage when used in kinked areas. This may result in loss of color or other damage to the signal. A bent pin can be forced back into its original shape, but this may cause the pin to break.
These connectors are typically manufactured to be compatible with an S-video RCA cable and include additional features such as component video using an adapter.
HDMI
Also digital output. Its main difference from DVI is that HDMI, in addition to transmitting a video signal, is capable of transmitting a multi-channel digital audio signal. Audio and visual information are transmitted over one cable at the same time. Initially developed for television and cinema, and later gained wide popularity among PC users. It is backward compatible with DVI using a special adapter. The maximum length of a regular HDMI cable is up to 5 meters.
HDMI is another attempt to standardize universal connectivity for digital audio and video applications, so it immediately received strong support from electronics giants (companies such as Sony, Hitachi, Panasonic, Toshiba, Thomson, Philips) contributed to the development, and as a result, most modern devices for outputting high-resolution images have at least one HDMI output.
Among other things, HDMI, like DVI, allows you to transmit copy-pasted sound and image in digital form over one cable using HDCP. True, to implement this technology you will need a video card and a monitor, attention! — supporting this technology, oh how. Again, there are currently several versions of HDMI, here's a short summary of them:
- HDMI 1.3 - the first version standard (1.0) had a throughput of 5 Gbit/s, while in version 1.3 the channel expanded to 10.2 Gbit/s. The clock frequency was also increased to 340 MHz, which made it possible to connect high-resolution displays with a large number of colors. It is now possible to transmit compressed audio without loss of quality thanks to the new Dolby standards. And starting with version 1.3, mini-HDMI appeared, which is now widely used on video cards.
- With the advent of HDMI 1.4, support for stereo images (3D), 4K and 2K resolutions (3840x2160 and 4096x2160, respectively) appeared. micro-HDMI was developed for miniature devices. A distinctive feature of version 1.4 is the ability to create an Ethernet connection at speeds of up to 100 Mbit/s - and all this over the same HDMI cable.
The distinctive features of standard HDMI 2.0 include: increased bandwidth up to 18 Gbps, which, for example, will allow you to transmit Full HD 3D images at a speed of 120 frames per second; increased frequency of transmitted audio up to 1536 kHz for the highest sound quality; added support for monitors and TVs with an aspect ratio of 21:9.
7-pin connector
Non-standard 7-pin mini-DIN connectors (called "7P") are used in some computing devices (PCs and Macs). The 7-pin connector is compatible with the standard 4-pin S-Video connector. Three additional sockets can be used to supply composite (CVBS) and RGB or YPbPr video signals. The use of S-Video cable wiring varies among manufacturers. In some implementations, the remaining pin must be grounded to enable the composite output or disable the S-Video output. Some Dell laptops have a 7-pin digital audio output.
DisplayPort and its little brother MiniDP
The standard DisplayPort connector has 20 pins, is rectangular, has one asymmetrical corner for proper orientation, and small latches that help keep connected cables in place.
To disconnect the plug, you will need to press a button.
DisplayPort
— signal interface standard for digital monitors. DisplayPort is intended to be used as the most modern interface for connecting audio and video equipment, primarily for connecting a computer to a display. Through adapters you can connect to other types of connectors.
In fact, DisplayPort is a universal connector that has:
- digital video pins
- analog video pins
- digital pins sound
DisplayPort 1.2 has a maximum data transfer rate of 21.6 Gbps over a distance of up to 3 meters, which is faster than HDMI Type B (2x10.2 Gbps). It also supports multiple independent streams; the standard auxiliary channel capacity has been increased from 1 to 720 Mbit/s.
Thus, via the DisplayPort 1.2 interface you can connect up to two monitors that reproduce an image of 2560 x 1600 pixels at a frequency of 60 Hz, or up to four monitors with a resolution of 1920 x 1200 pixels. When using a single monitor, the supported resolution increases to 3840 x 2400 pixels at 60 Hz; a monitor with support for a refresh rate of 120-165 Hz is supported at resolutions up to 2560 x 1600 pixels. This allows DisplayPort 1.2 to work with stereoscopic imaging technologies
Previously, DisplayPort did not offer any payments, but as of March 5, 2015, payments are 20 cents per device. Manufacturers of HDMI devices pay $10,000 annually, plus a minimum of 4 cents per device (15 cents if the HDMI logo is not shown on the product and in promotional materials).
The Mini DisplayPort connector is 10 times smaller than a standard DVI connector.
Here is the MiniDP port itself
Adapter to VGA
Adapter to DVI
HDMI adapter
9-pin video input/video output
9-pin connectors are used in graphics systems that have the ability to input video as well as output it via an S-Video Scart cable. Here too, there is no standardization between manufacturers as to which pin does what, and there are two known variations of the connector used. As you can see from the diagram above, although S-Video cable signals are available on the appropriate pins, none of the connector options accept an unmodified 4-pin S-Video connector, although they can be configured by removing the plug key.
DisplayPort
Appeared in addition to DVI and HDMI, since Single-Link DVI can transmit a signal with a resolution of up to 1920 × 1080, and Dual-Link a maximum of 2560 × 1600, then a resolution of 3840 × 2400 is not available for DVI. The maximum resolution capabilities of DisplayPort are no different from the same HDMI - 3840 x 2160, however, it still has unobvious advantages. One of these is, for example, that companies will not have to pay tax for using DisplayPort in their devices - which, by the way, is mandatory when it comes to HDMI.
In the photo, red arrows indicate latches that prevent the connector from accidentally falling out of the connector. HDMI, even version 2.0, does not provide any clamps.
As you already understood, DisplayPort's main competitor is HDMI. DisplayPort has an alternative technology to protect transmitted data from theft, only it is called a little differently - DPCP (DisplayPort Content Protection). DisplayPort, like HDMI, supports 3D images and audio content transmission. However, audio transmission via DisplayPort is only available one-way. And transmitting Ethernet data via DisplayPort is generally impossible.
DisplayPort also benefits from the fact that it has adapters for all popular outputs, such as DVI, HDMI, VGA (which is important). For example, with HDMI there is only one adapter - to DVI. That is, having only one DisplayPort connector on the video card, you can connect an old monitor with only one VGA input.
By the way, this is what is happening - now more and more video cards are being released without a VGA output at all. The maximum length of a regular DisplayPort cable can be up to 15 meters. But DisplayPort can transmit its maximum resolution at a distance of no more than 3 meters - often this is enough to connect the monitor and video card.