Digital television: what is it?
Standard definition vs high definition
Advantages of high quality digital TV
Digital TV Wifire
FAQ
It's hard to believe that just a few years ago digital television was an inaccessible and rather low-budget pleasure. However, technology is developing so rapidly that today almost everyone can connect to digital TV and enjoy watching their favorite programs in high quality.
What is “digital HD TV”, what is the difference between digital TV and regular TV? What are the benefits of connecting to HD television? We have prepared an article to help you find answers to these questions.
Digital television: what is it?
Digital television is a television broadcasting system in which the transmission of video and audio signals from the transmitter to the receiver (TV, computer, telephone) occurs in a compressed digital format.
An active transition to digital TV standards began in Russia in 2009, when the federal program “Development of Television and Radio Broadcasting in the Russian Federation for 2009-2015” began its operation. The basis for a unified broadcasting standard was the European DVB-T2 standard.
At the moment, DVB-T2 digital transmitters operate almost throughout the entire territory of the Russian Federation. 20 free channels are available for users to receive and watch.
Digital TV offers you various benefits and additional services. But what do the terms SD, HD, 3D, and Ultra HD associated with the topic of digital television mean? In this material we will try to explain their basic essence, as well as the differences between them.
First of all, it should be explained how digital and analogue television differ from each other, especially since both of them are available in Georgia.
Technically, an analogue image is transmitted in the form of a continuous wave, while a digital television image is a coded stream of digital data. From a practical point of view, digitalization of data makes it possible to send more information to your television receivers. As a result, you will get a much clearer picture, better sound and more channels. Accordingly, if you have a modern digital TV in your home and receive a signal via satellite, digital cable and digital terrestrial transmitter, you can be sure that you are getting the highest quality.
New digital television formats require more broadcasting capacity, and satellite is indispensable here. Satellite is the most reliable and efficient (existing) means of transmitting television programs to the continent, especially to mountainous regions, where there are practically no restrictions on the number of digital satellite television channels that can be broadcast. Accordingly, through a satellite it is possible to cover the entire population of the world.
The satellite signal is transmitted via a Direct-To-Home/DTH satellite dish, and the satellite signal is also transmitted to terrestrial DTH providers for subsequent transmission. Satellite television offers viewers a greater choice of channels and experience when compared to other forms of television broadcasting. Standard definition ( SD ) and high definition ( HD )
When we talk about SD and HD, first of all we are dealing with the term “resolution”. Simply put, it is the picture quality that your TV device can produce.
The term "standard definition", or SD TV, became relevant when high-definition television began to be used - before that, all television was standard (both analogue and digital), and the specifications of the specified format were considered acceptable. The fidelity of standard television is the comparative basis for the analysis of all other formats; any format above its limits is considered a high-definition format. The SD format was quite good for standard 24-inch TV sets, but then the population began to buy LCD and plasma TVs with screens 2-2.5 times larger, and the difference between SD and HD resolutions became quite obvious. For example, when watching a football match in SD you can see the ball, the players and the green background, but in HD you can also see the grass and the faces of the fans.
In conclusion, High Definition (HD) television is a digital broadcasting format that allows you to get higher quality images on your TV screens. HD channels provide images with richer, more saturated colors and fine details; Accordingly, the viewing process becomes more vibrant, interesting and attractive. If we look at the numbers, we can say that an HD image typically consists of 2 million (1080x1920) pixels. This means approximately 5 times more detail than SD (720x576) images, making HD broadcasts more natural and attractive. The more pixels there are in an image, the more detail you see, resulting in better rendering of curves and diagonal lines.
One of the incentives for creating HD content, besides sporting events, is the nature filming of major broadcasters; if you have ever watched BBC or Discovery nature programs, you will have seen how high quality they are. The effect of High Definition TV can be appreciated by watching sporting events, documentaries and other films, costume dramas - no matter what program you choose, the HD picture will be much better.
Naturally, transmitting an HD signal requires more broadcast power than standard definition video, and, accordingly, the power of terrestrial and cable digital television is only sufficient for a few high-definition channels. Satellites, on the other hand, have a large channel capacity, and therefore the satellite is the de facto leader in HD broadcasting. According to the results of the annual SES satellite monitoring, today the satellite is the largest HD platform, the number of users in Europe has reached 29 million households, with 80% of them using SES satellites.
Step forward - 3D television
3D television (3DTV), using various technical means to create a stereoscopic image, gives the viewer the opportunity to perceive a three-dimensional image. This is the effect of zooming in on the image, which encourages you to sit in the front row in the cinema, on the stands, in the hall, in the arena, in order to better perceive the spectacle. Technological advancements have made 3D television possible, practical and accessible in your home.
Most modern 3D TVs use an active 3D shutter or a polarizing 3D system. Accordingly, viewers use special glasses, similar to glasses for 3D cinemas. There is a wide demand for such TVs in stores, but for complete enjoyment it is better to become a subscriber to a TV broadcaster with a package of 3D channels. Let us repeat once again that for broadcasting at home, a 3DTV satellite is the best means. Taking into account reliability and quality, satellite broadcasting is a leader, which has no competitor in terms of programs, quality and popularity of channels. Even higher level - Ultra HD
The evolution continues - Ultra HD is a new word in consumer TV technologies. This technology was first demonstrated in 2005, and the first launch of commercial channels in this format will be carried out in the coming years.
Ultra HD technology is called 4K, but nowadays it is better known as ultra-high definition or Ultra HD (UHD). The term was first coined in October 2012 by the Consumer Electronics Association as the trademarks 4K and 8K.
The resolution accuracy of Ultra HD TV is 3840 x 2160 pixels, so the image is transmitted with unprecedented clarity and detail. In addition, it makes the 3D viewing experience more comfortable and brings the viewer closer. Considering that we are buying TVs with ever larger screens, Ultra HD images are truly becoming indispensable.
The market is saturated with new HDTVs. All leading manufacturers presented Ultra HD TVs at major trade shows this year. In fact, all the major events that will take place in the world from 2014, such as the 2014 FIFA World Cup in Brazil, the 2015 Rugby World Cup in England, the 2021 UEFA European Championship, the 2021 Summer Olympics in Rio de... Janeiro and many others will be broadcast in Ultra HD format. Technology will offer us new entertainment options sooner than expected, and satellite is undoubtedly the only medium with the capacity to broadcast any digital television format - be it SD, HD, 3D or Ultra HD.
Material prepared by satellite operator SES
Standard definition vs high definition
Depending on the image resolution, digital TV is divided into SD (“standard definition”) and HD (“high definition”).
SDTV is a type of television broadcasting standard based on the 625/50 (576i) and 525/60 (480i) active frame resolution standards. Standard definition television uses a 4:3 screen format, close to the classic cinema format.
HDTV is a television broadcasting system with a resolution increased by 2 times compared to the standard one. The HD standard is a screen aspect ratio of 16:9 and a resolution of 1920x1080 pixels. High-definition television allows you to keep the line structure of the image invisible and the details clearly visible, thanks to which you can view the image from a closer distance or use a larger screen. In addition, multi-channel audio is expected to be transmitted in Dolby Digital quality.
What other screen parameters should you pay attention to when choosing?
Other important selection factors:
- Update frequency.
A parameter showing how many times per second the image is updated. Standard frequency is 60 Hz. If the value is lower, it may result in blurred images. It is better to look at devices with a frequency of 120 Hz and higher. - Contrast.
A high contrast ratio brings out more shades and shadows on the screen, thereby significantly increasing detail. As can be seen from the above advantages of devices that support Full HD resolution, they have a better contrast parameter. But before making a final decision, visually test the brightness, contrast and other capabilities of a particular device. - Number of ports.
They may be needed to connect a game console or speakers. Take a close look at their number and think whether it is enough. It is better to take a TV that has at least four of them.
Advantages of high quality digital TV
Digital TV hd has a number of undeniable advantages compared to digital television SD and analogue television broadcasting. This:
- resistance to signal interference;
- improved image quality
- multi-channel audio
- a large number of broadcast channels.
- ability to quickly connect/disconnect TV channel packages.
Ultra High Definition Television UHDTV
In August 2012, two more sets of digital television standards 4K UHD TV 2160p
and 8K UHDTV
4320p
.
of 2160p
have already appeared on sale .
To implement the 4320p
So far, only demo samples exist, for example, presented by the Japanese company NHK, which developed the Super Hi-Vision broadcast format with support for 8K UHDTV resolutions. One hour of uncompressed video in this format takes about 25 terabytes.
The page was created in addition to an article with recommendations on how to choose a TV when purchasing to clarify some issues regarding HDTV resolutions and standards in TVs and television.
Digital TV Wifire
Do you want to start watching your favorite TV programs in high quality? Digital HD TV is more affordable than you think!
WifireTV is television that you can watch anywhere and anytime:
- on SmartTV;
- on a smartphone/tablet;
- on any TV.
Wifire allows you to control your TV broadcast: stop watching, record episodes of programs and movies, and watch missed program excerpts. This is a completely new functional approach designed to provide user comfort.
And a pleasant surprise awaits you: by connecting HD digital TV on one gadget, you can watch the selected channel package on four more devices absolutely free!
To find out more, fill out an application on our website. Customer service specialists will contact you and tell you about all current offers and promotions.
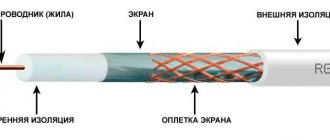
Standard Definition Television SDTV
The popular SECAM and PAL color television systems in our country, widely used in broadcasting and cable broadcasting, transmit 625 lines and 50 half-frames per second in an interlaced manner. Alternately odd and even lines. As a result, the visible image is formed from 25 full frames per second.
Interlaced display of a frame on the screen allows you to use half the video signal bandwidth, which is especially important for RF modulation in terrestrial analog television, so this method is widely popular in terrestrial and satellite broadcasting systems for television programs.
Due to the existence of beam reversal when forming frames and lines in televisions with a cathode ray tube, some of the lines are not involved in image transmission, but are used to transmit technical information - color synchronization and data transmission in teletext mode. In LCD or plasma TVs, the use of such a video signal in popular PAL or SECAM systems, when scaling with a graphics controller, implements the 526i
, in which 526 lines (out of 625 existing) are used to form a visible image.
The index i
indicates that the scanning is interlaced.
An NTSC video signal transmits 525 lines and 30 frames in 60 half-frames. Implemented in graphic format using the 480i
.
The rapid evolution of TV technology
That 4K TVs have gone from high-end to mainstream in such a relatively short period of time is a bit of a shock. Moreover, 4K is already the entry level. Why initial? Because most companies, including Sony, are discontinuing HDTVs. Even the most basic models now have 4K resolution. Samsung, for example, announced just one HDTV for 2021 - a 32-inch model from The Frame design line, which by definition is not entry-level. LG is also not going to produce HDTVs this year. Panasonic hasn't made any official announcements, but chances are there won't be any new models with HD resolution.
4K TVs are disappearing from the high-end world: Samsung announced this year that there will no longer be 4K TVs in its premium lineup. From now on, Samsung's top TVs are exclusively 8K QLED. In other words, 8K is now High End and 4K is mid to low end. This year, anyone can buy a real 8K TV, but a couple of years ago we only saw such equipment at exhibitions.
Terrestrial television has not kept up with the industry at all - there is no business model that could provide an incentive. TV companies need to change their entire production process, which is expensive. Such updates happen once every 10 years. Even if TV production switches to 4K, broadcasting at that quality will still be too expensive. Terrestrial broadcast capacity is limited. The same can be said about direct satellite broadcasting and IPTV - there are restrictions everywhere. The idea is that one 4K channel will take up the same amount of space as four HD channels. You can, of course, use compression, but then the whole point of Ultra HD will be lost. Advertisers won't pay more for ads if they're shown on 4K channels, and TV companies won't be able to make pay-per-view for those channels too expensive.
It turns out that 4K content is completely dependent on streaming platforms, for which there is no such problem as bandwidth. If there is one, it’s not a problem with the streaming services themselves. The paradox is that transmission capacity is growing every year, but this does not apply to broadcasting. On the contrary, terrestrial TV is being squeezed from all sides - radio waves are needed by mobile operators.
Of course, the demand for television companies does not directly depend on the resolution of their content, but the current situation still gives television producers reasons for concern. Literally before our eyes there is a transition from regular television to VoD services.